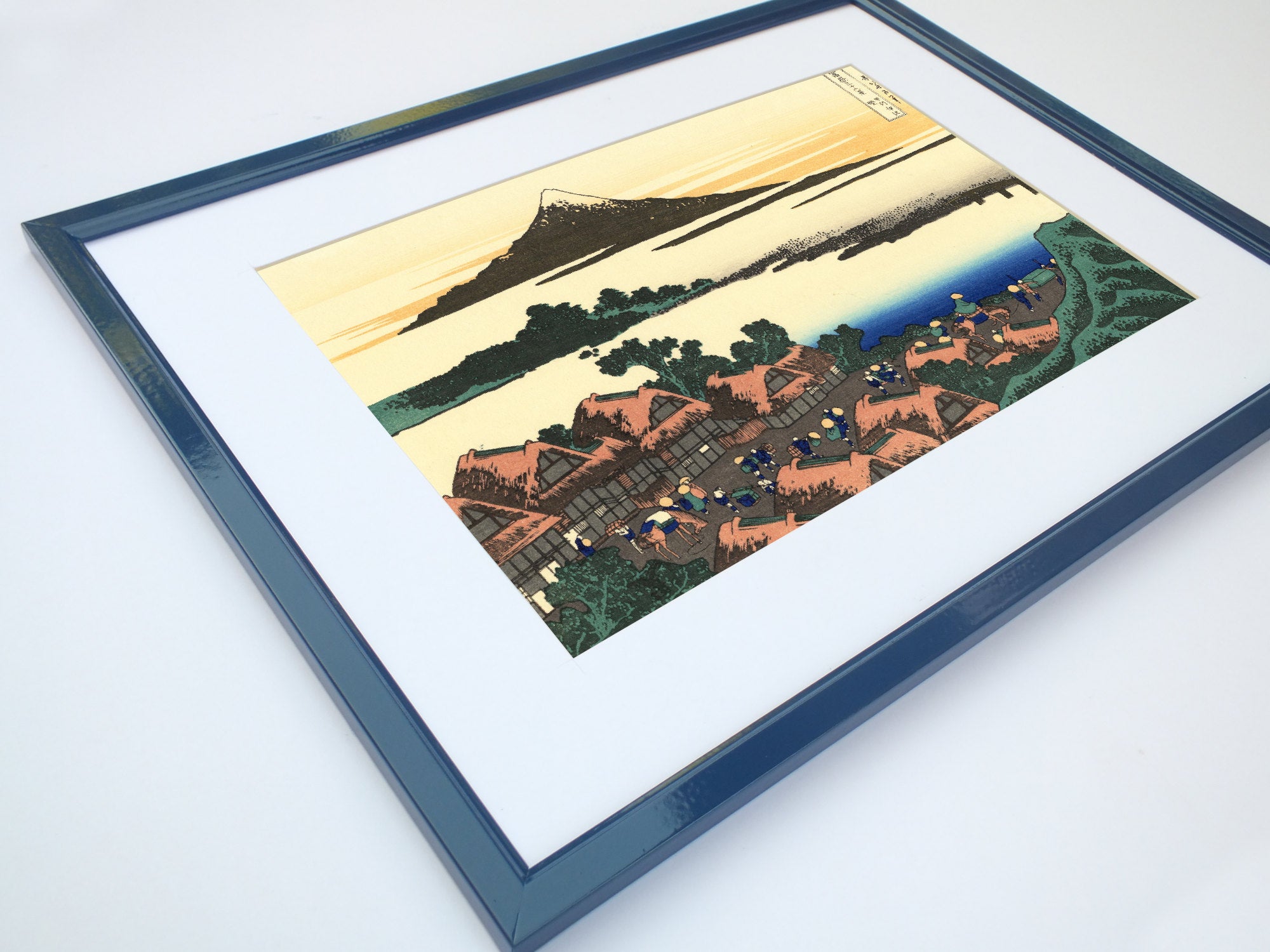
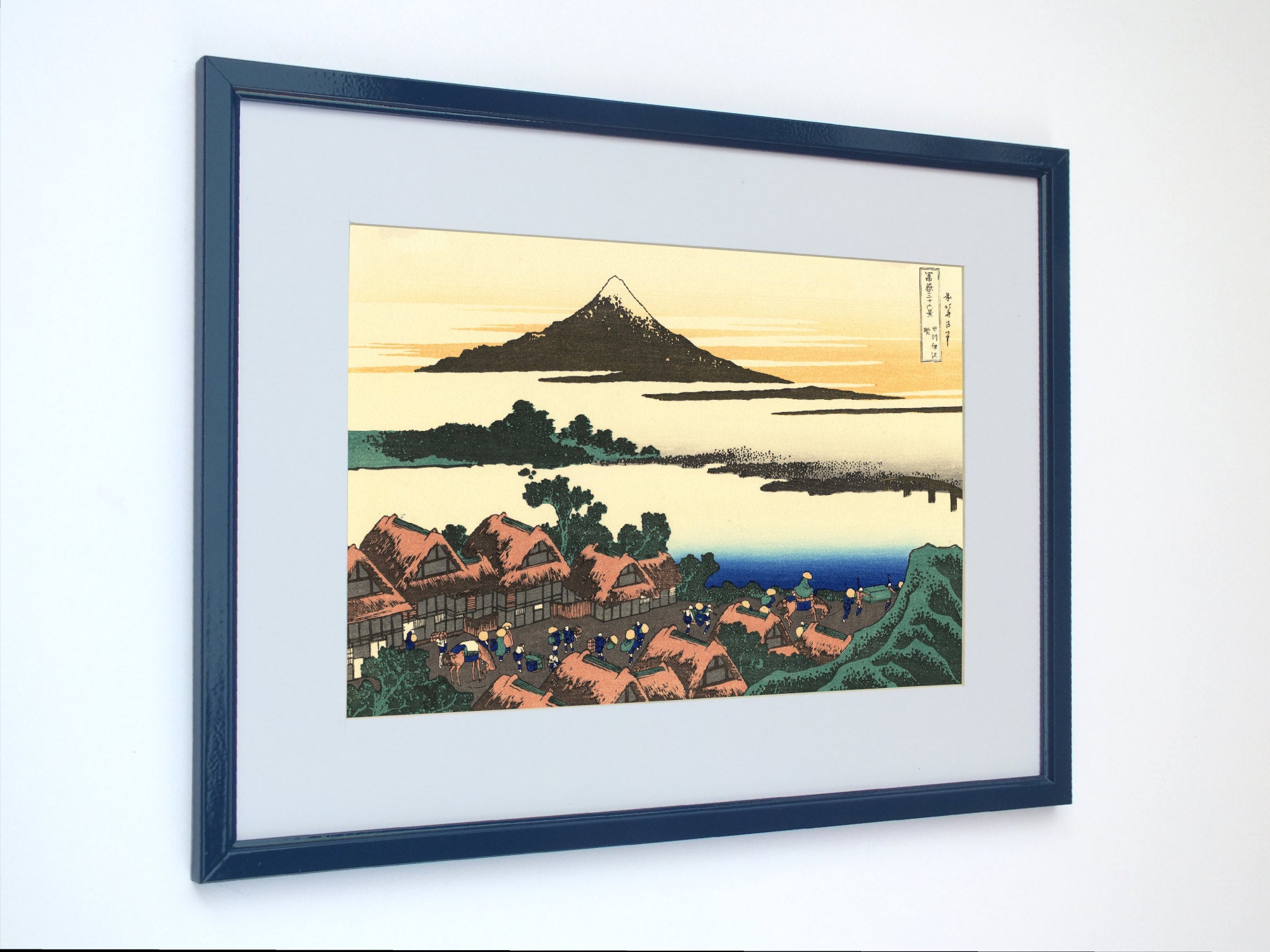
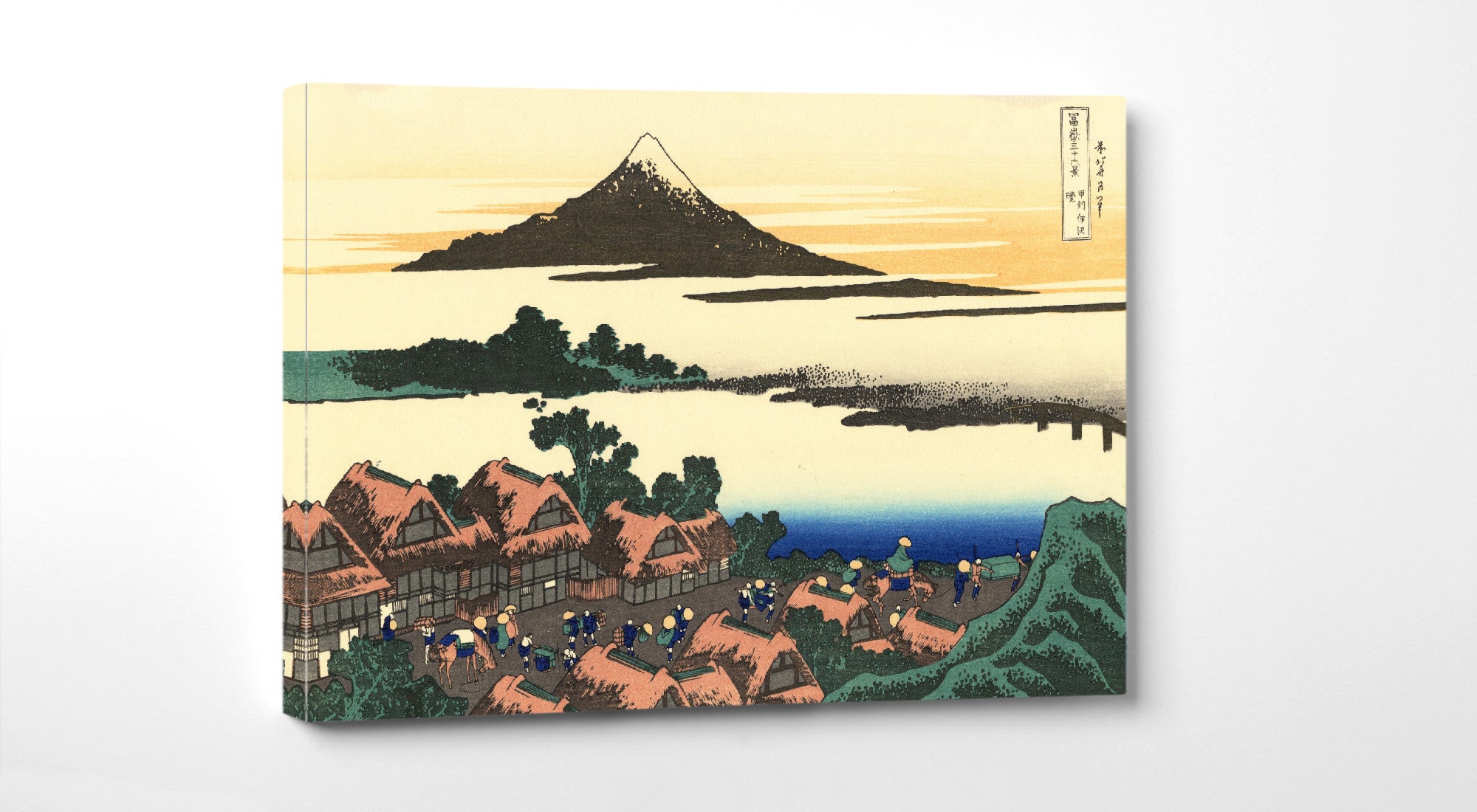
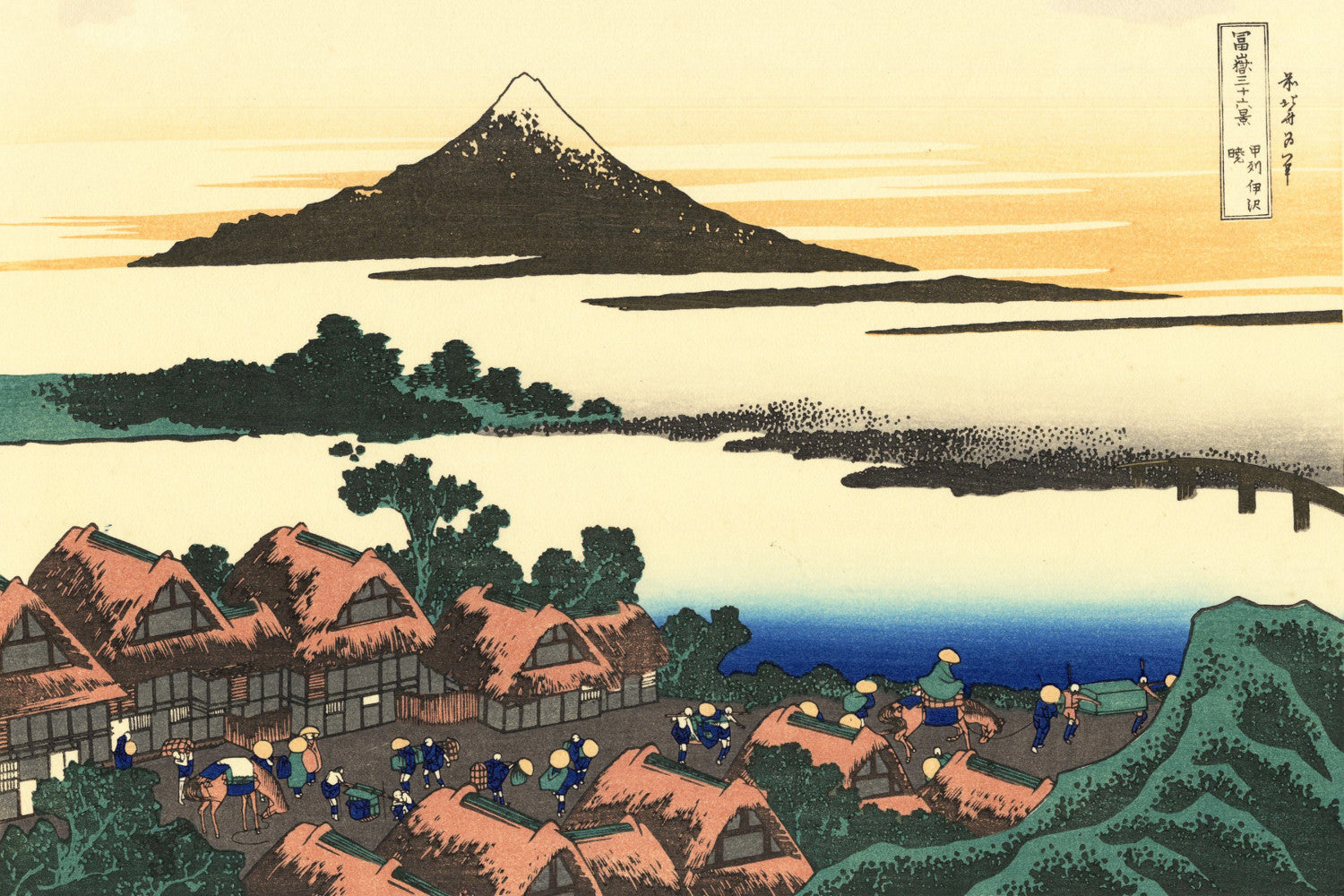
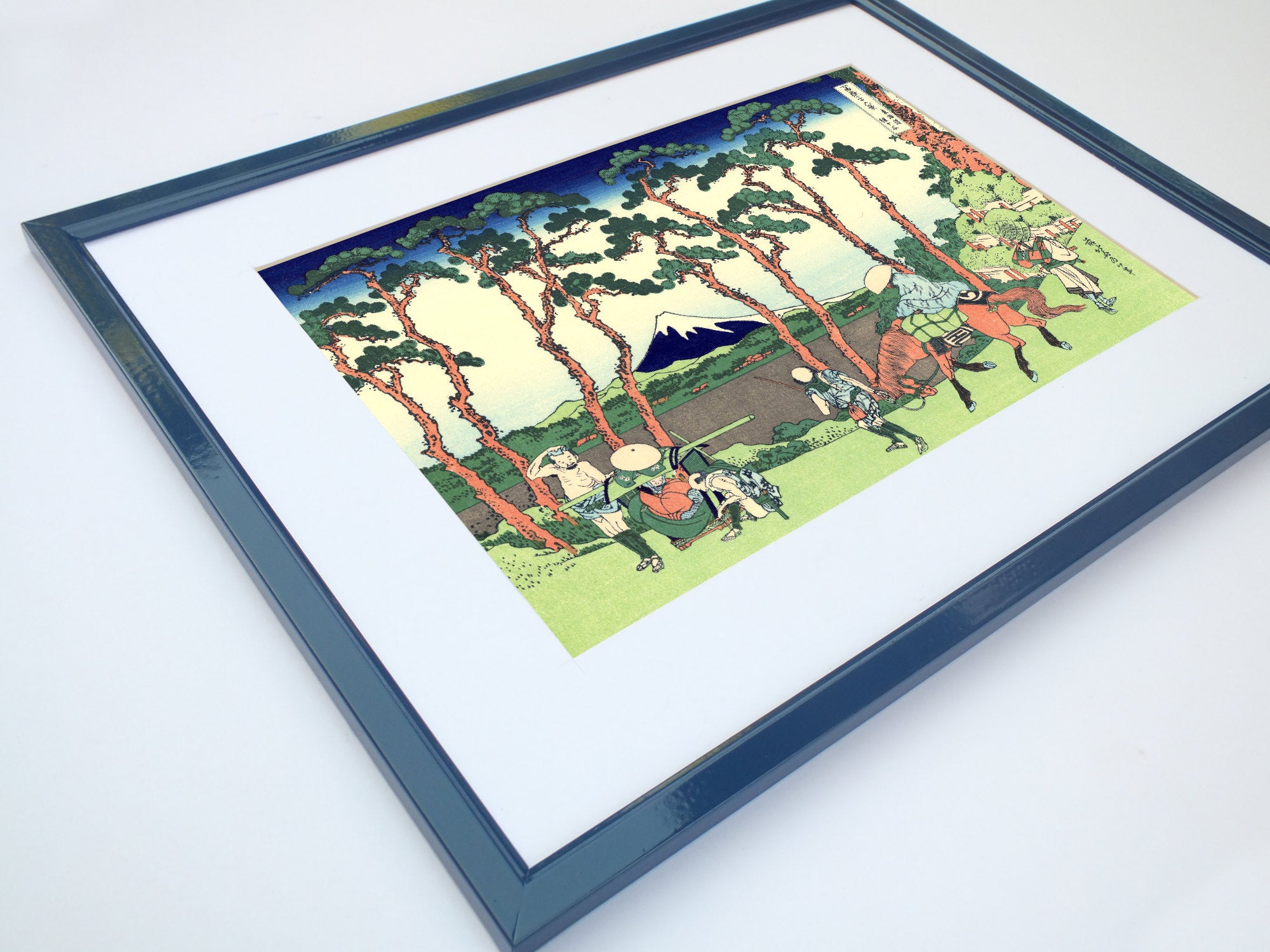
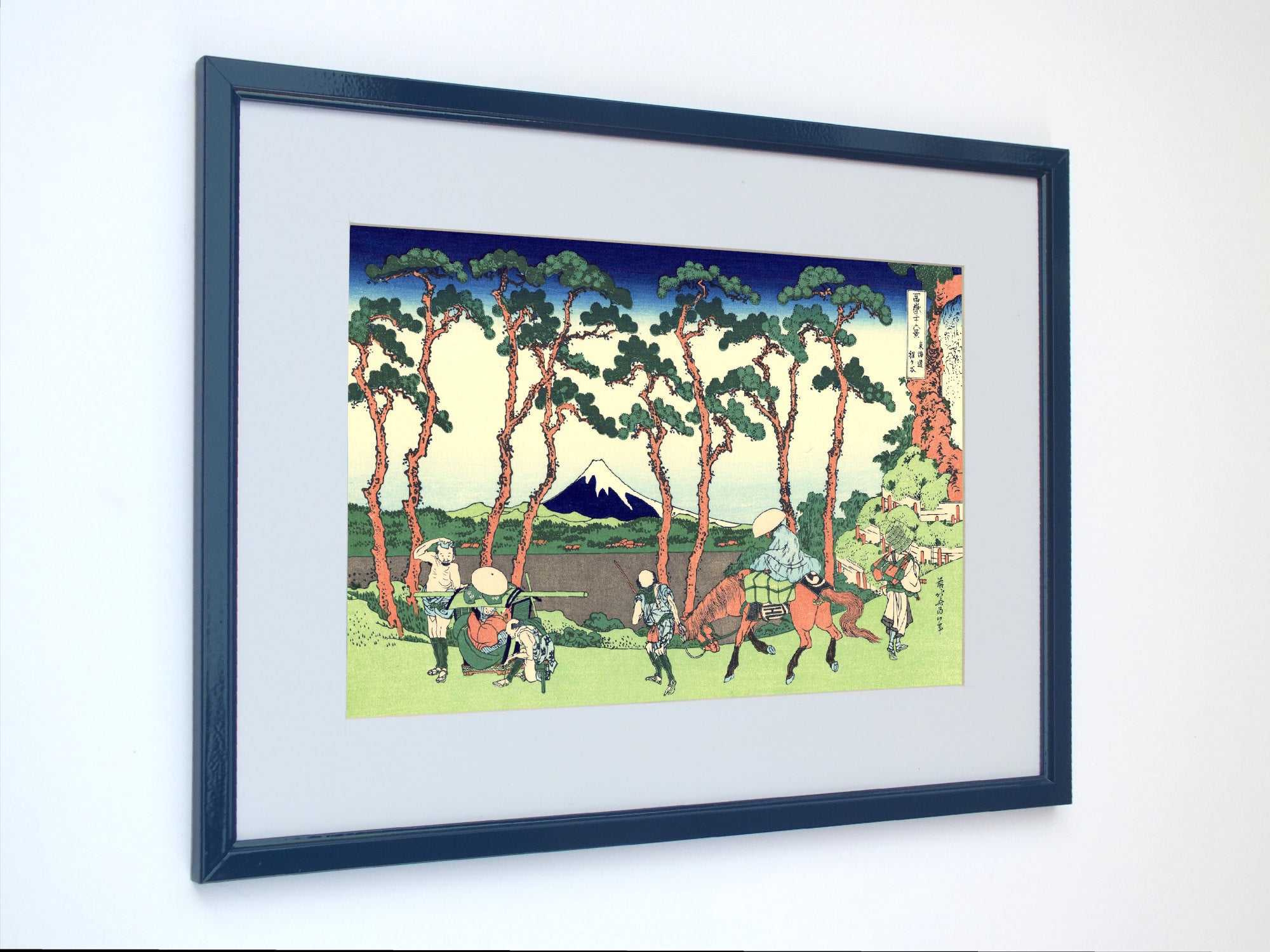
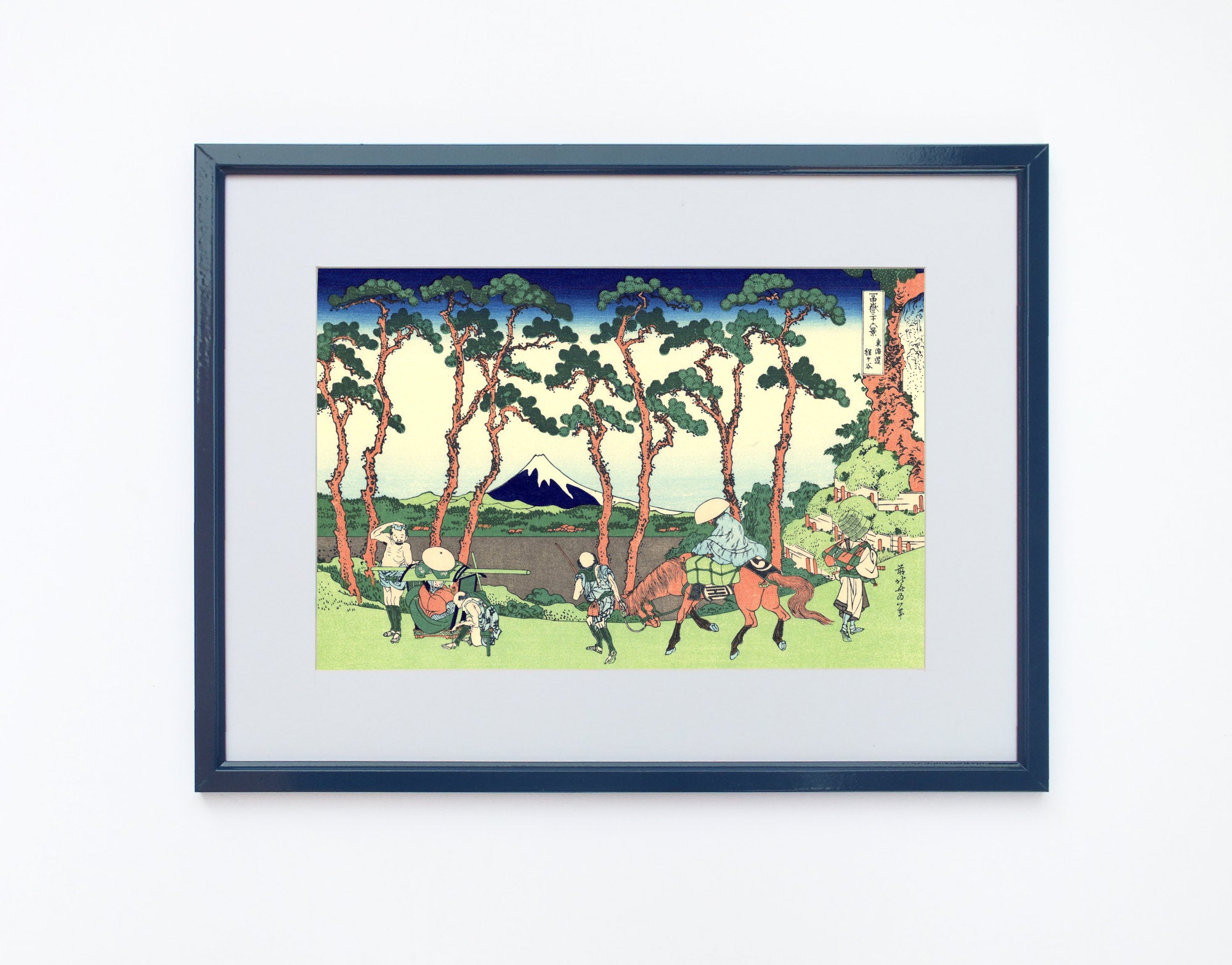
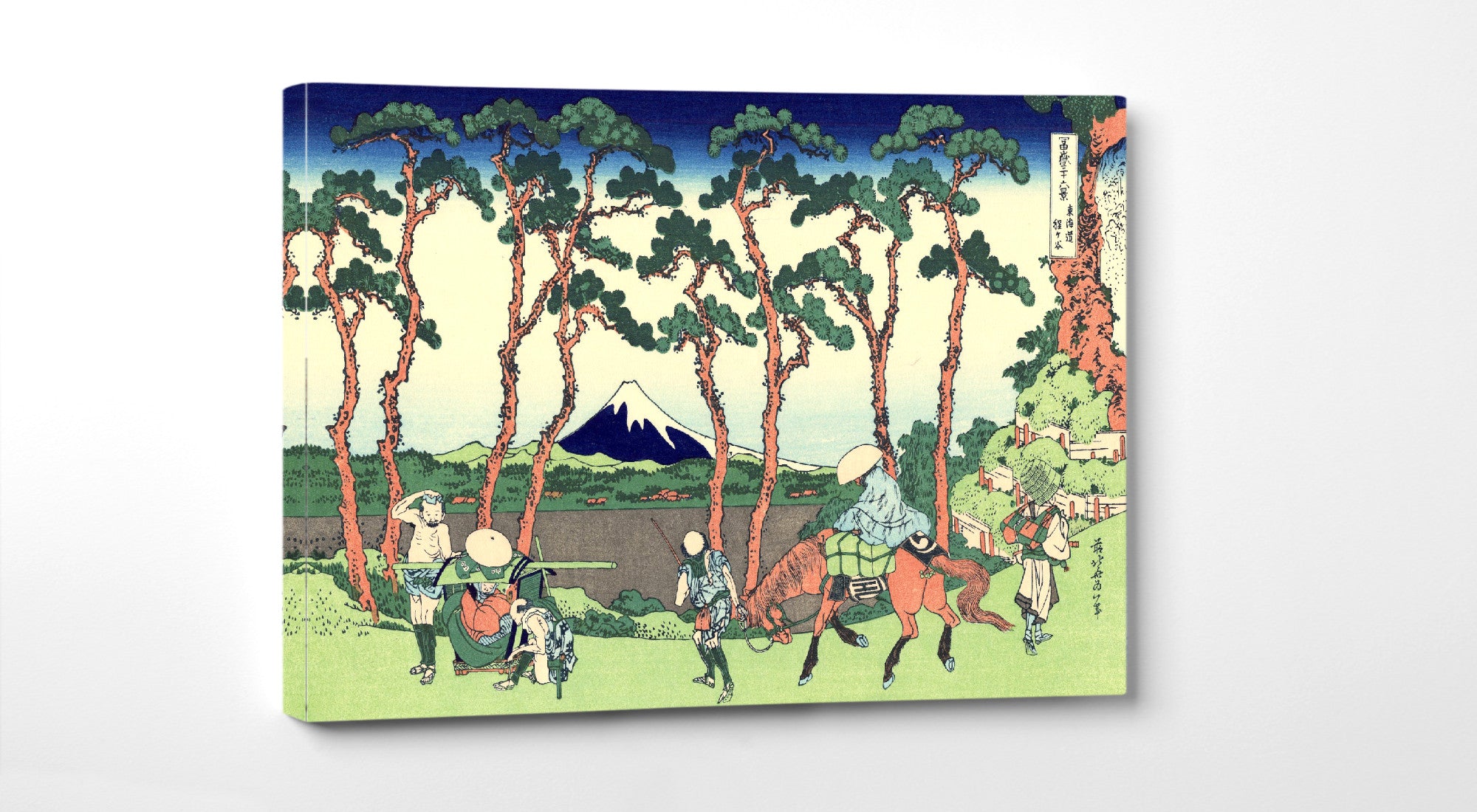
When thinking of Japanese art, many of the famous ukiyo-e paintings of 17th to 19th centuries spring to mind. The artists of these periods produced woodblock prints and paintings of such subjects as female beauties; kabuki actors and sumo wrestlers; scenes from history and folk tales; travel scenes and landscapes; flora and fauna; and erotica. The term ukiyo-e (浮世絵) translates as "picture[s] of the floating world".
In the early 17th century, the city of Edo (Tokyo) became the seat of the ruling Tokugawa shogunate. The chōnin class (merchants, craftsmen and workers), positioned at the bottom of the social order, benefited the most from the city's rapid economic growth, and began to indulge in and patronise the entertainment of kabuki theatre, geisha, and courtesans of the pleasure districts; the term ukiyo ("floating world") came to describe this hedonistic lifestyle. Printed or painted ukiyo-e works were popular with the chōnin class, who had become wealthy enough to afford to decorate their homes with them.
These wonderful images have had something of a renaissance over the past few years and we have collated a number of collections of the most popular ukiyo-e paintings and made them available in a wide range of sizes on both textured fine art paper and canvas.
Selected Ukiyo-e artists
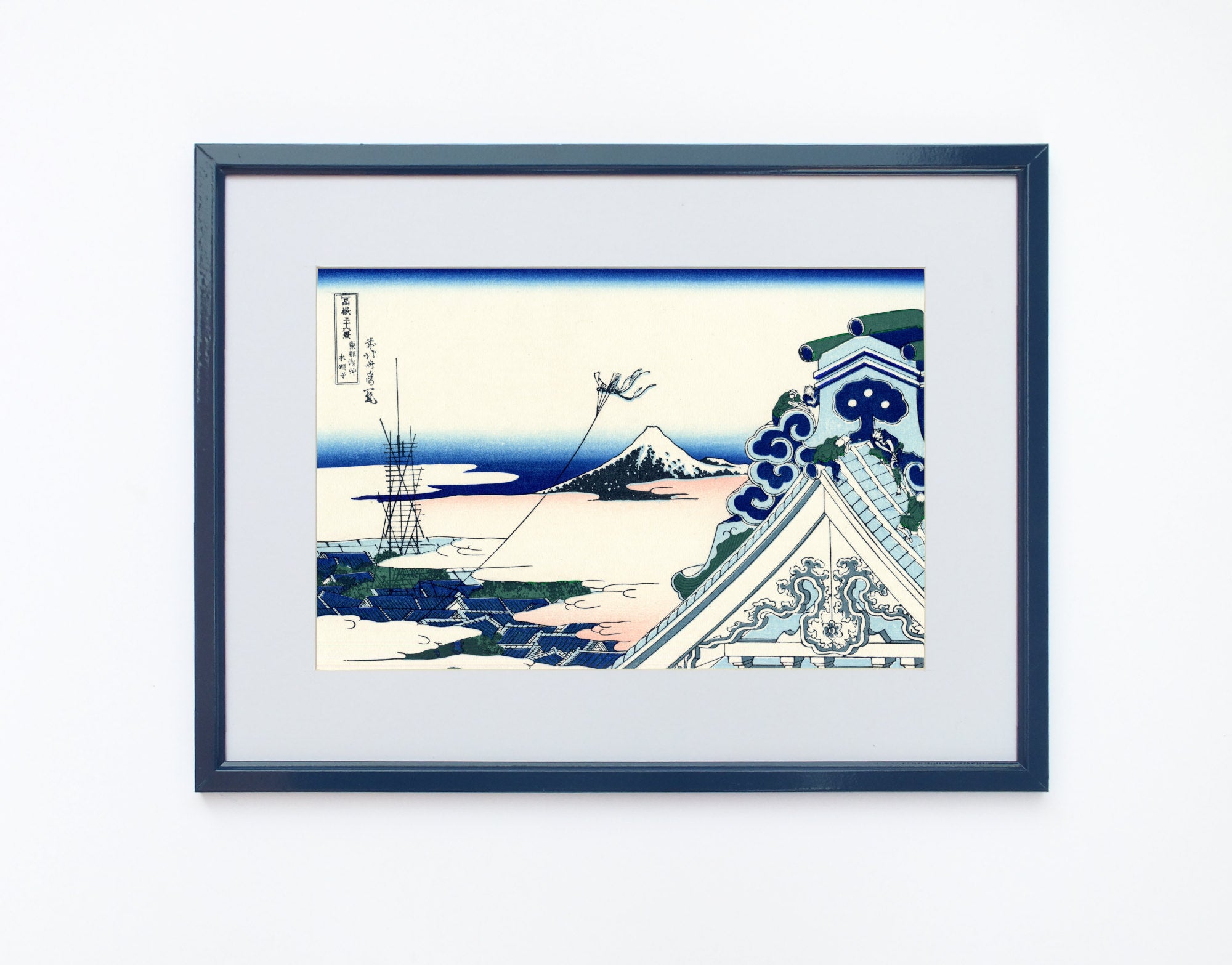
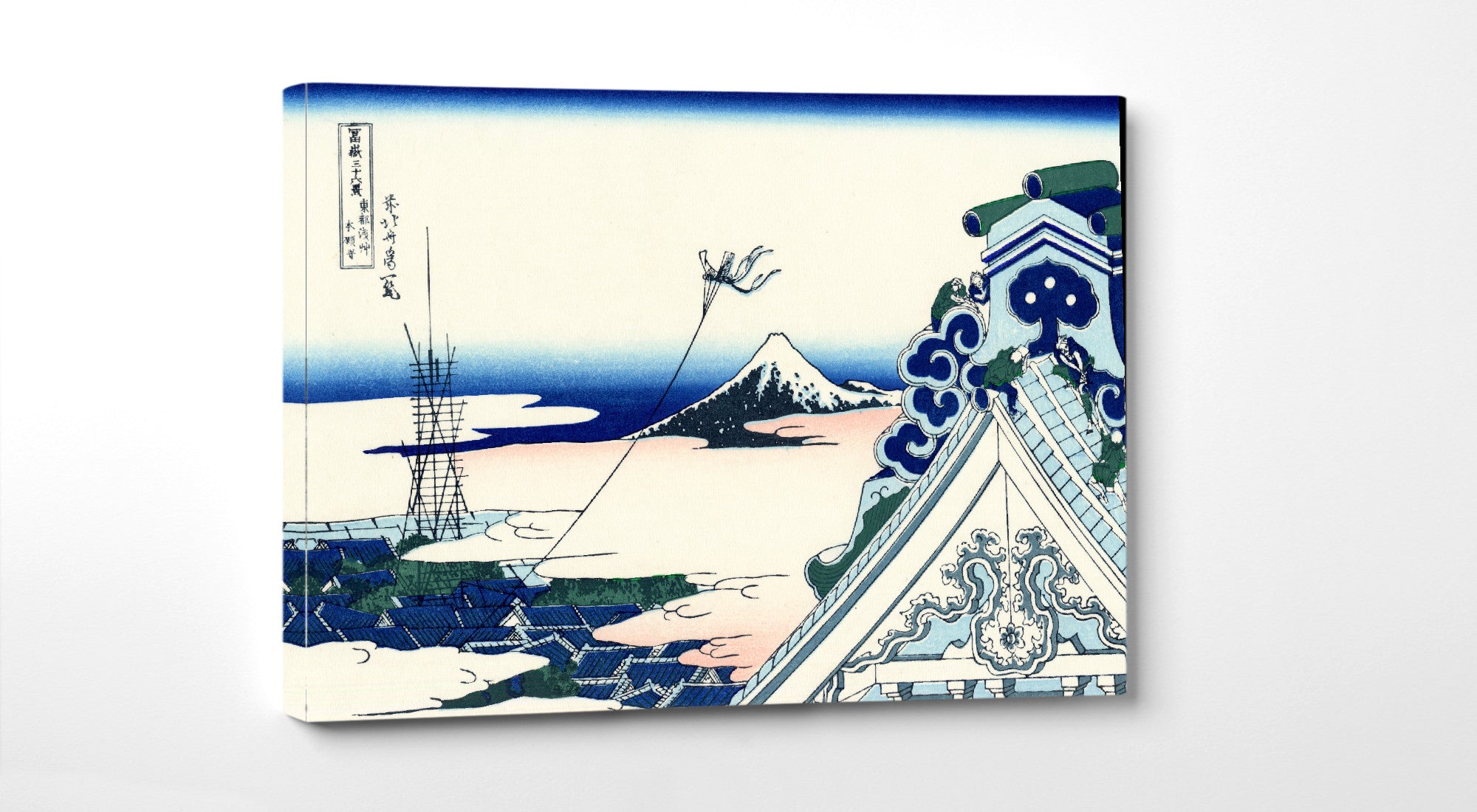
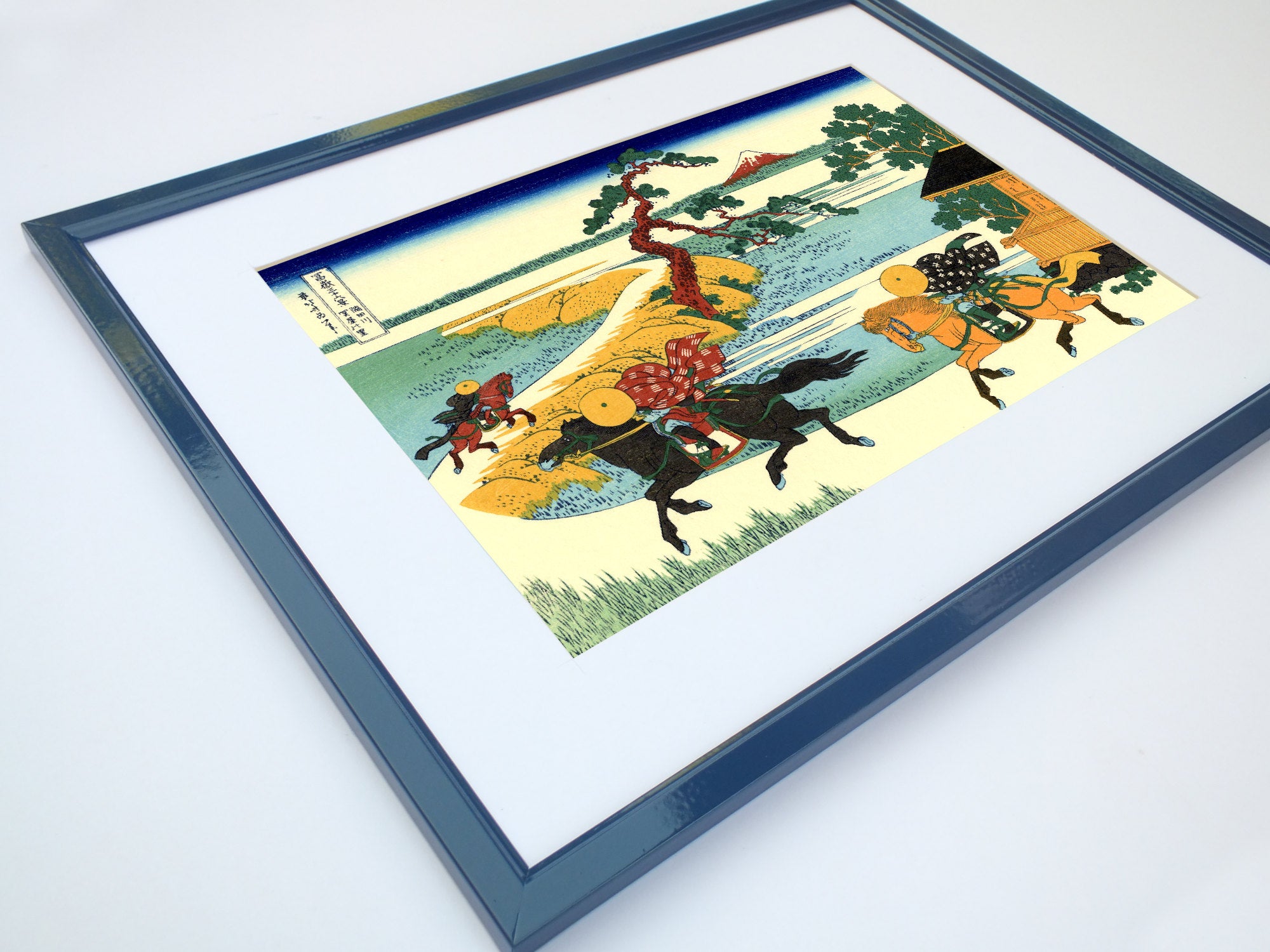
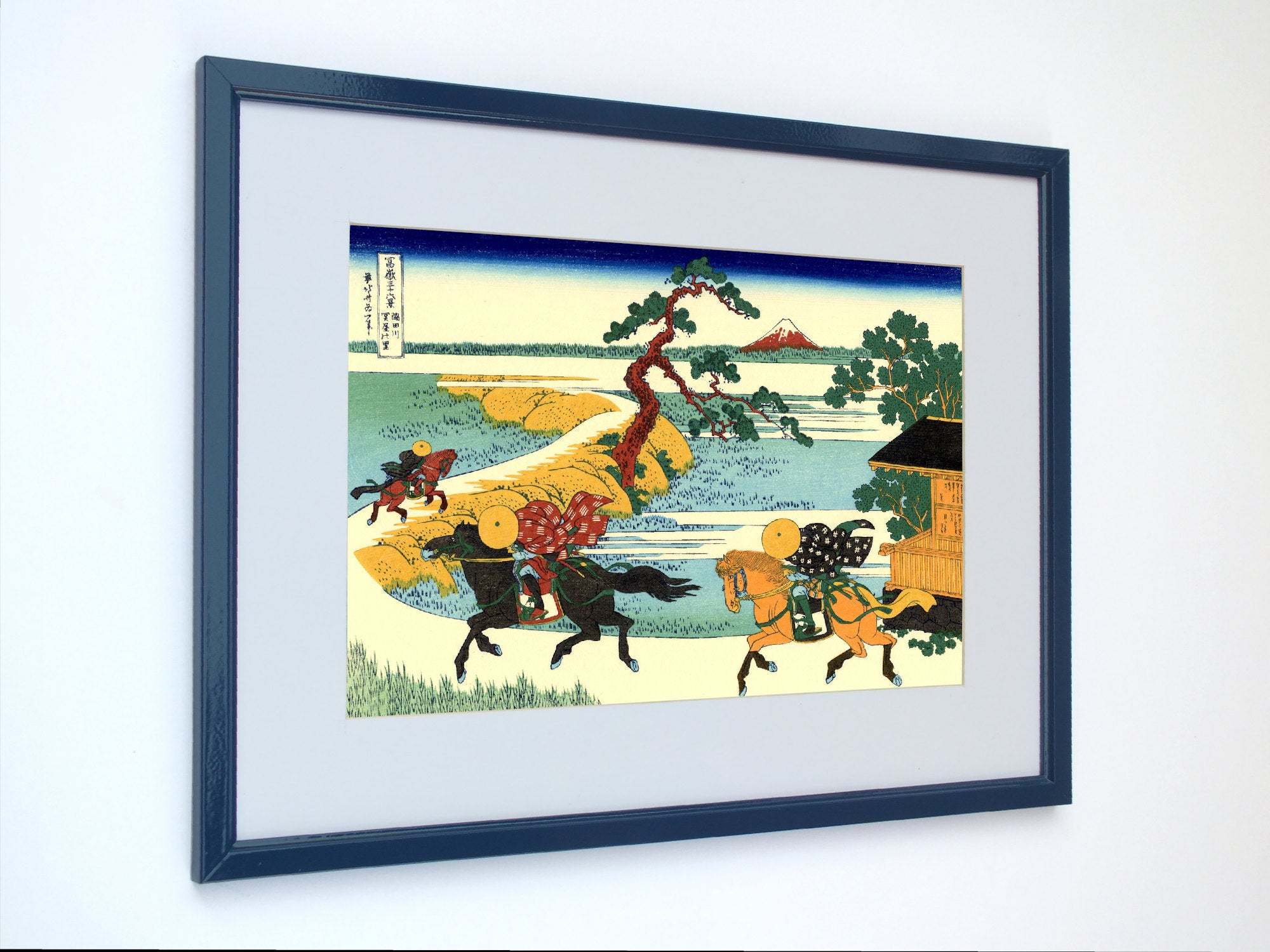
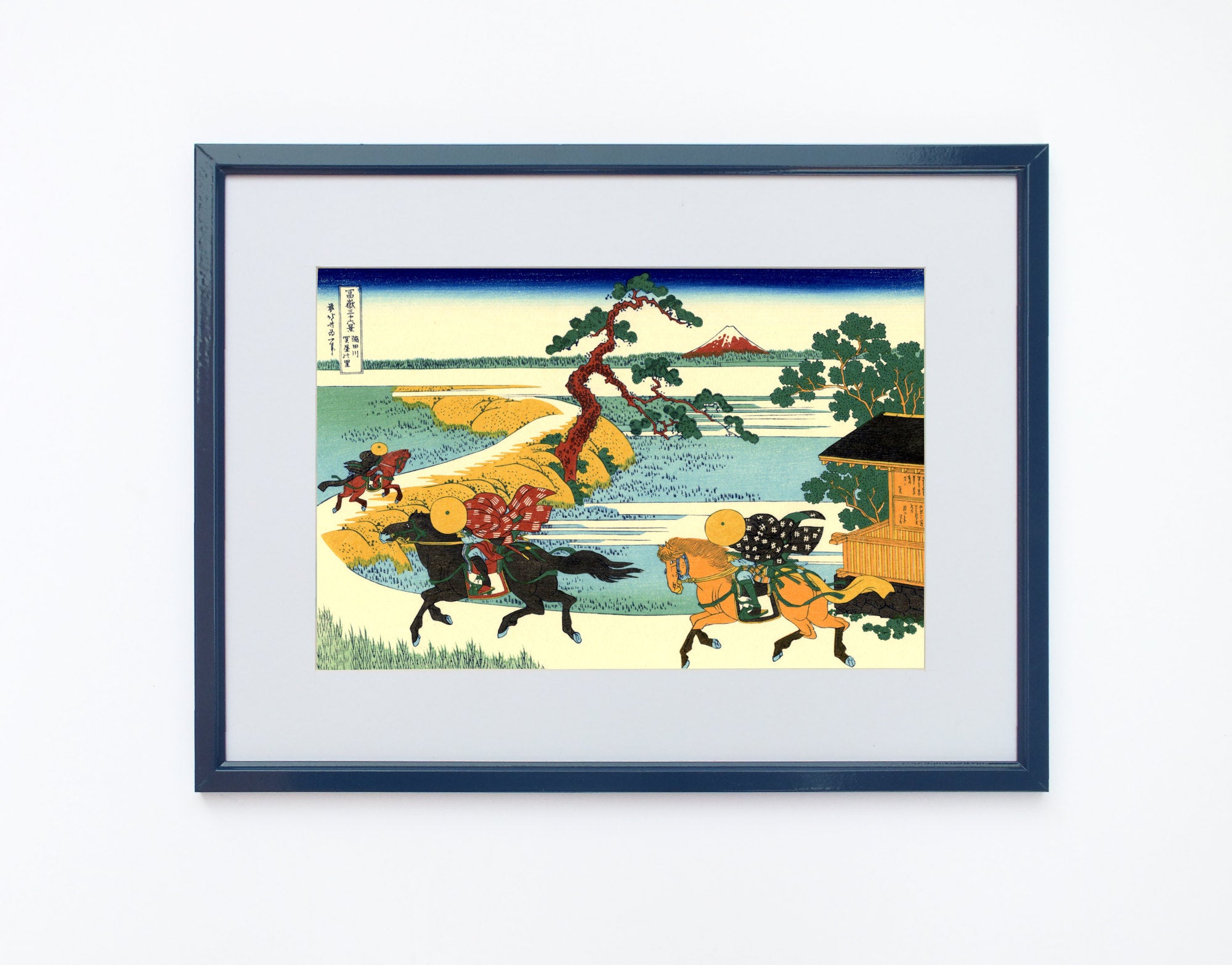
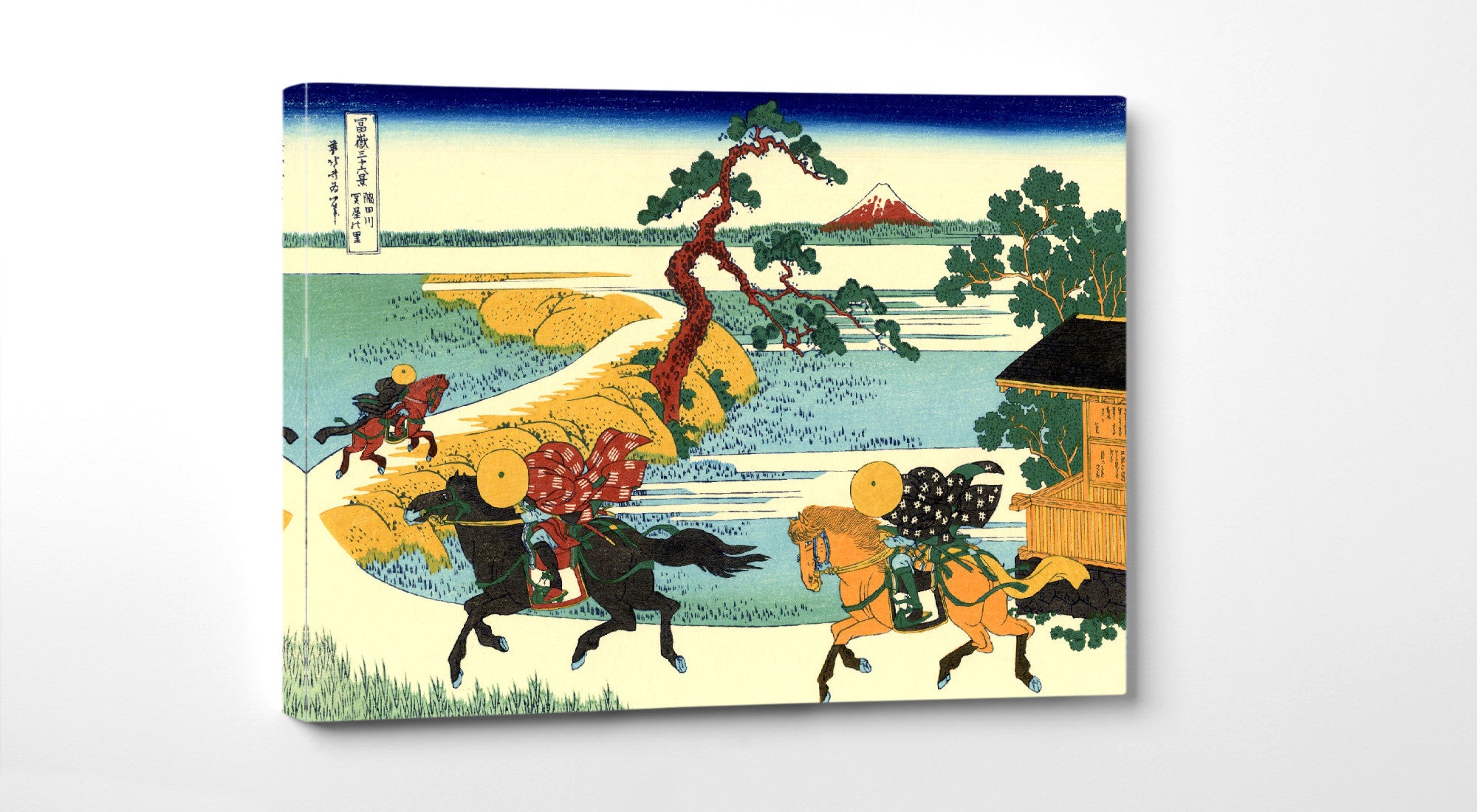
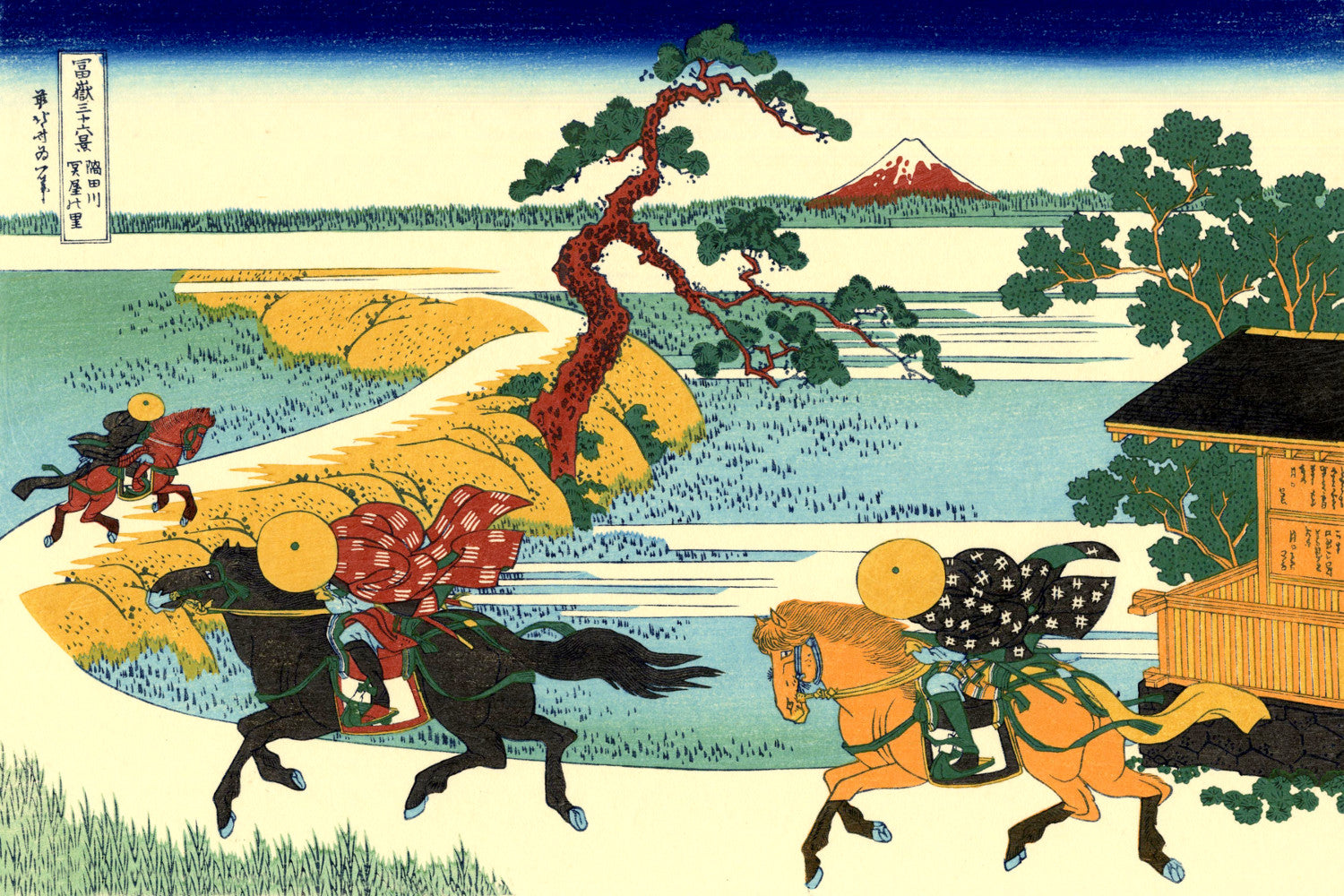
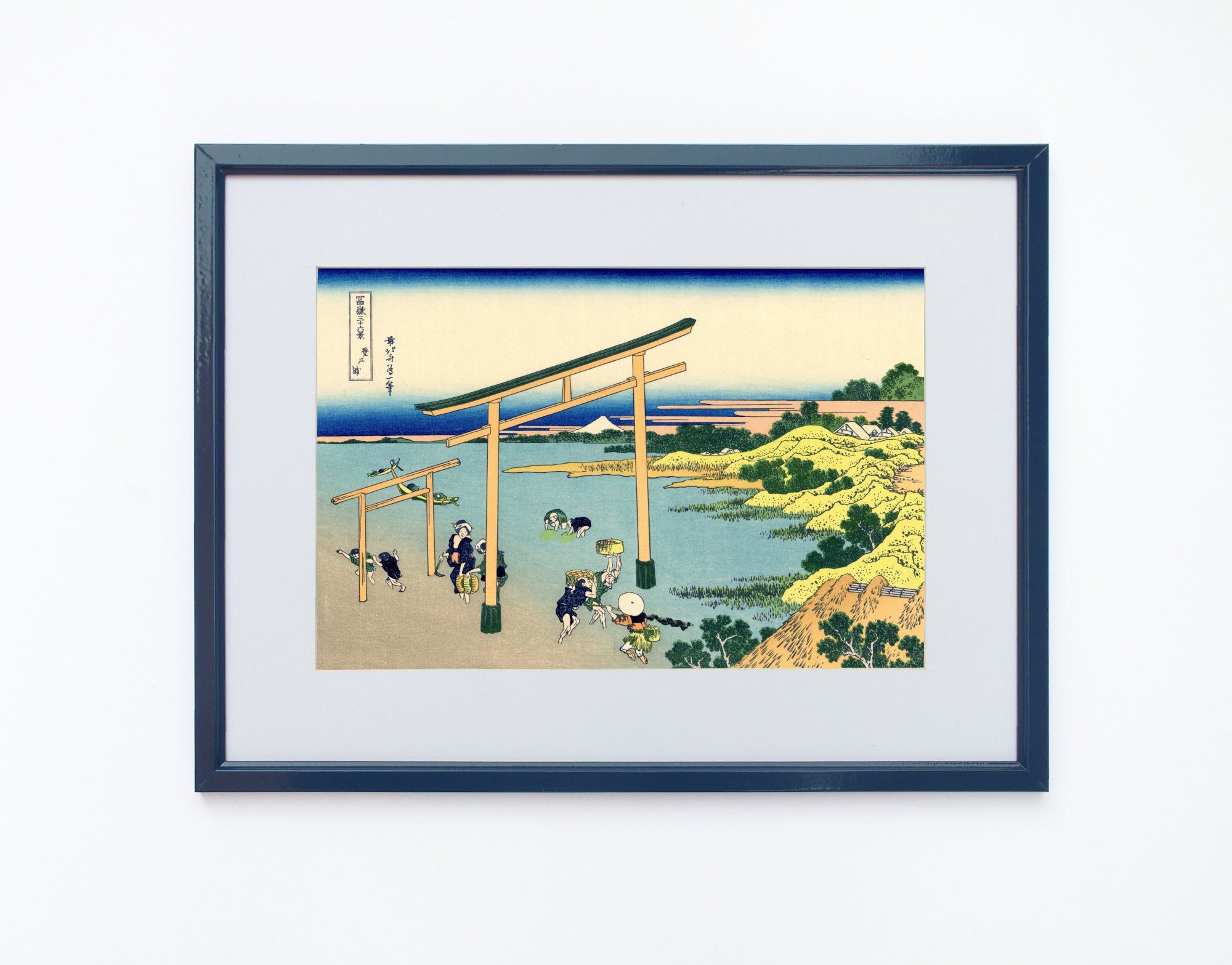
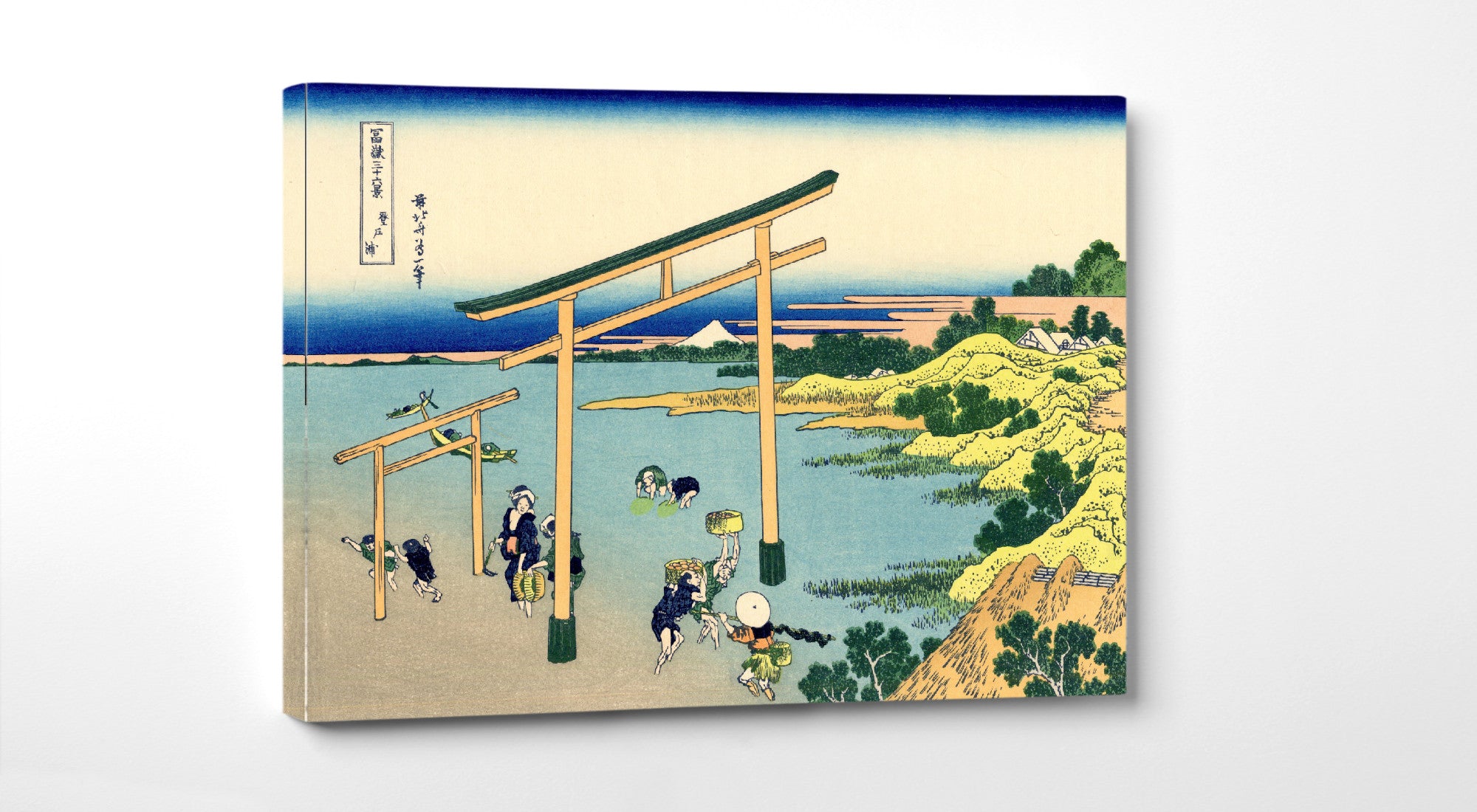
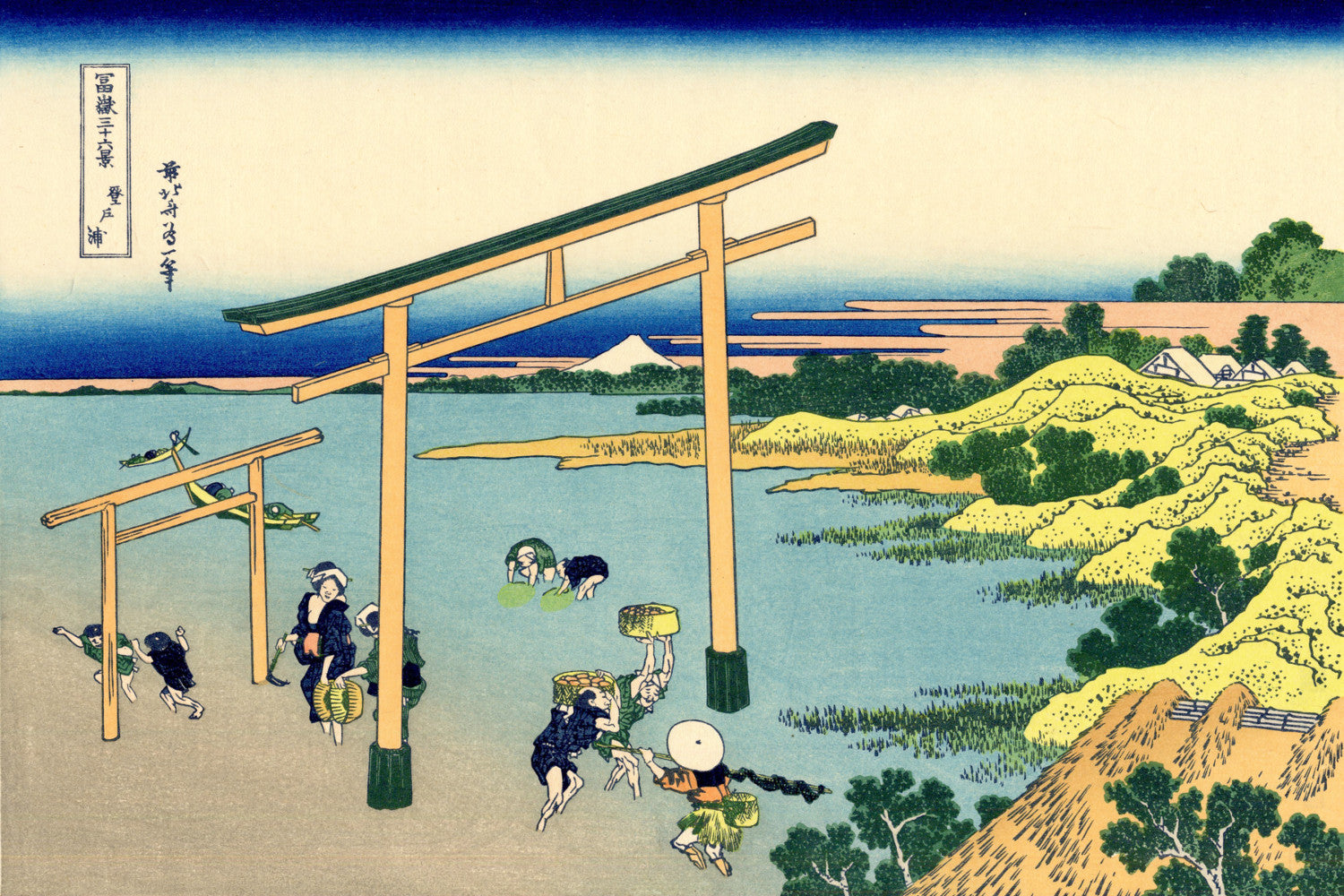
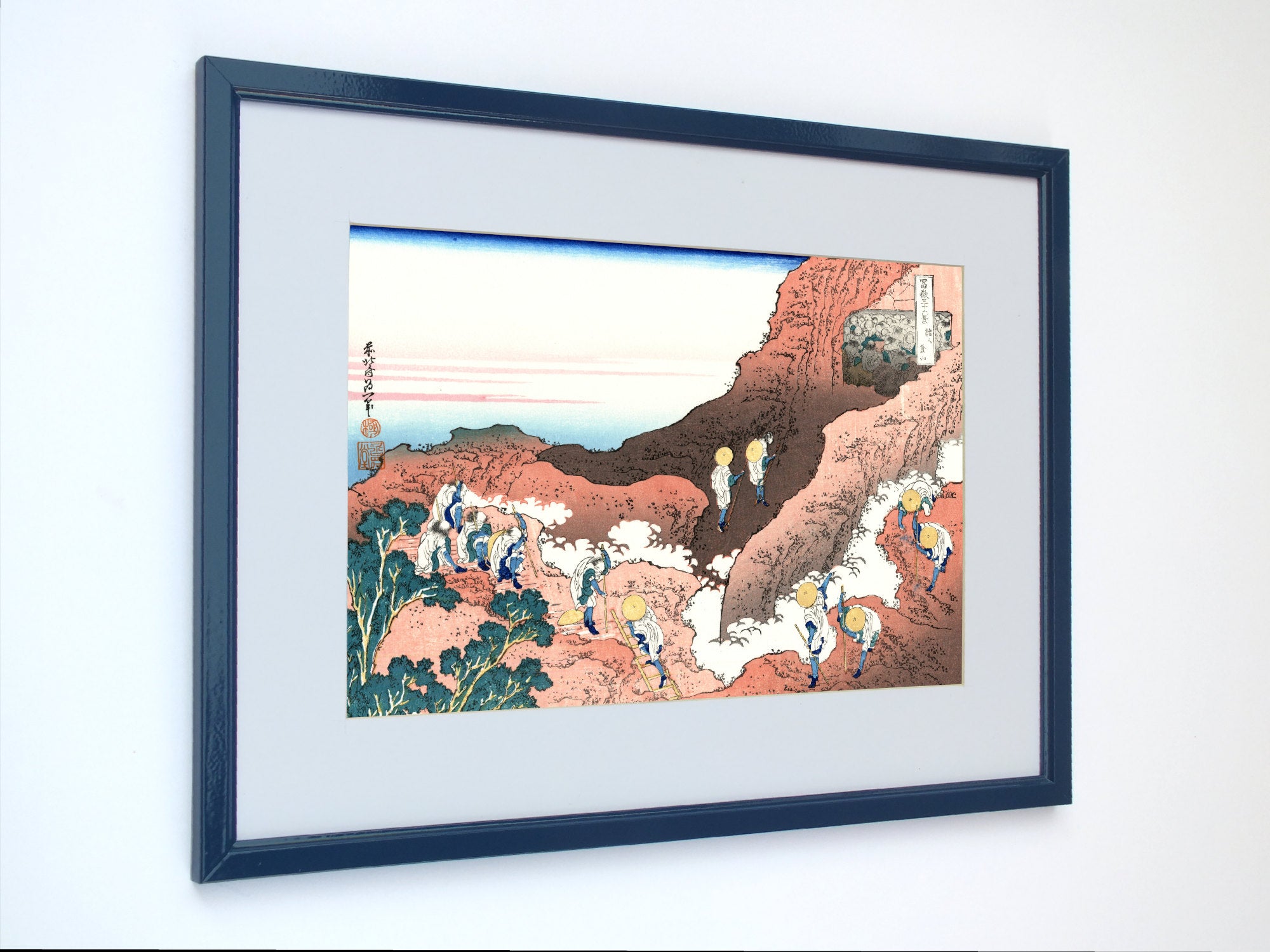
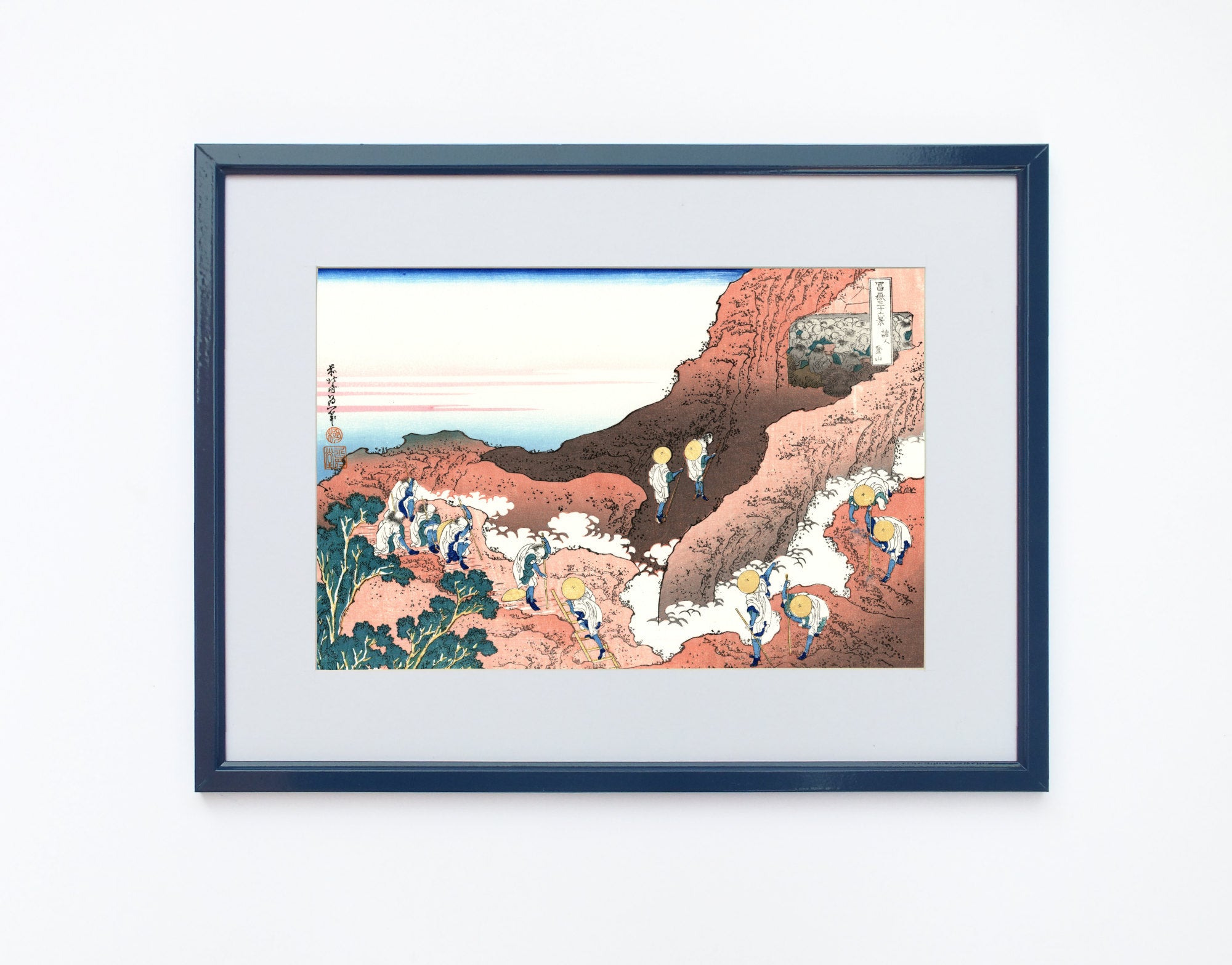
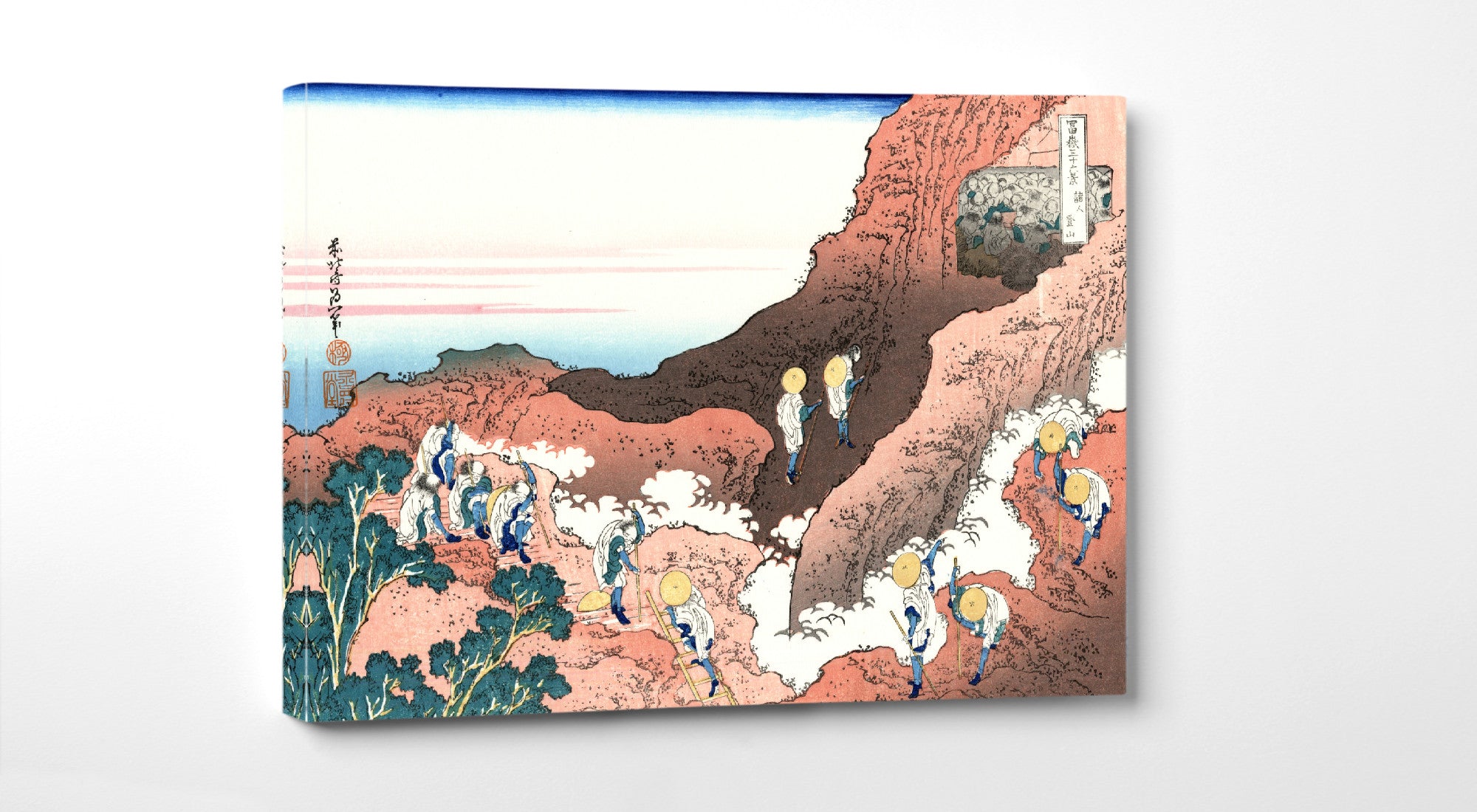
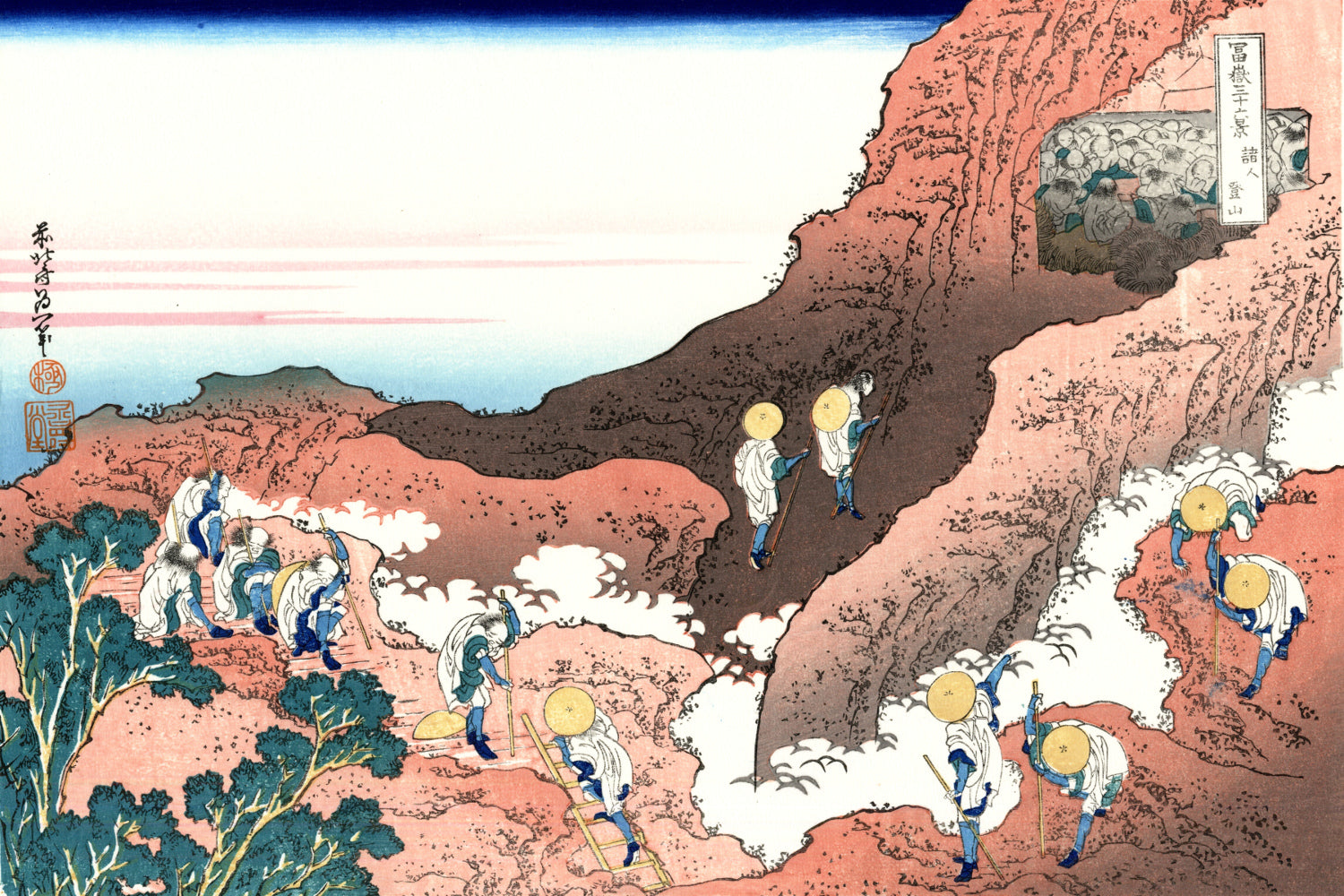
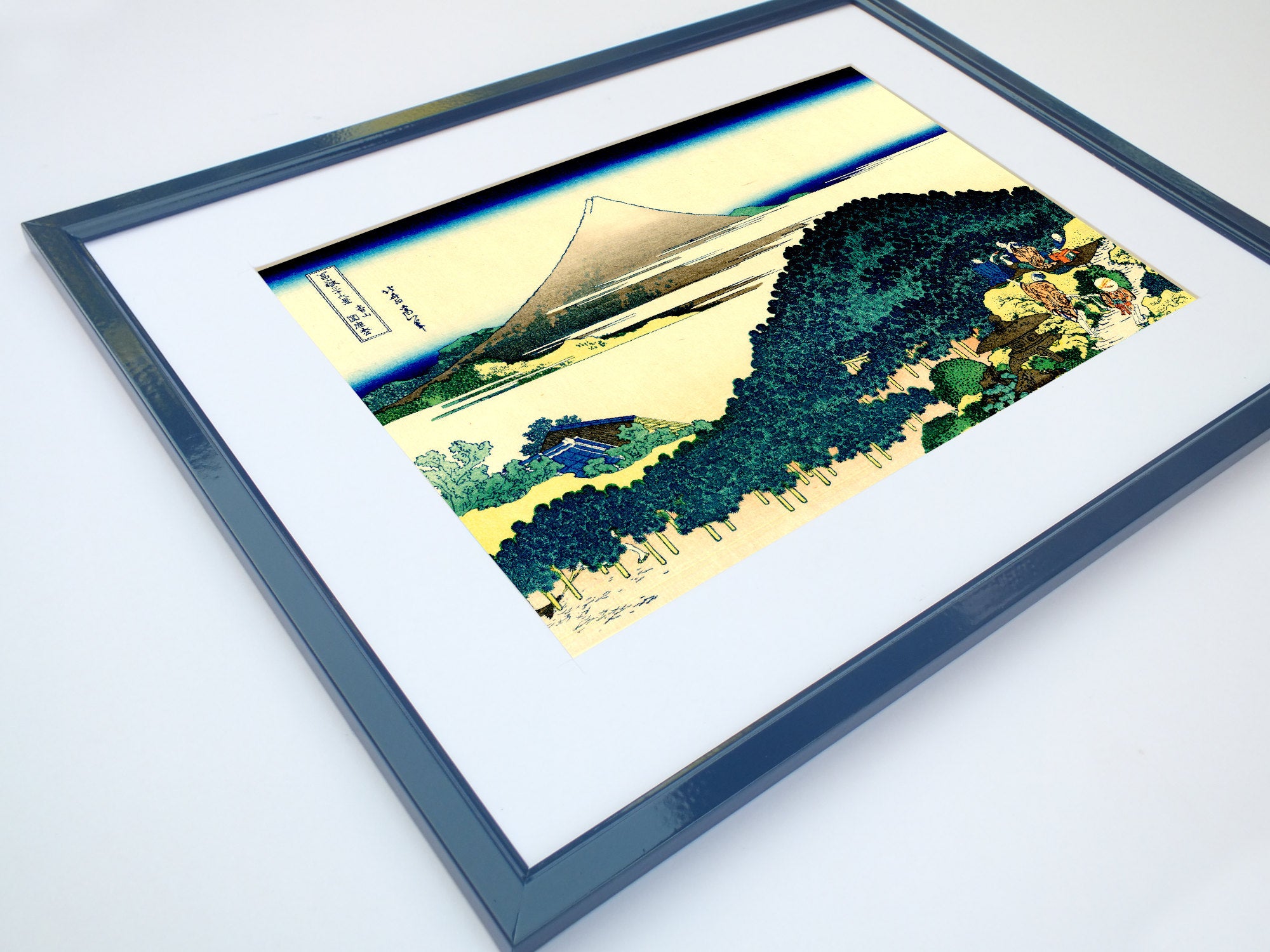
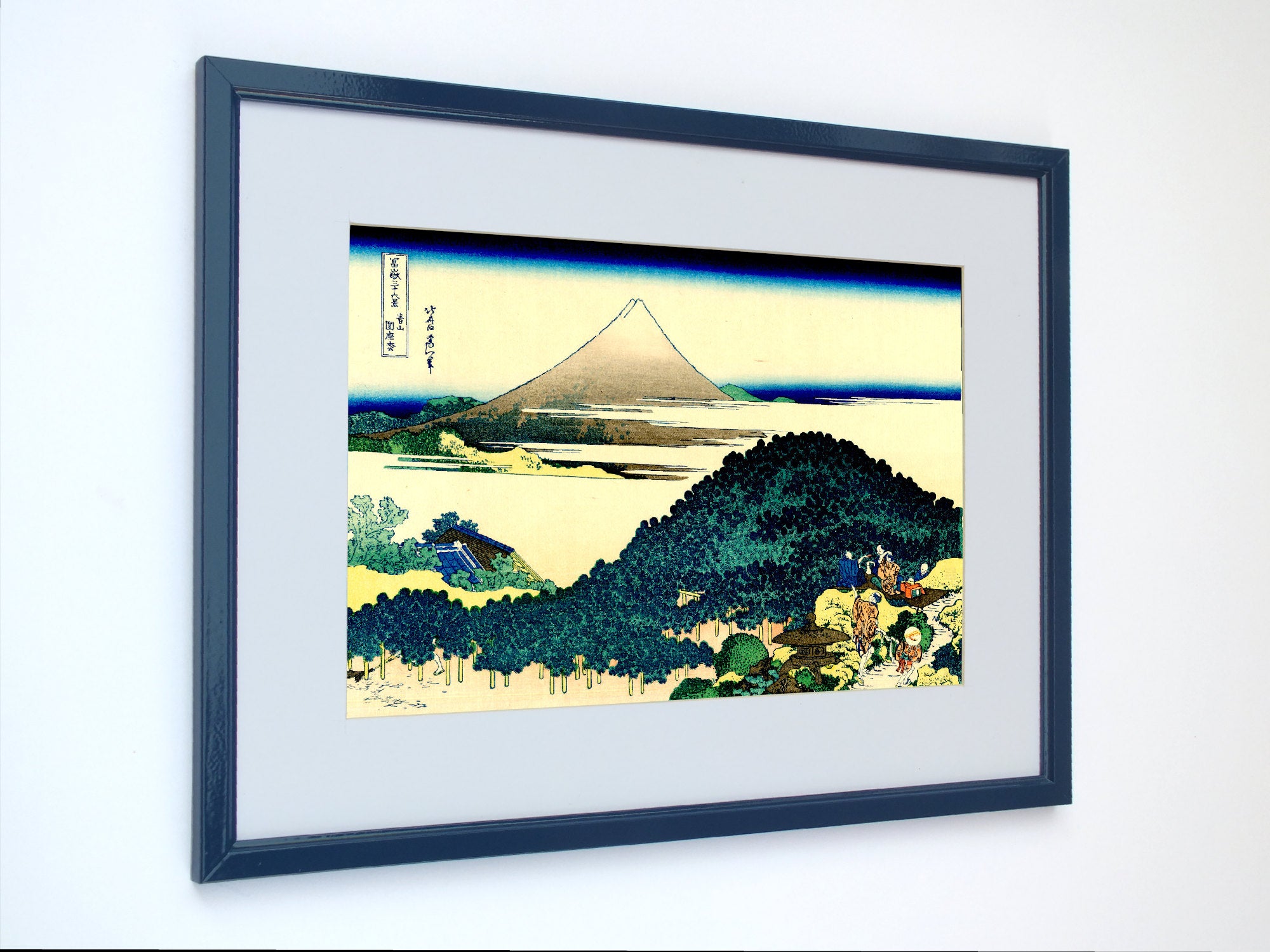
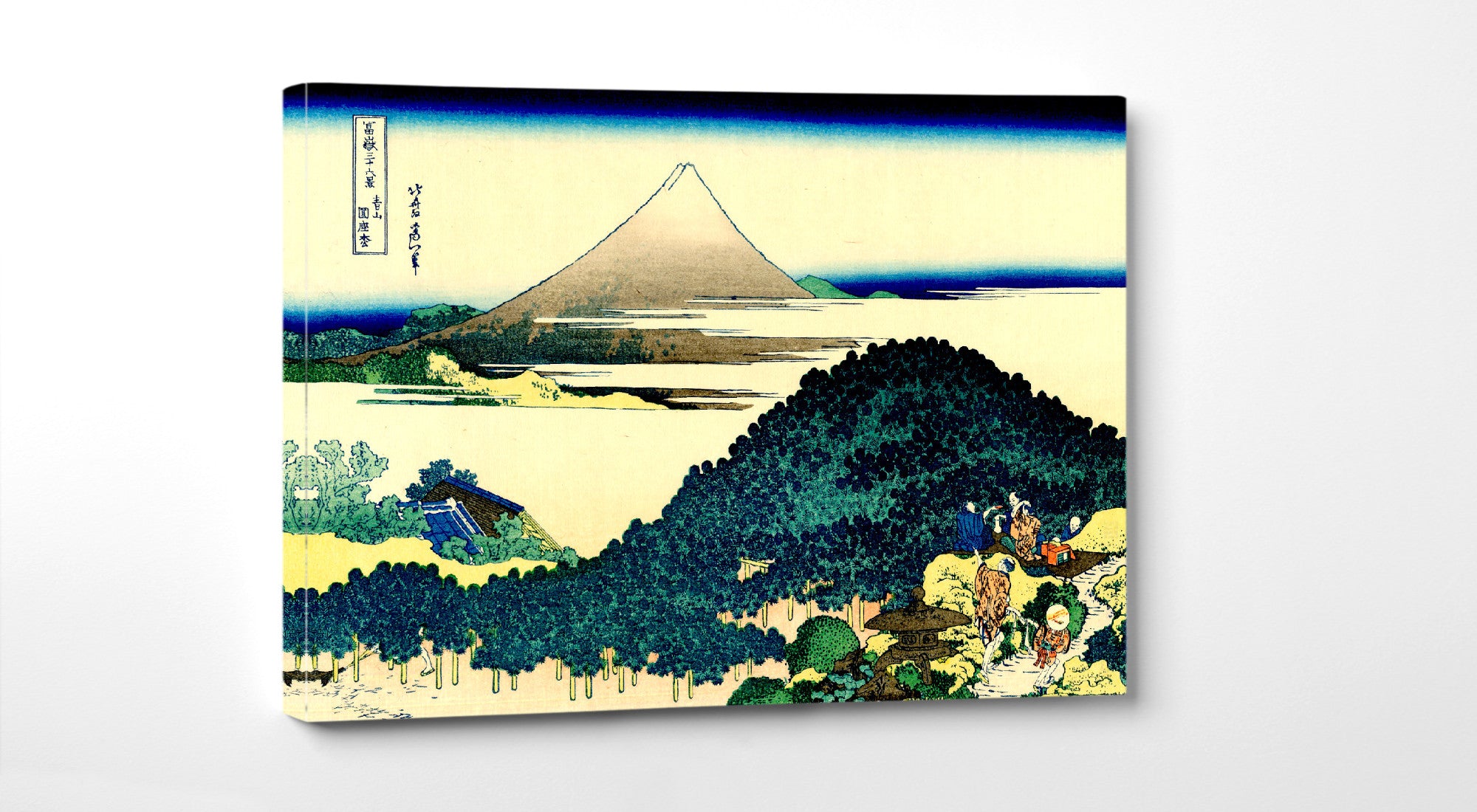
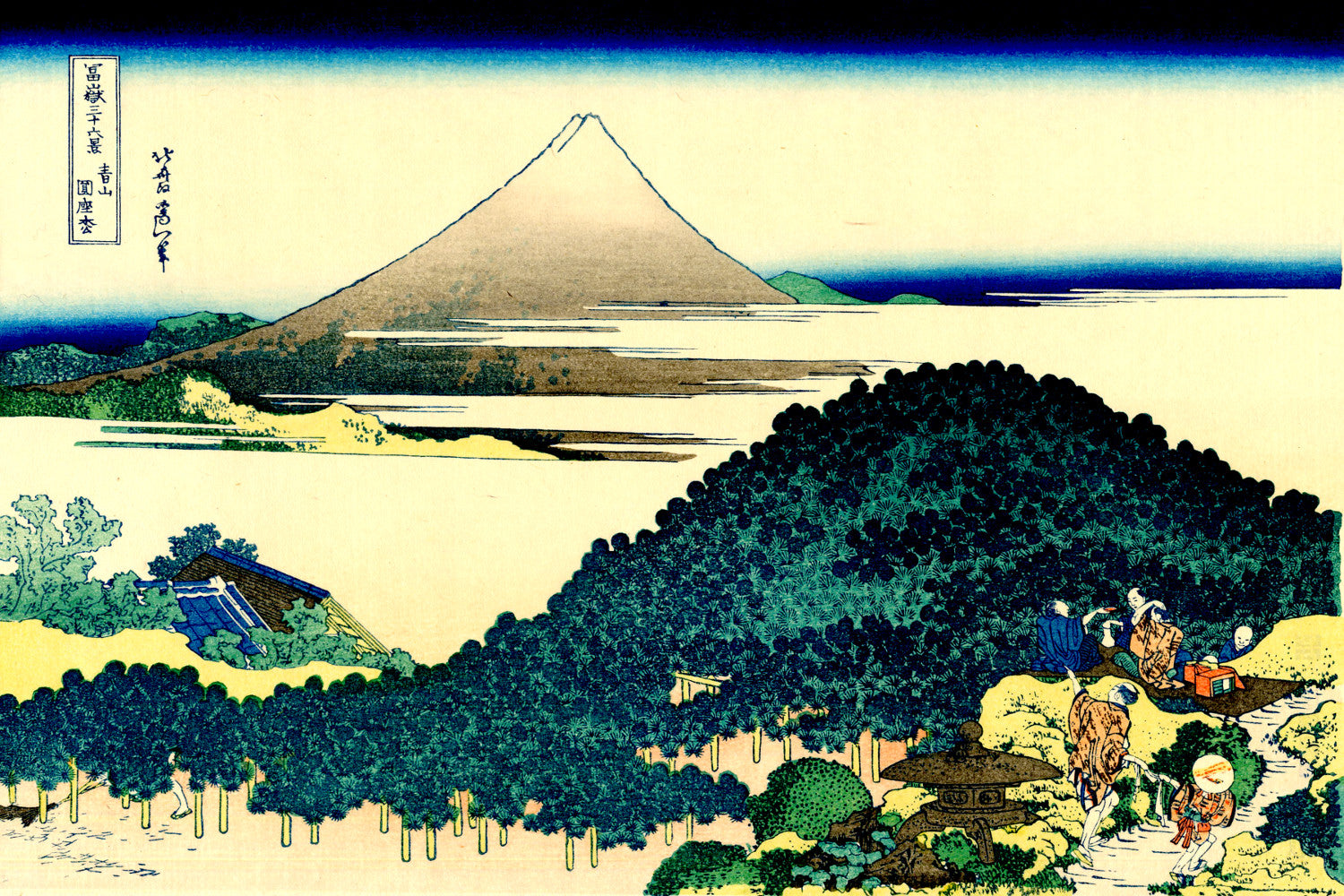
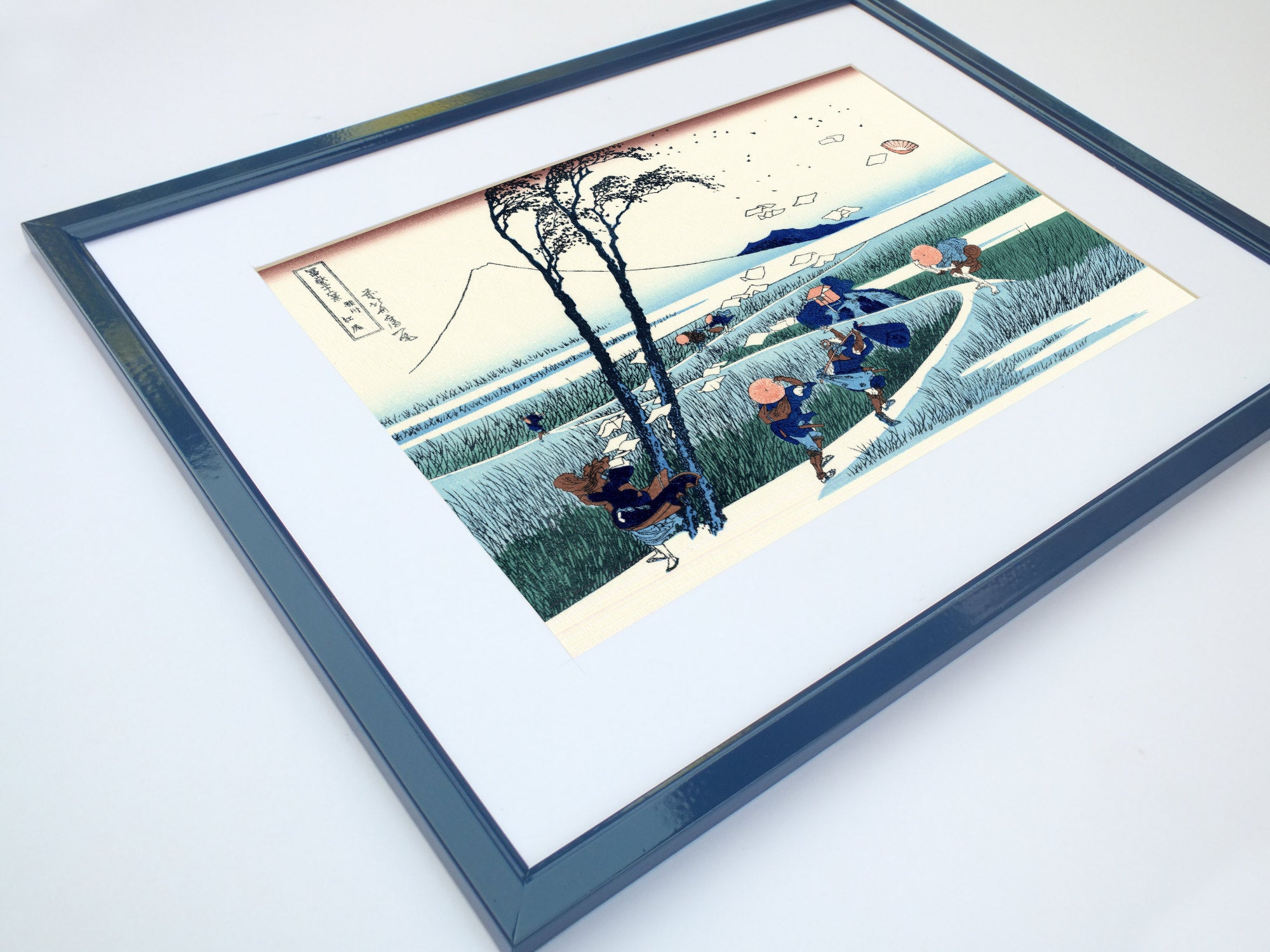
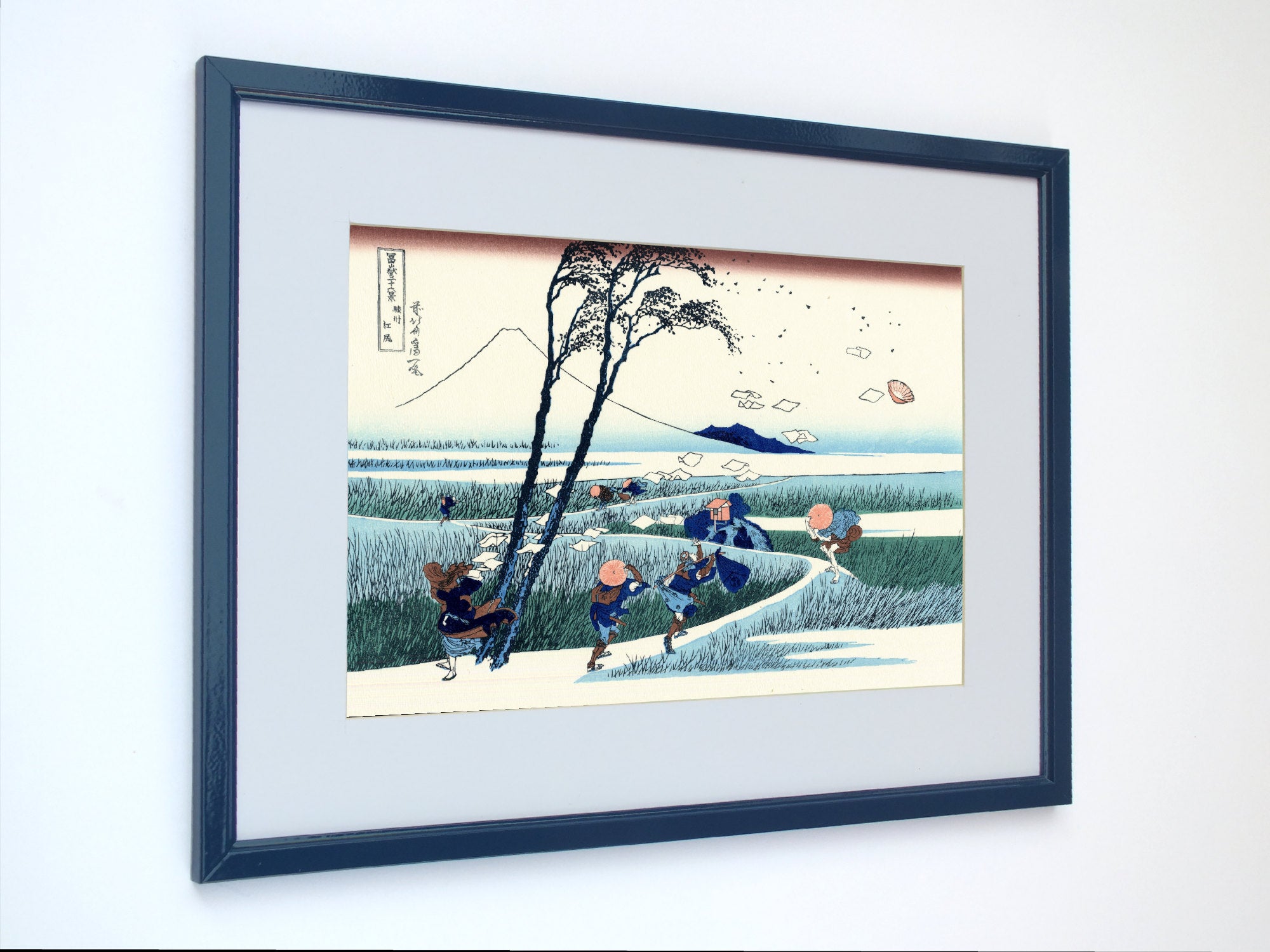
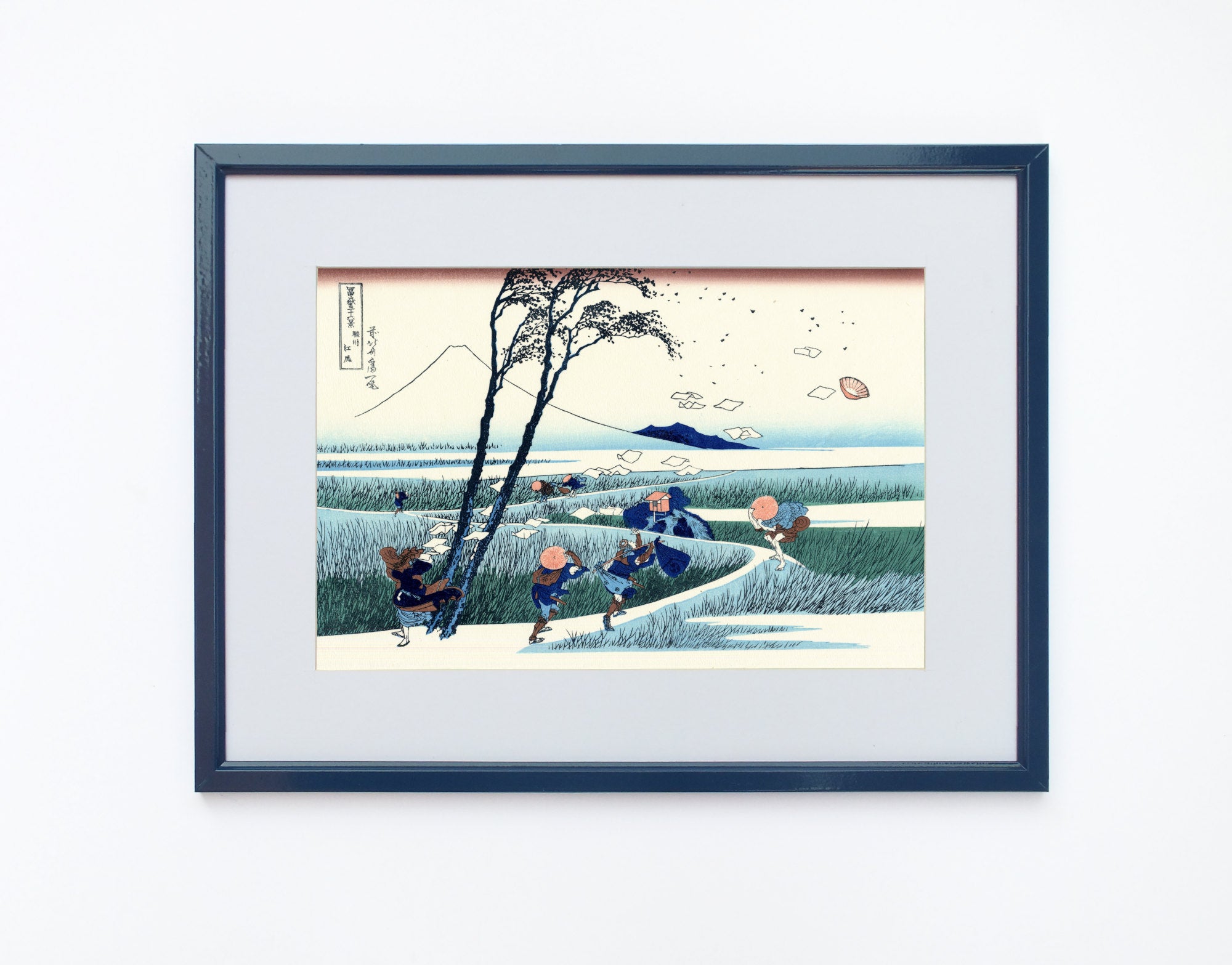
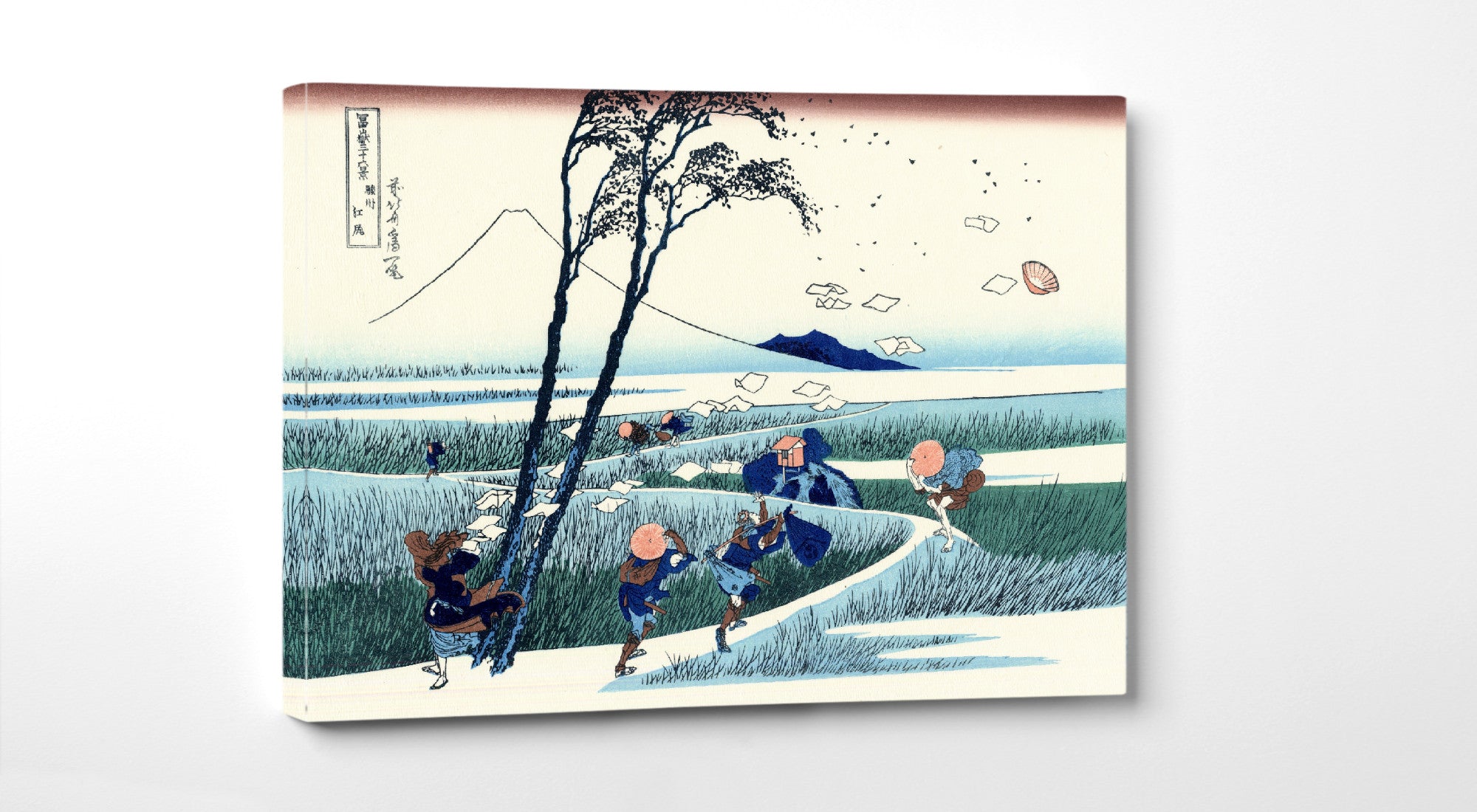
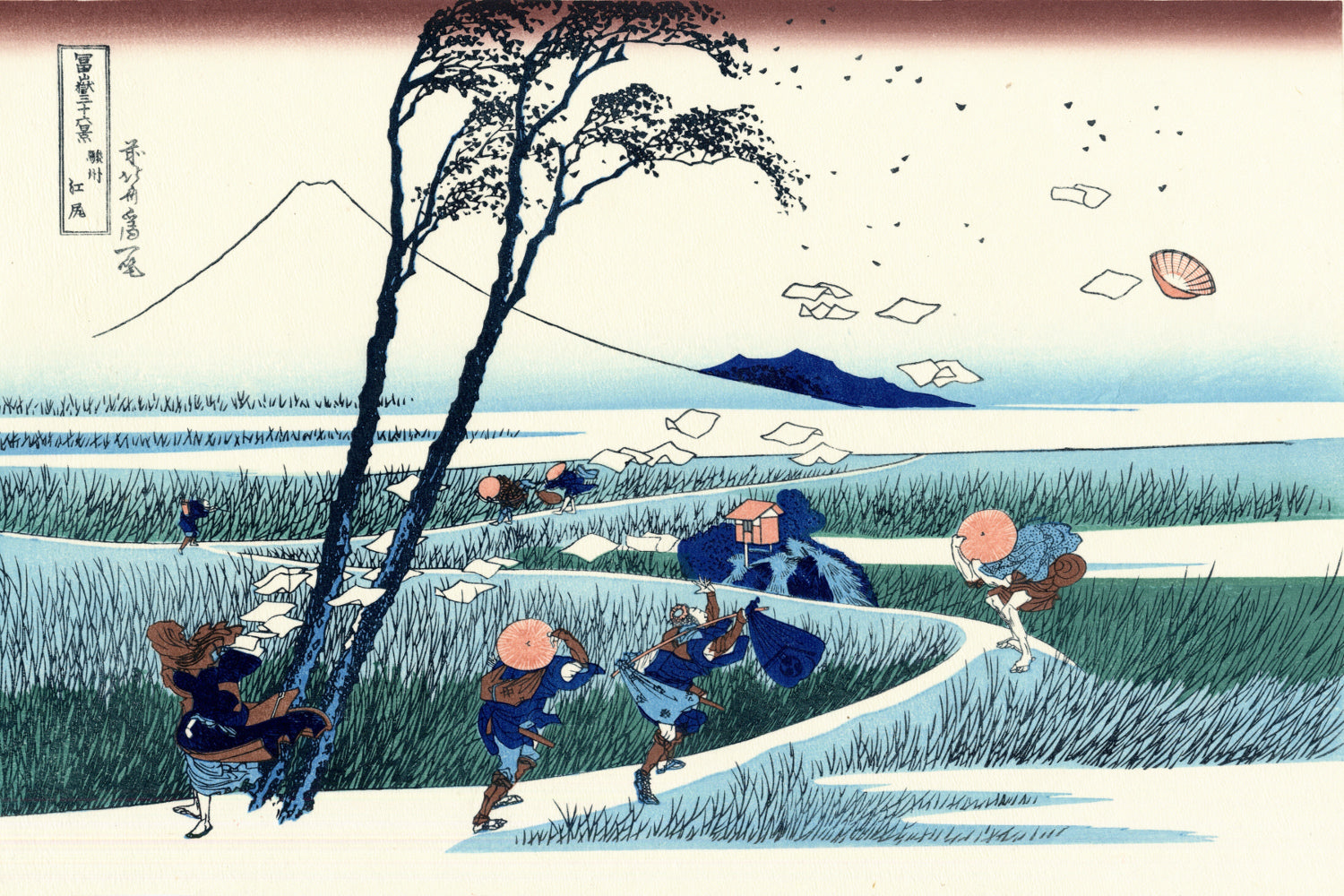
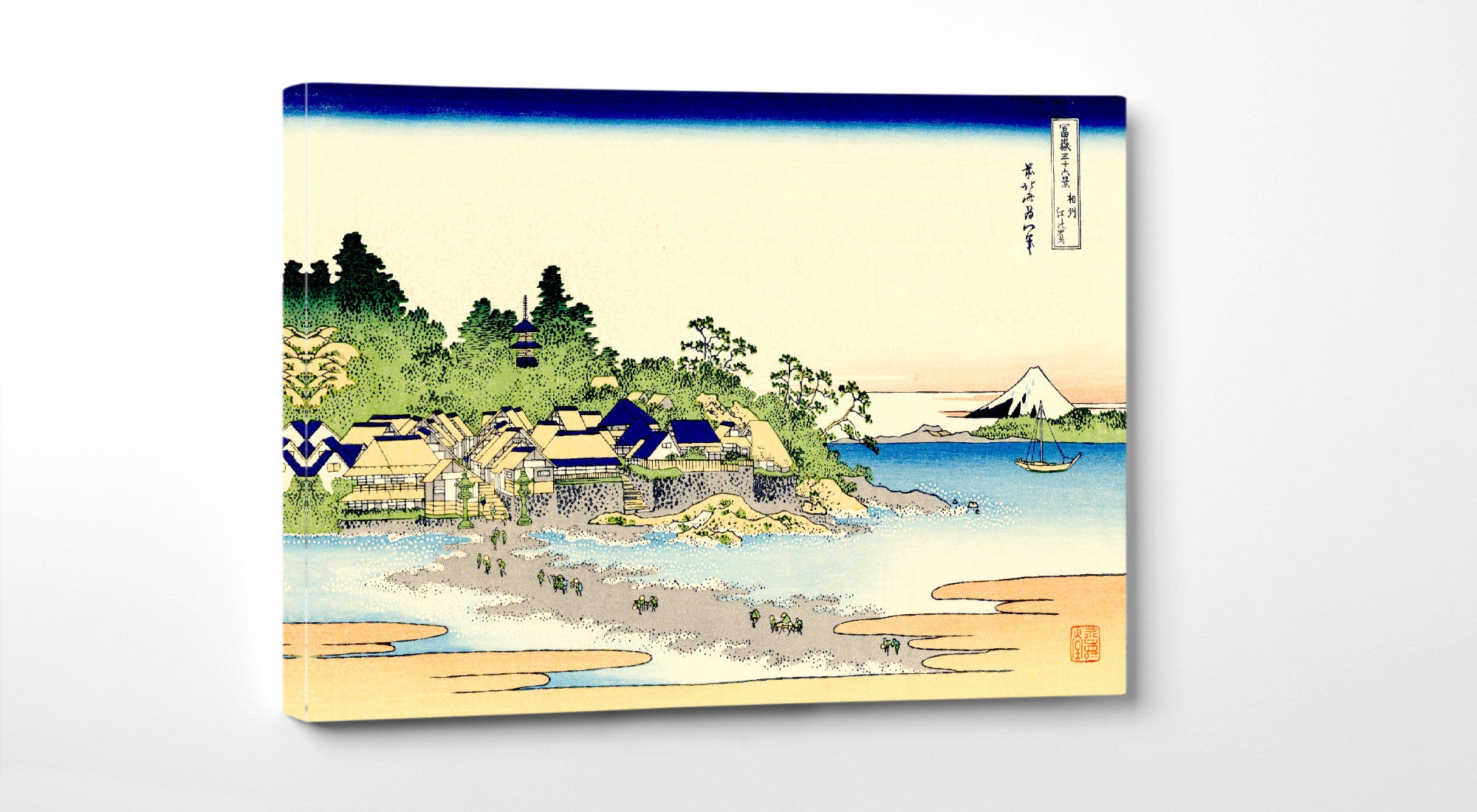
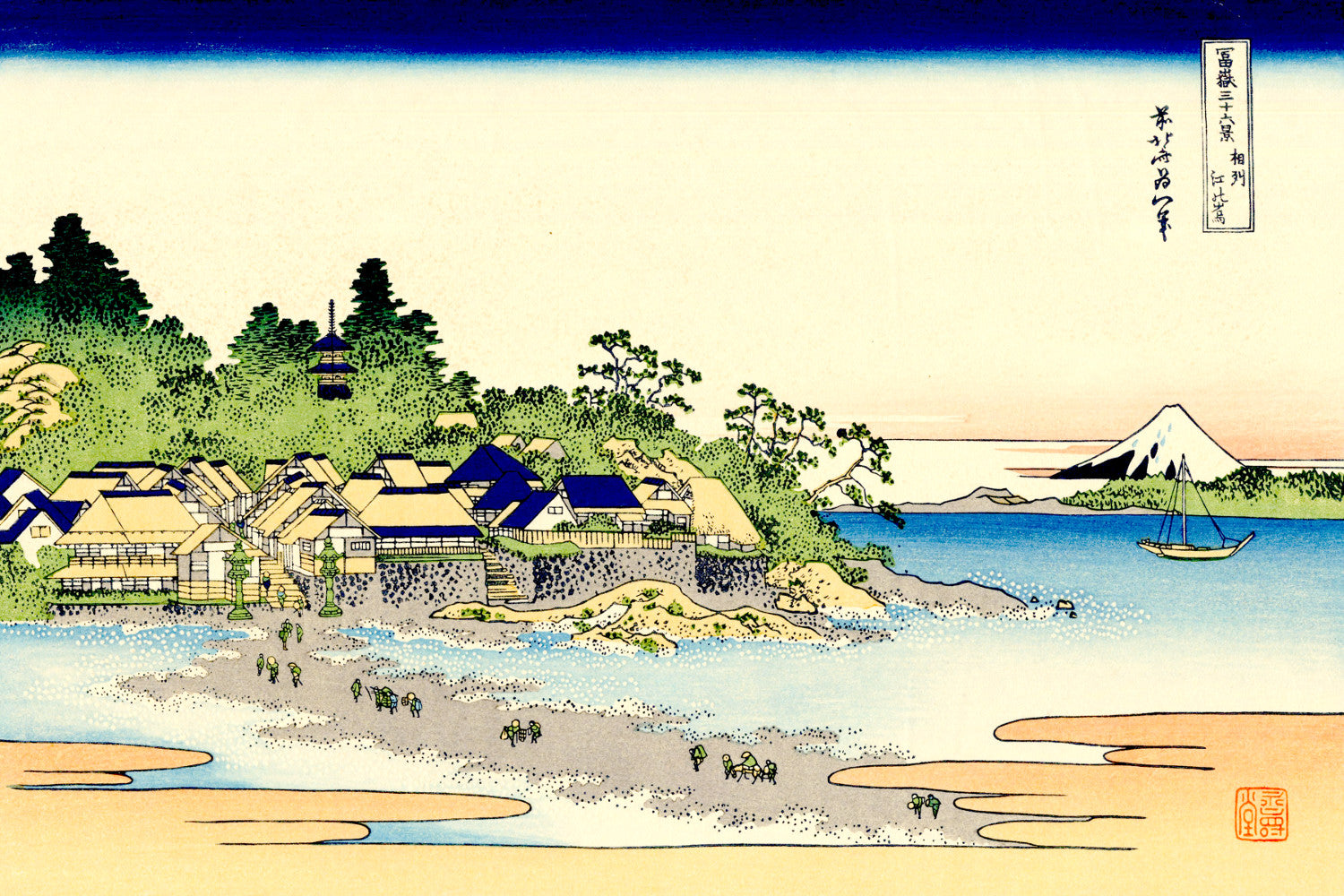
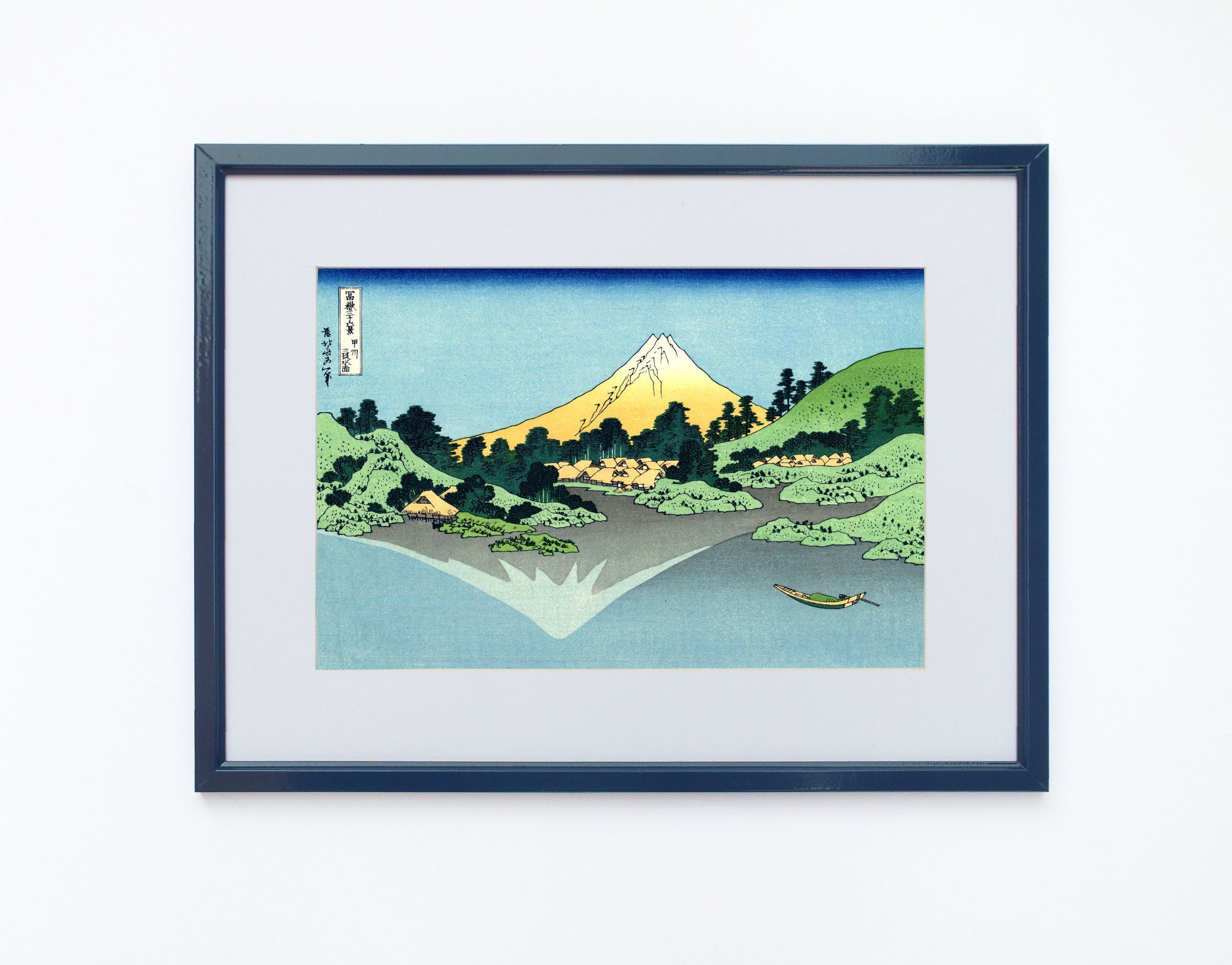
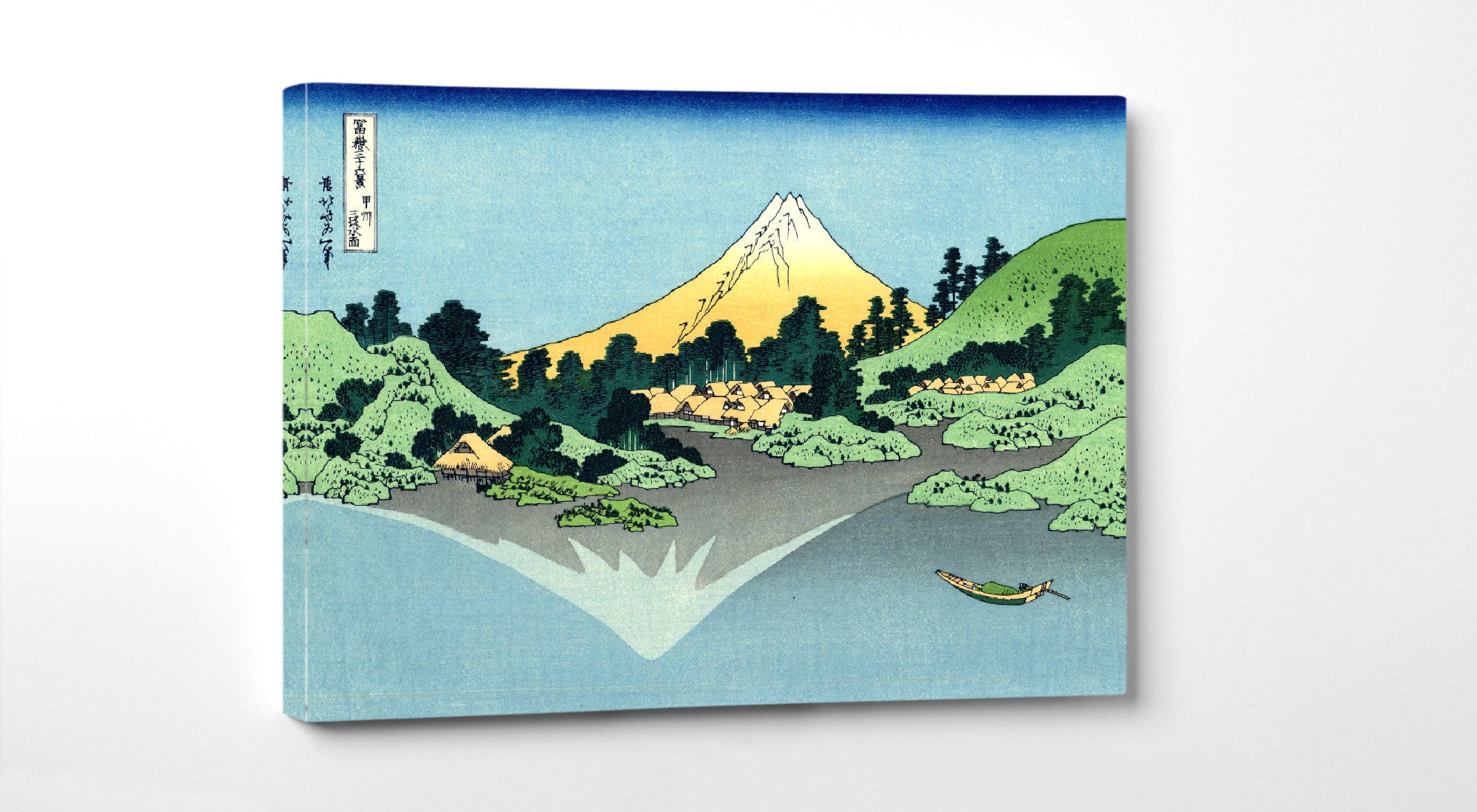
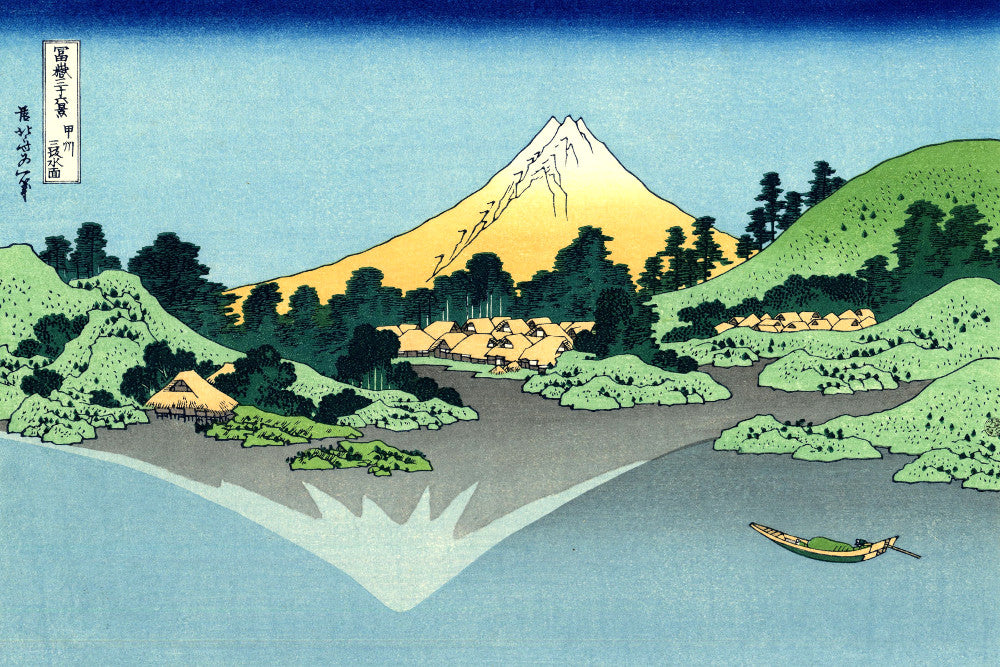
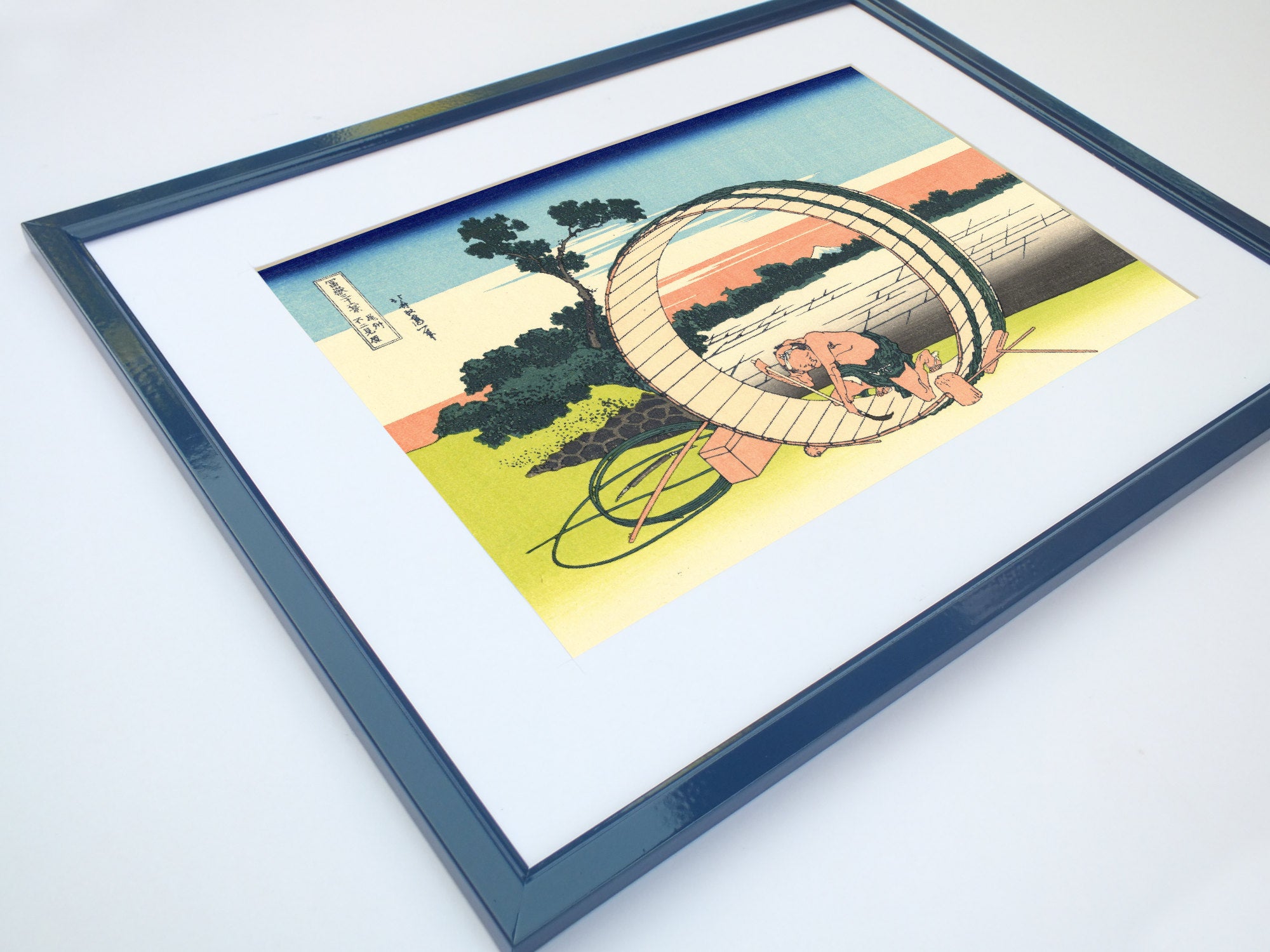
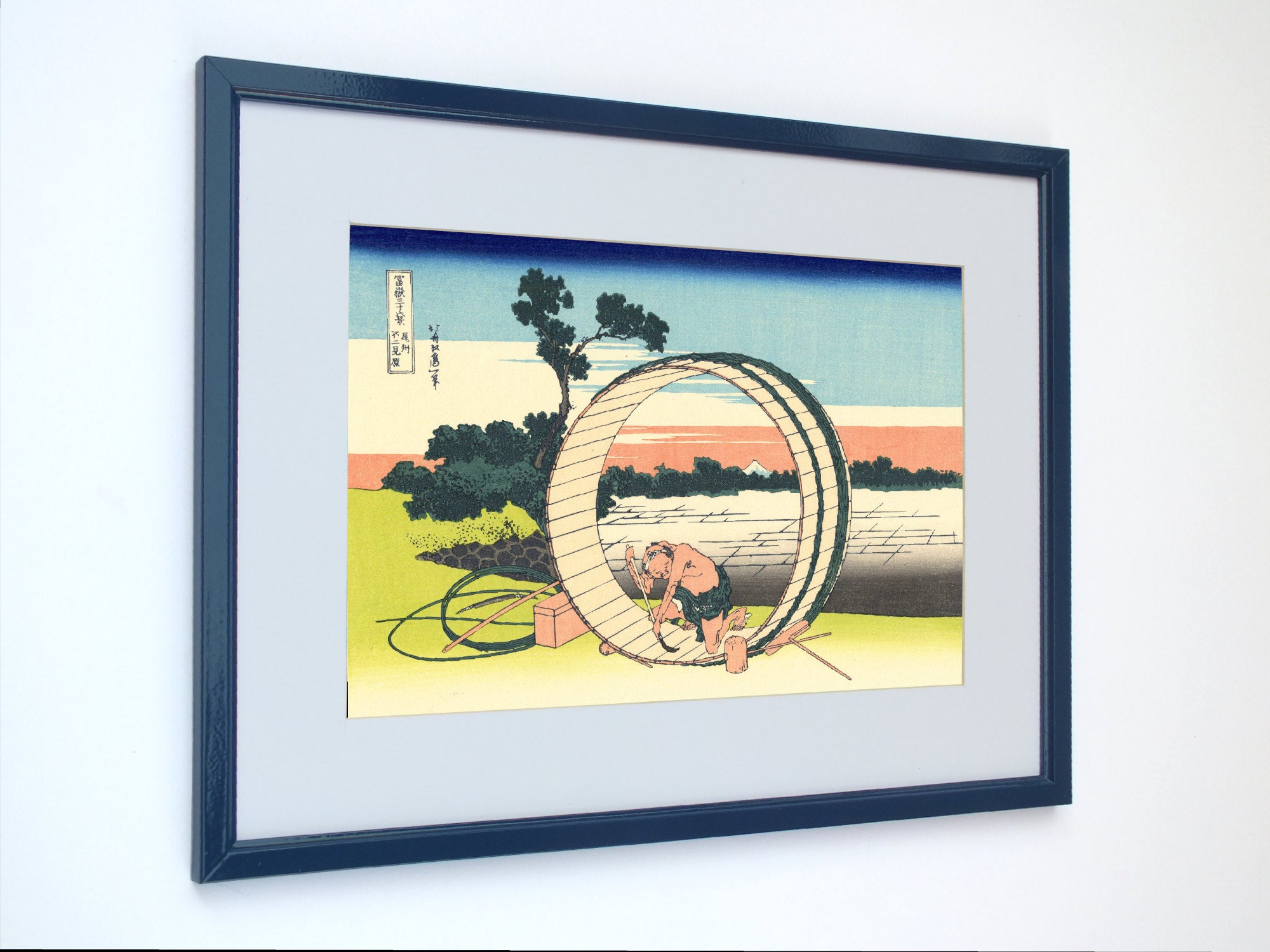
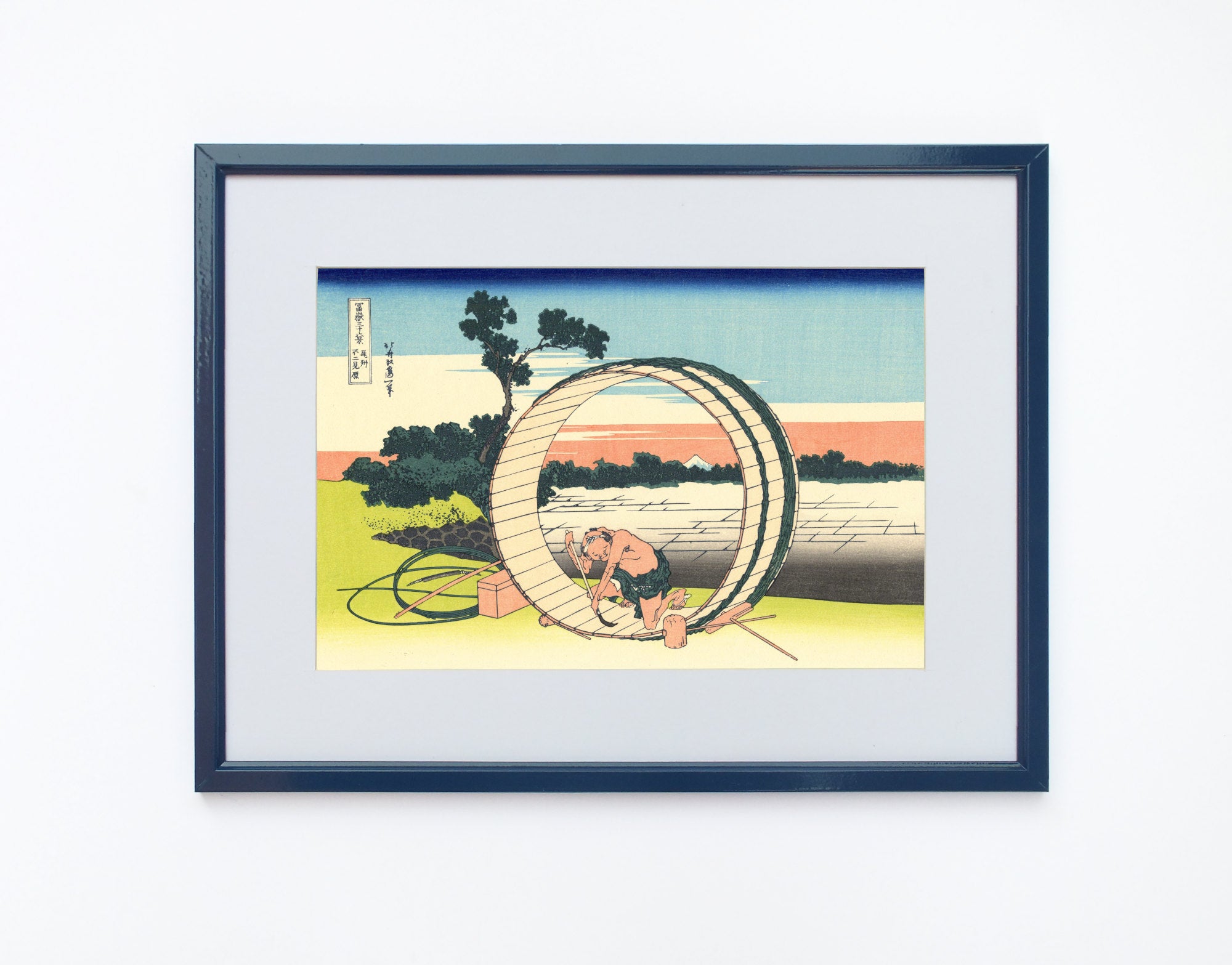
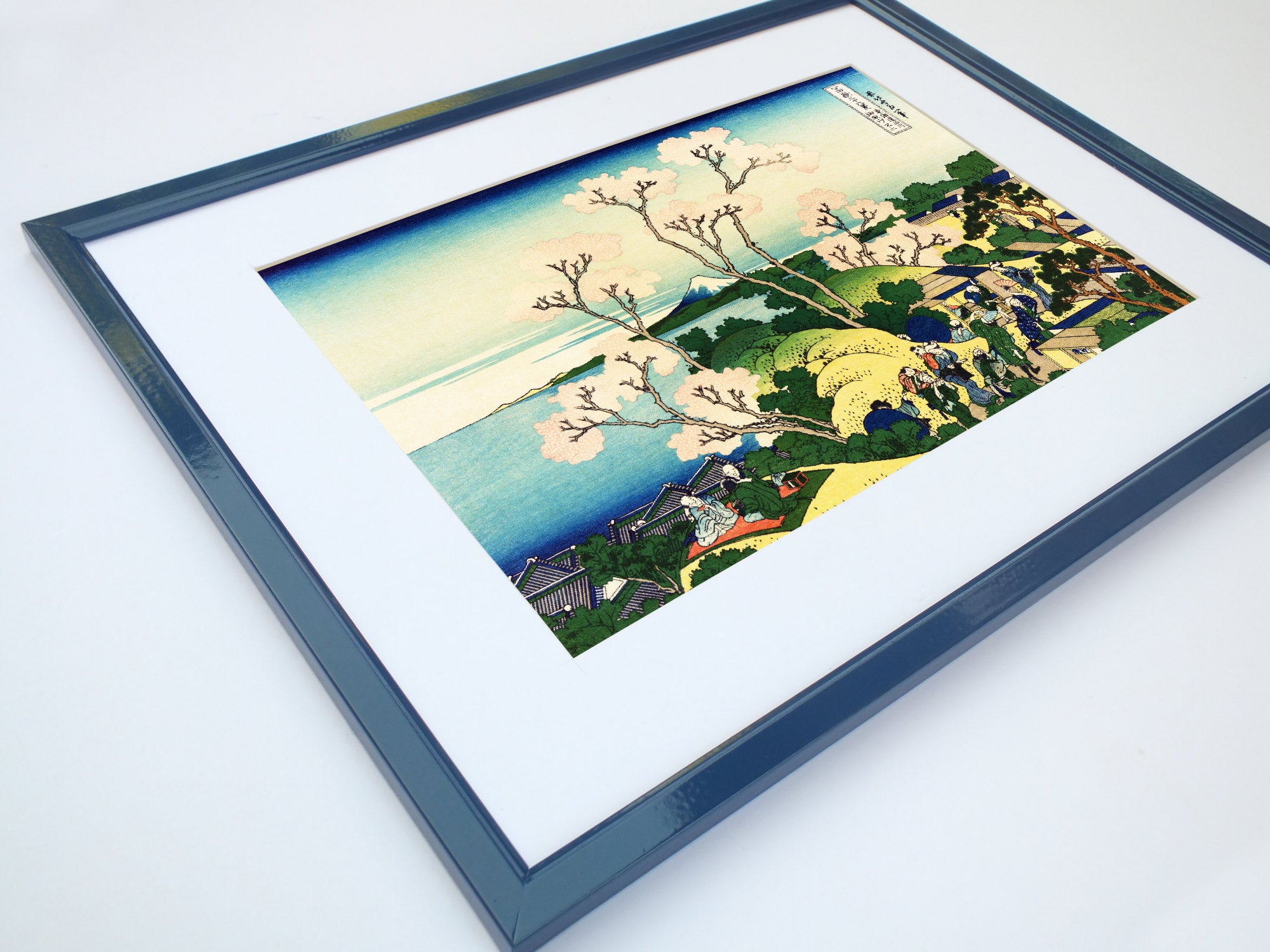
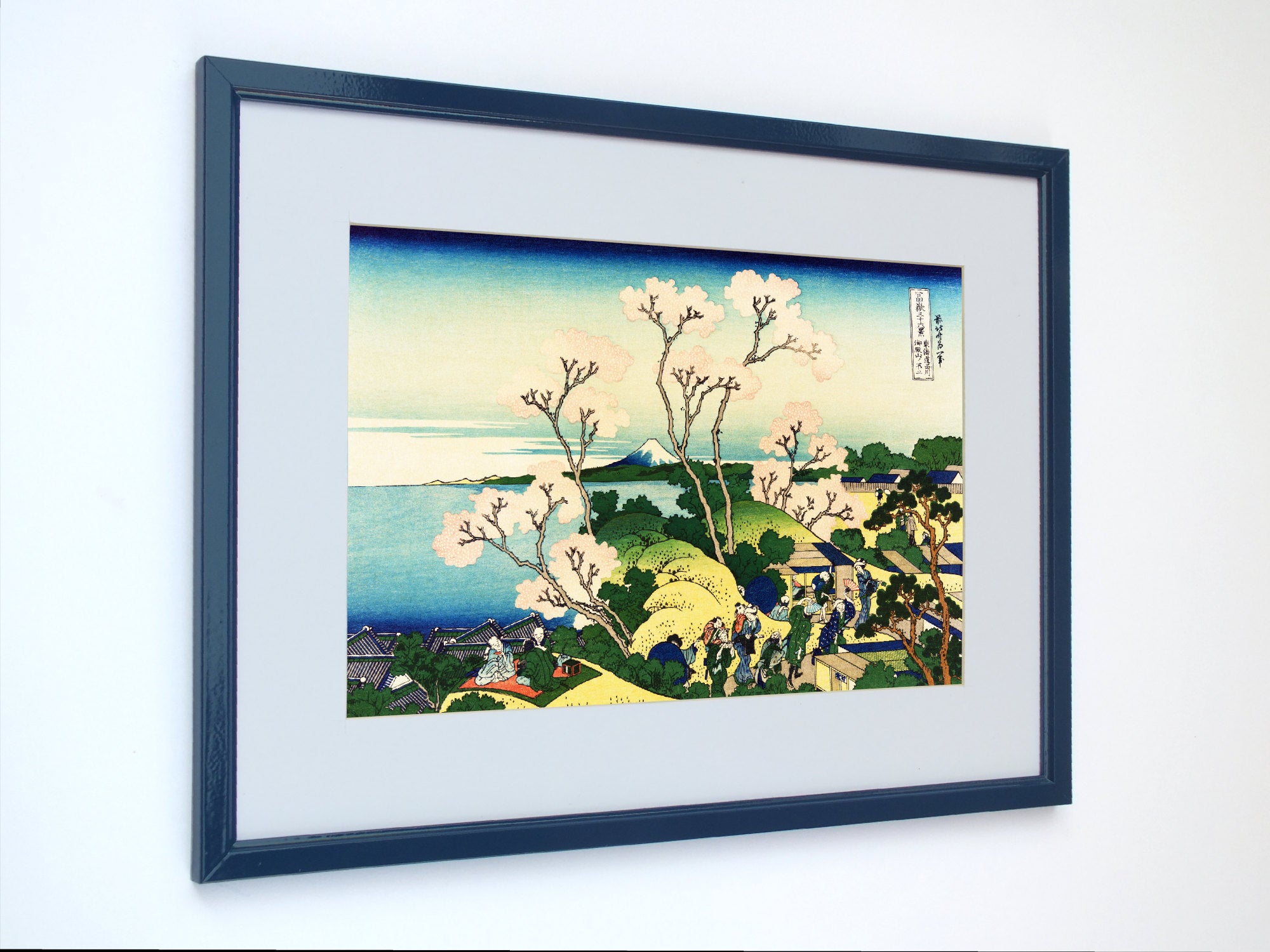
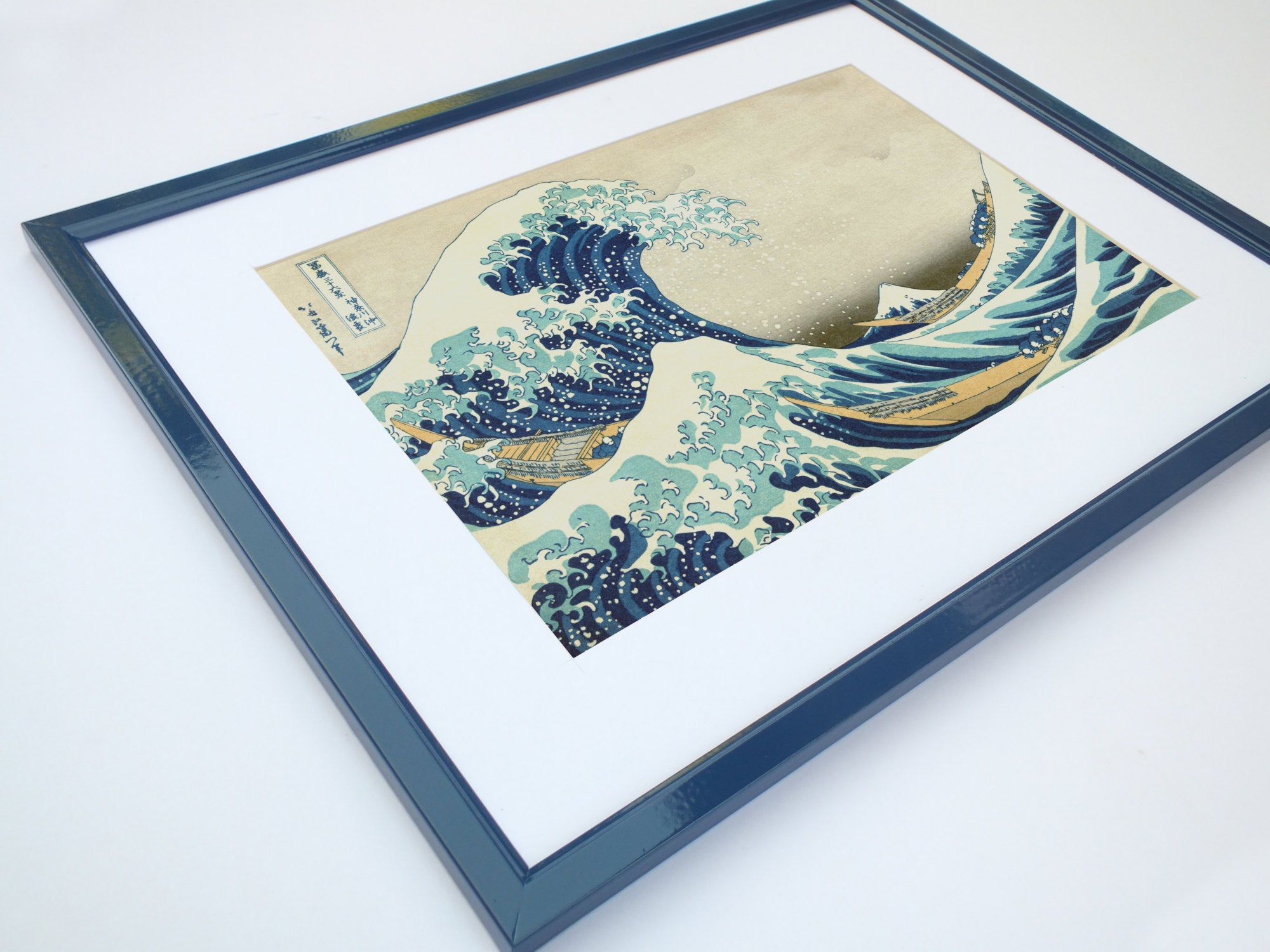
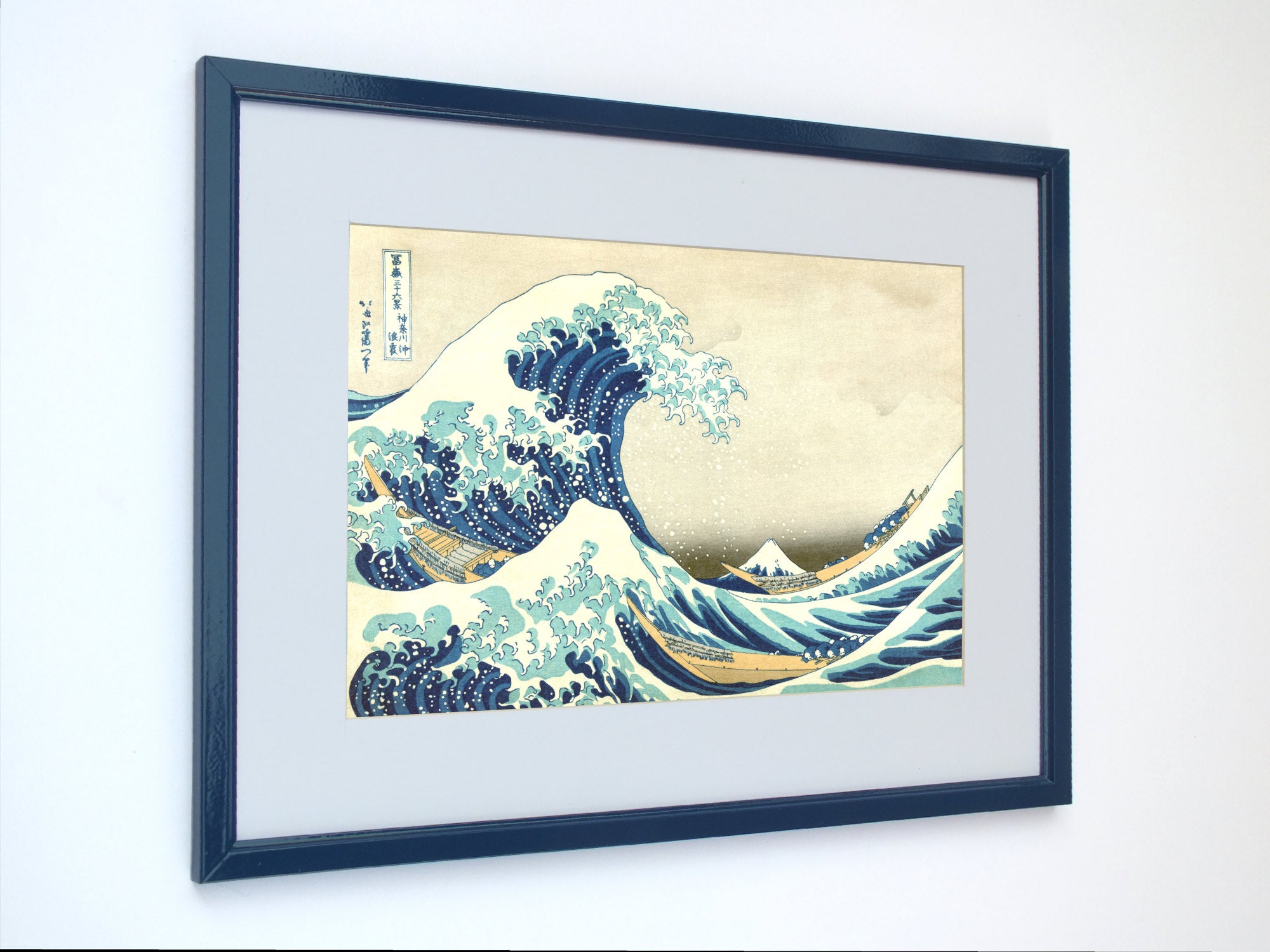
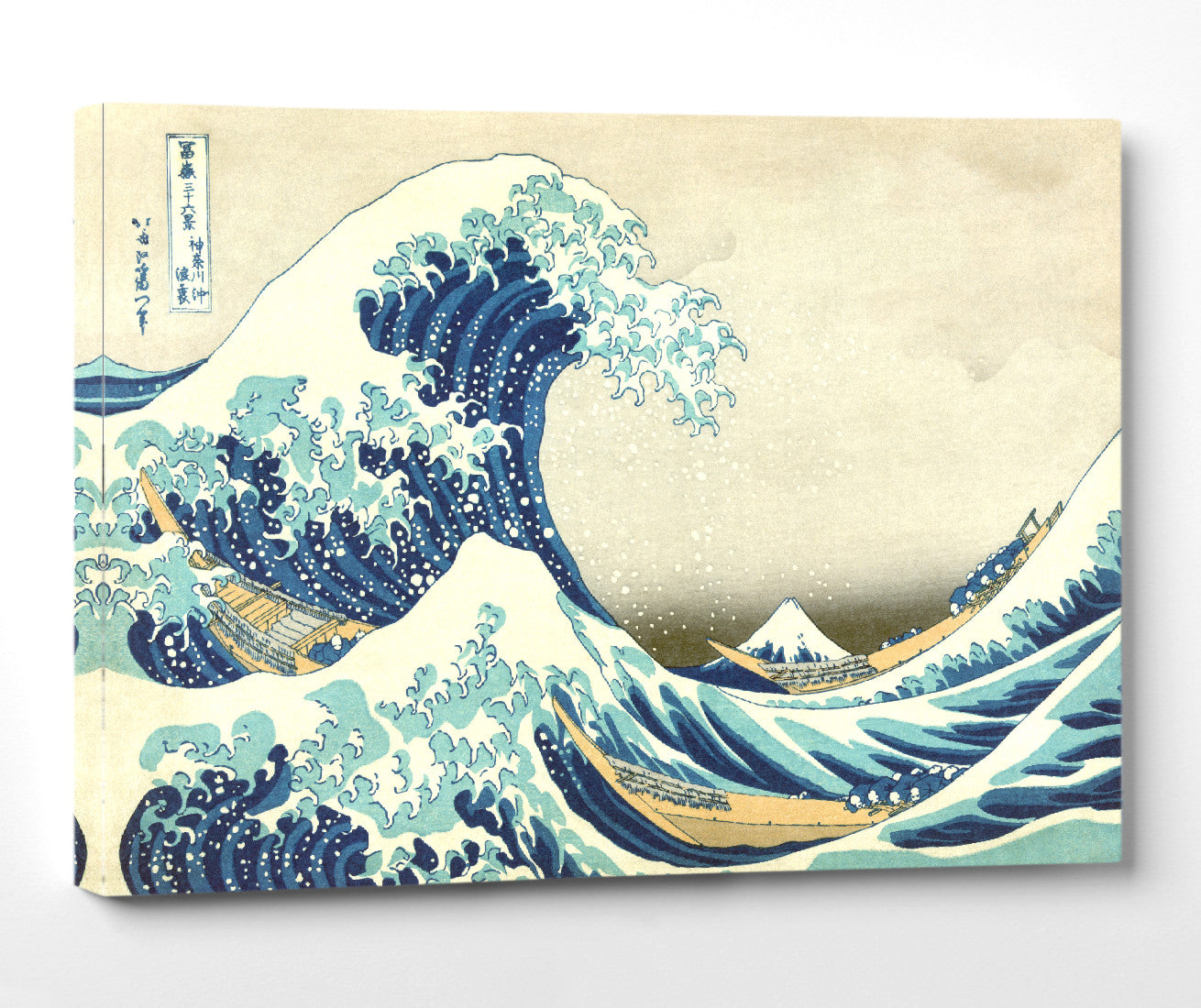
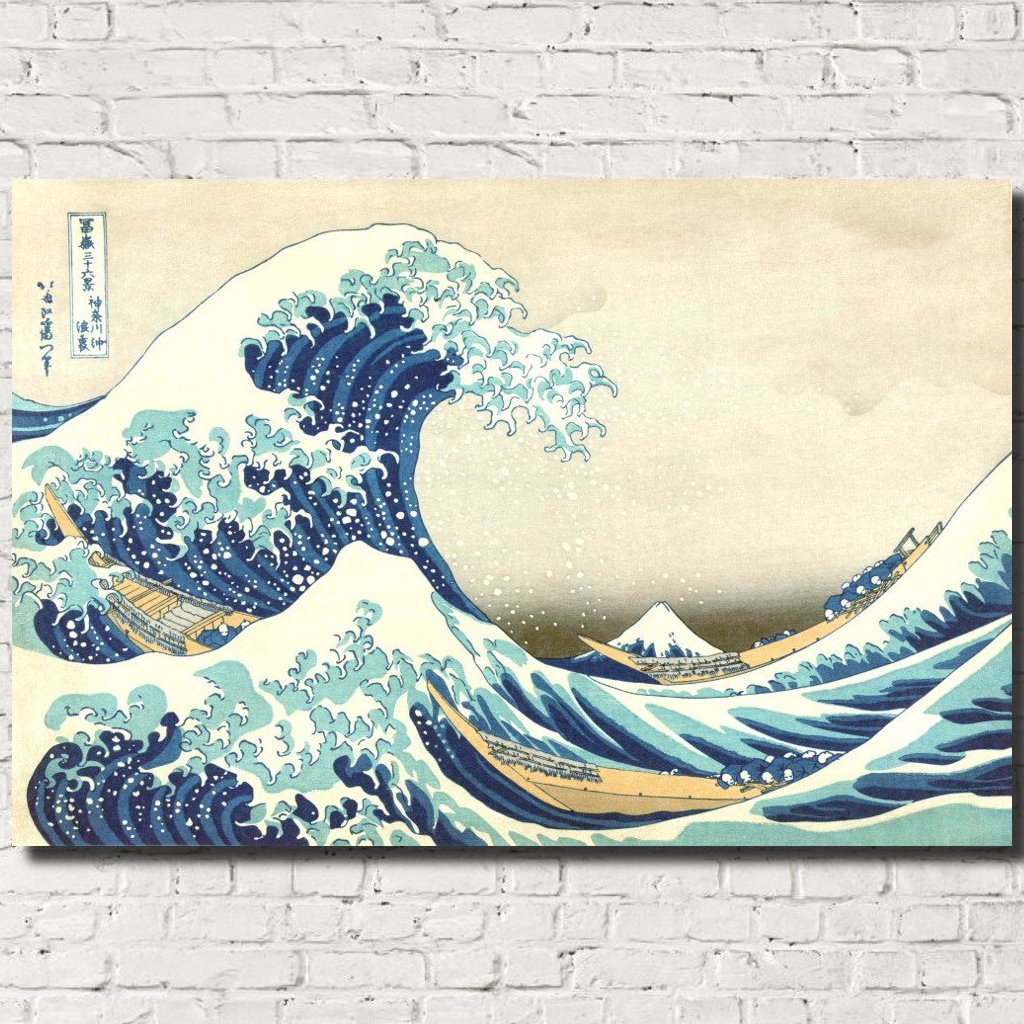
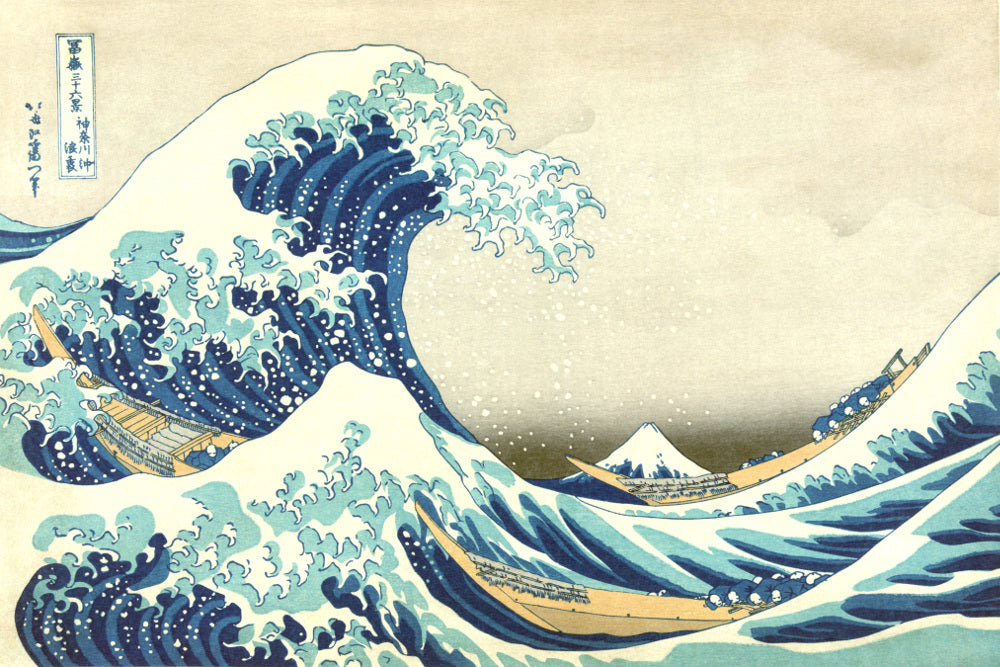
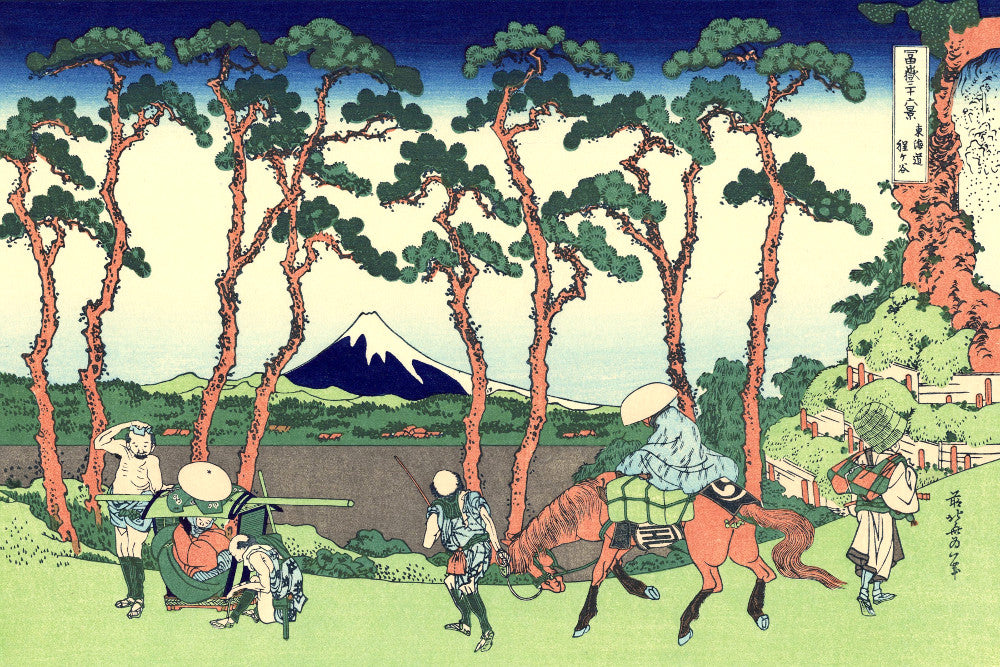
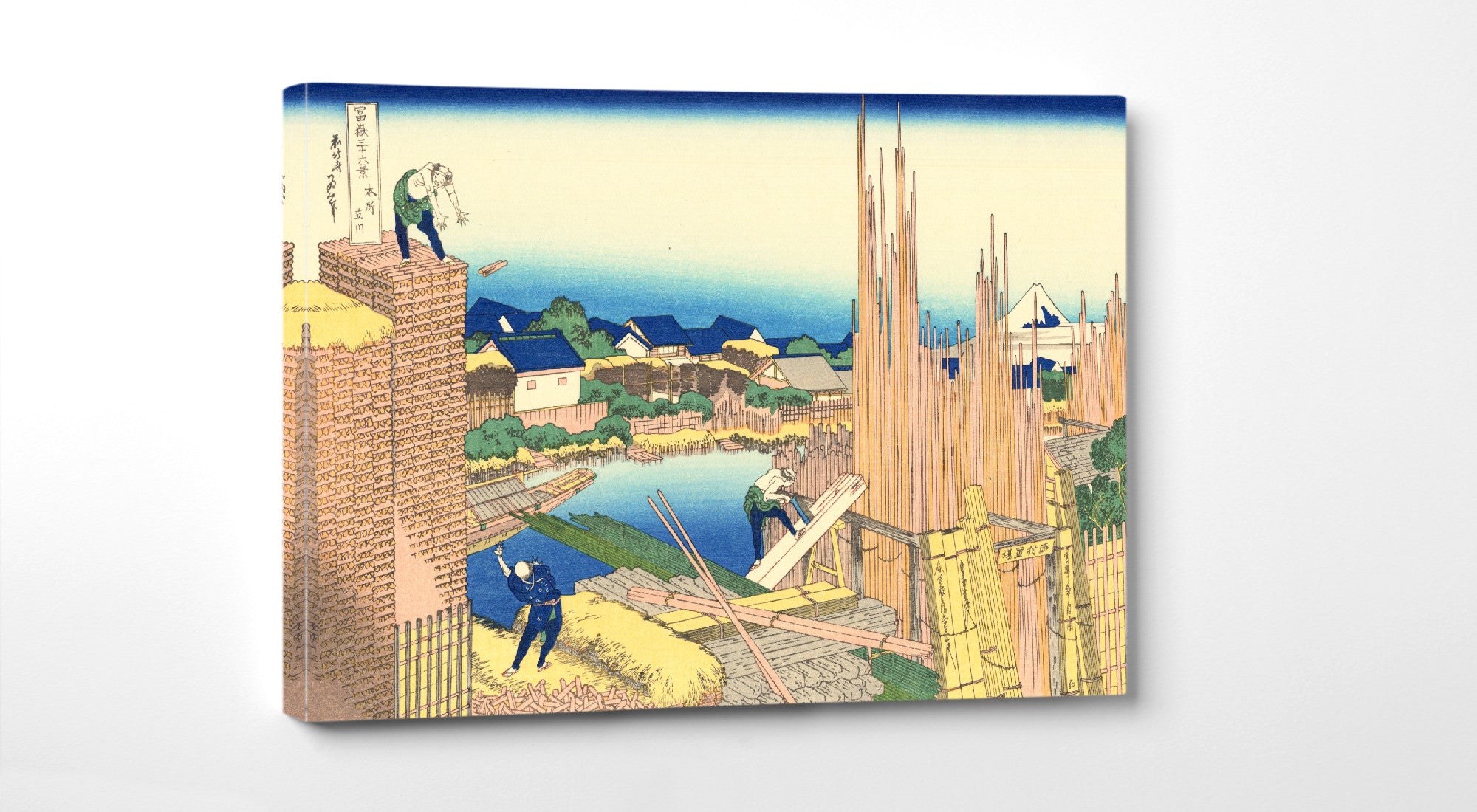
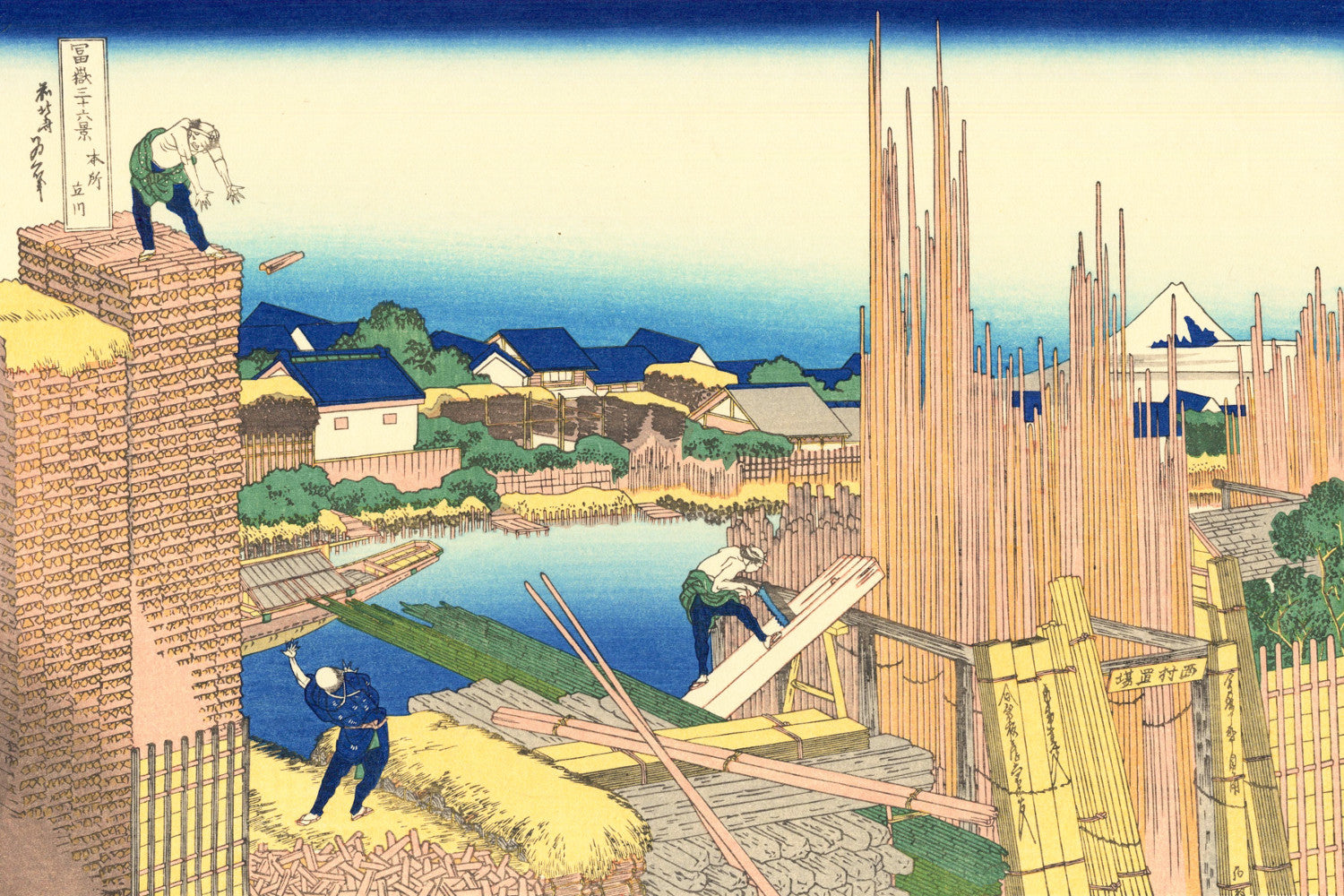
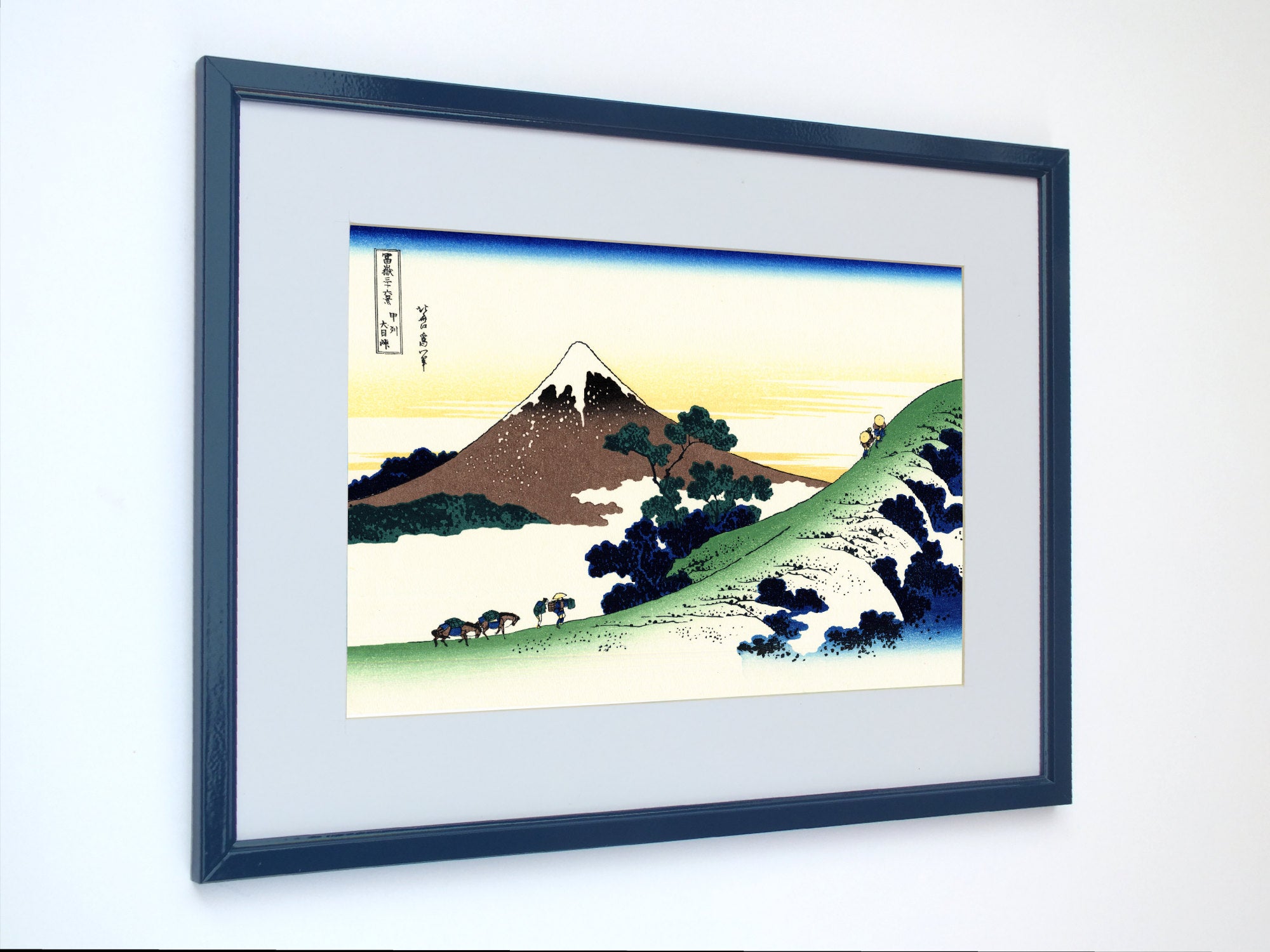
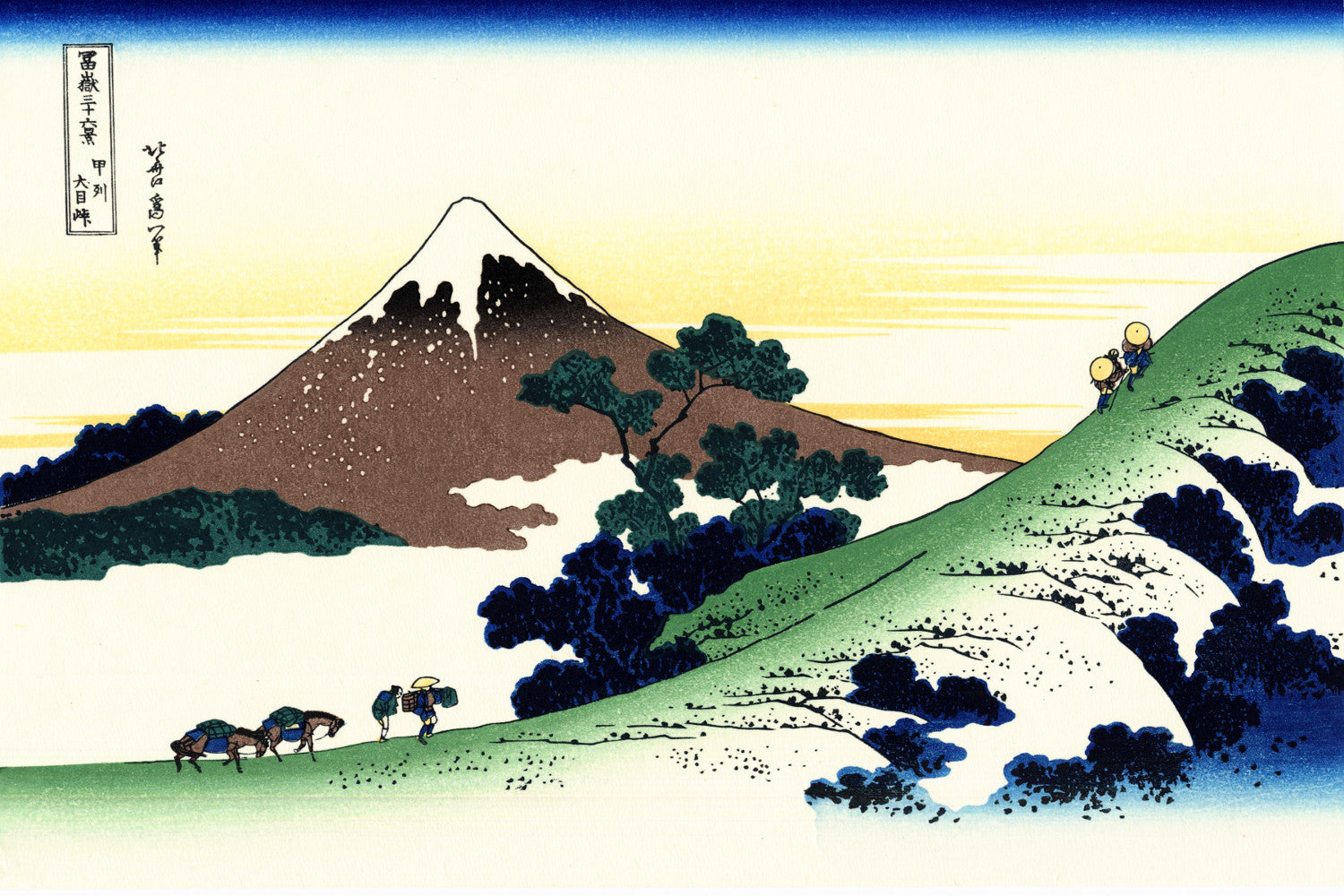
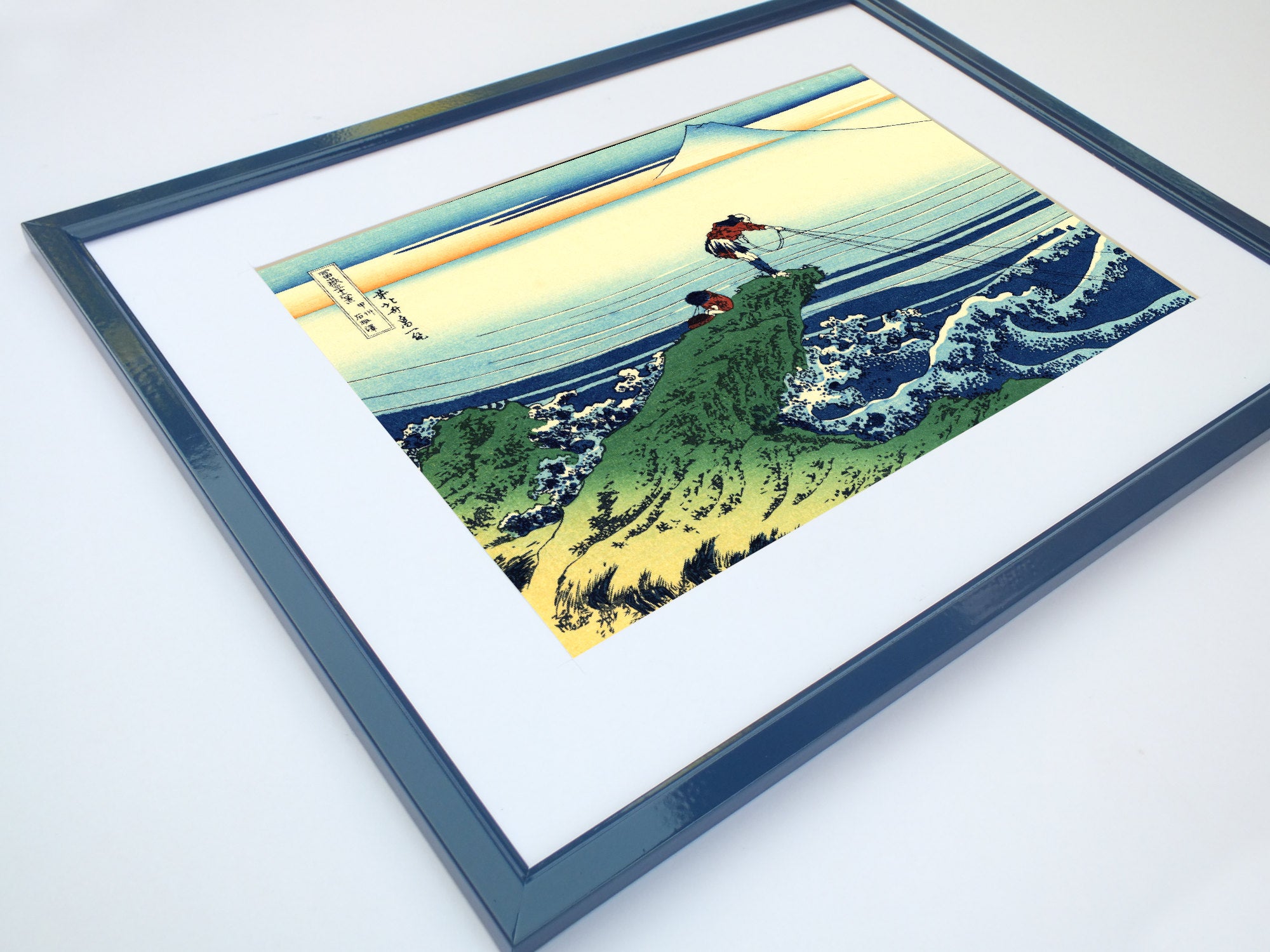
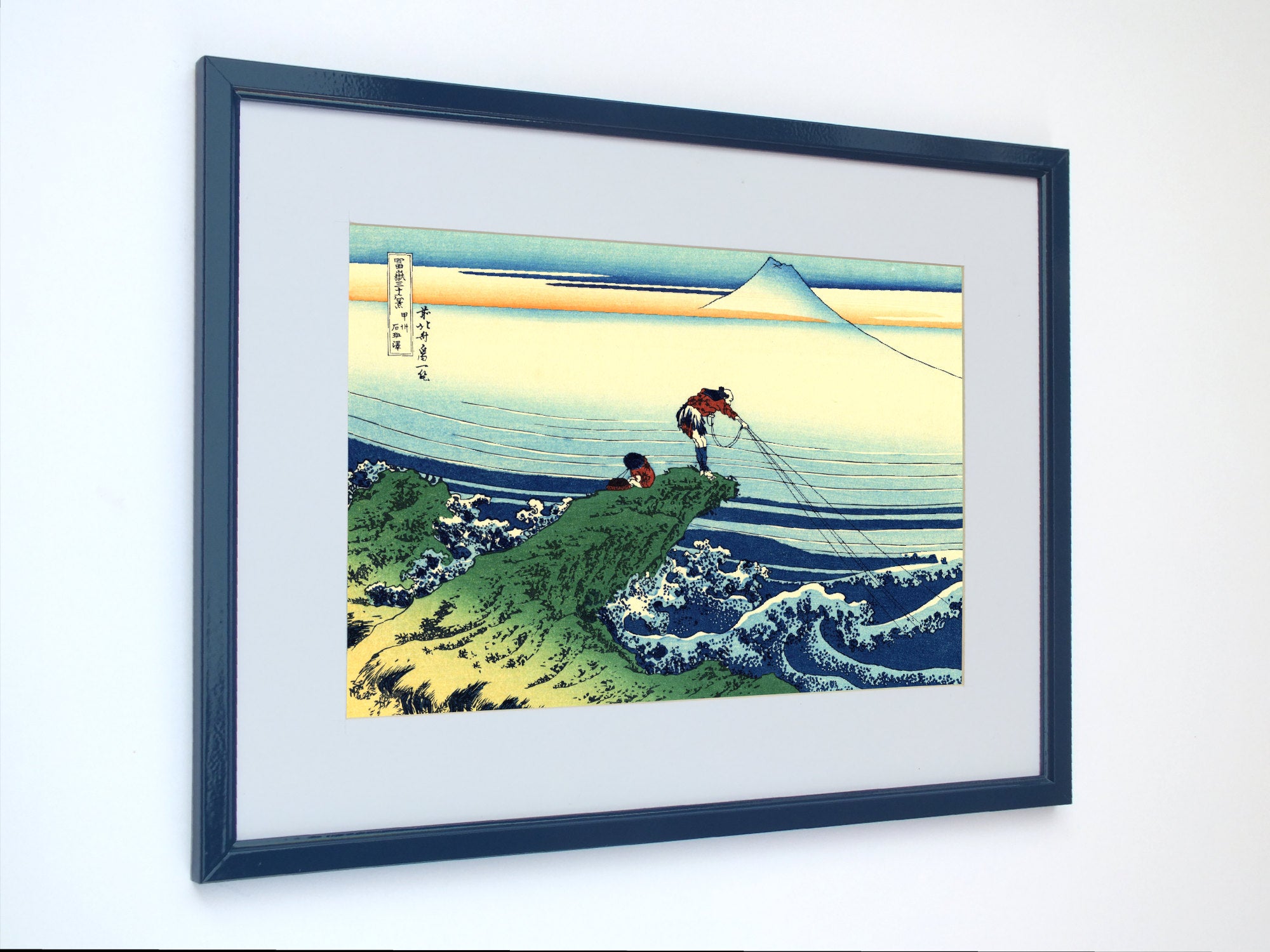
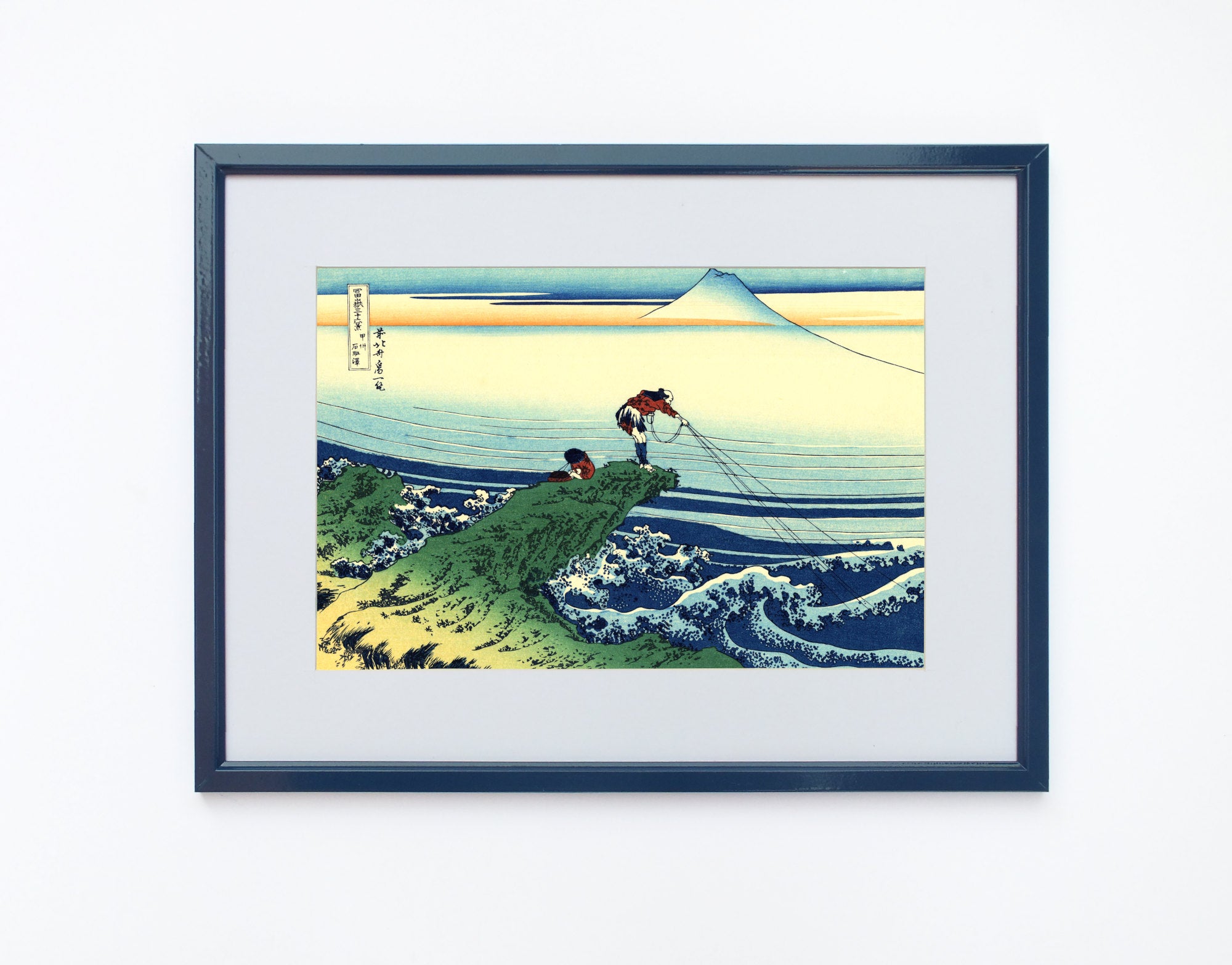
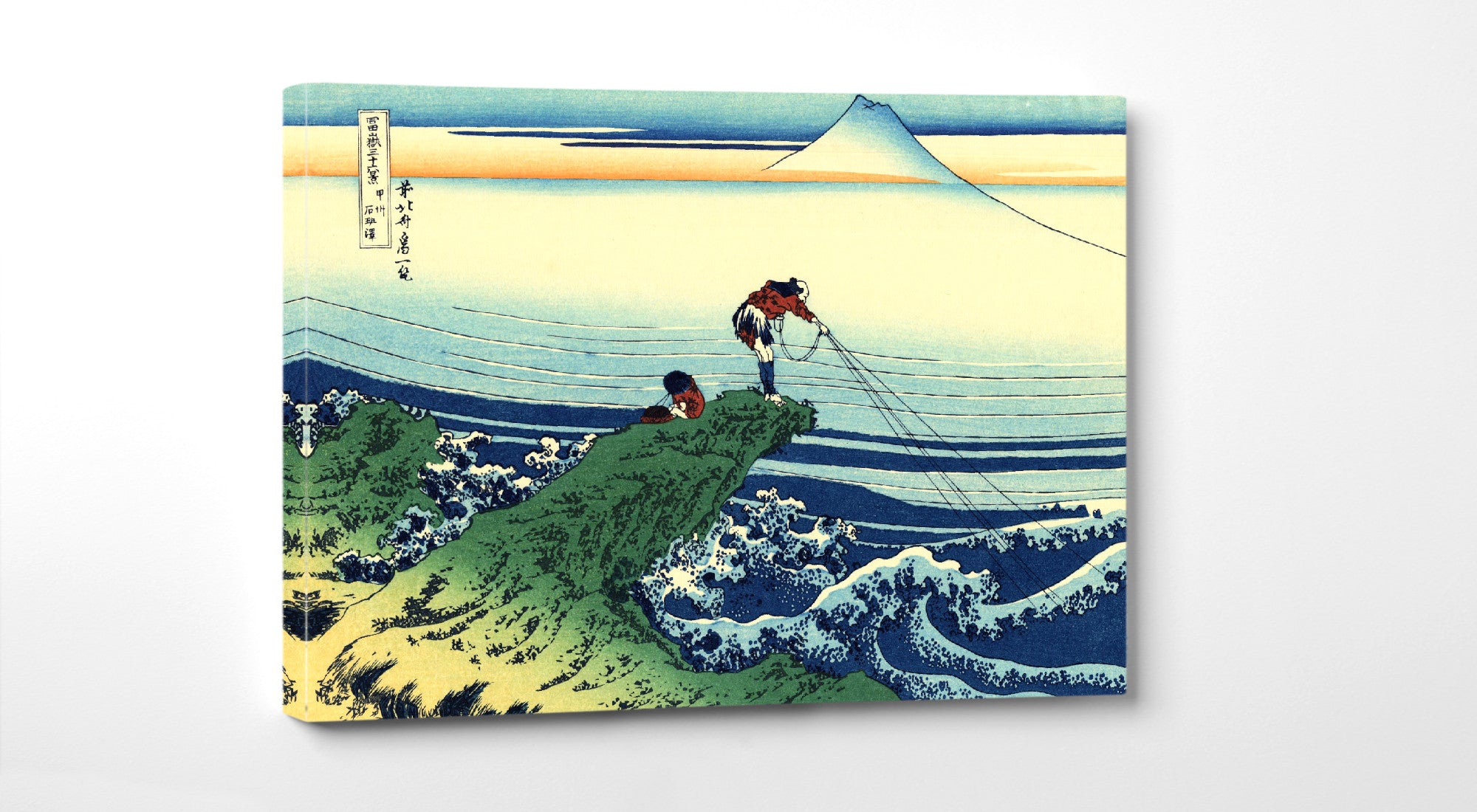
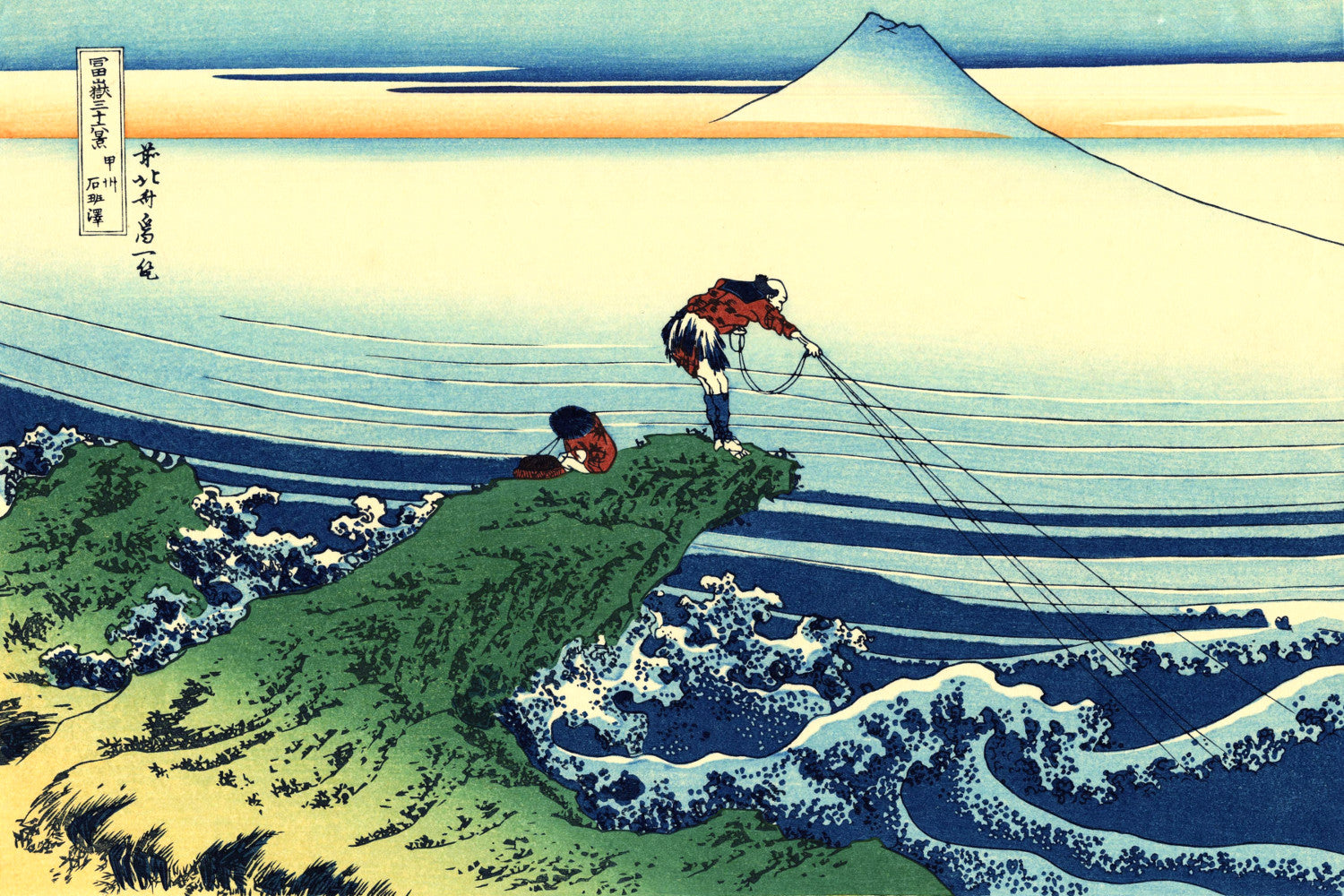
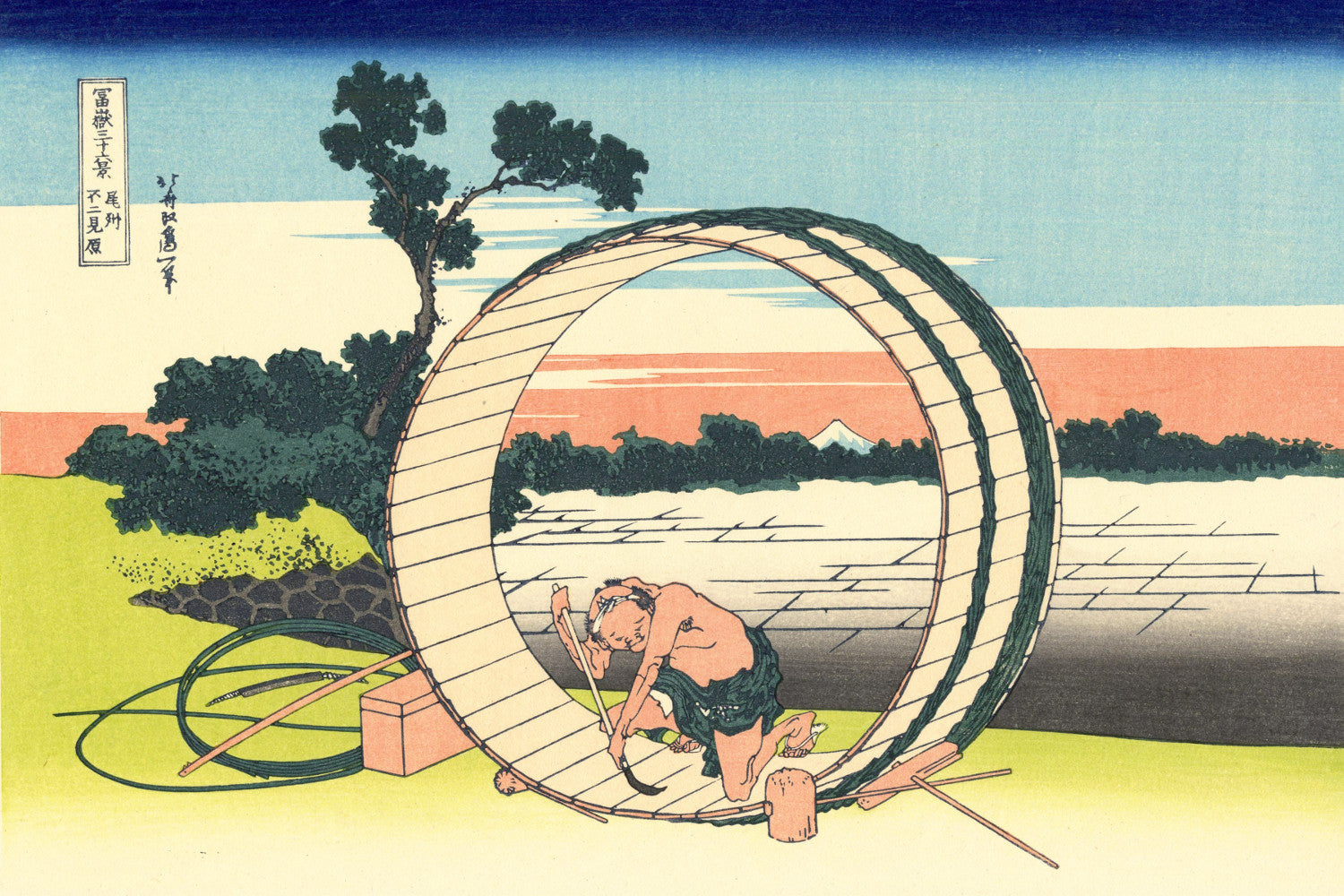
Katsushika Hokusai (葛飾 北斎, c. 31 October 1760 – 10 May 1849), known simply as Hokusai, was a Japanese artist, ukiyo-e painter and printmaker of the Edo period. Hokusai is best known for the woodblock print series Thirty-Six Views of Mount Fuji which includes the internationally iconic print The Great Wave off Kanagawa.
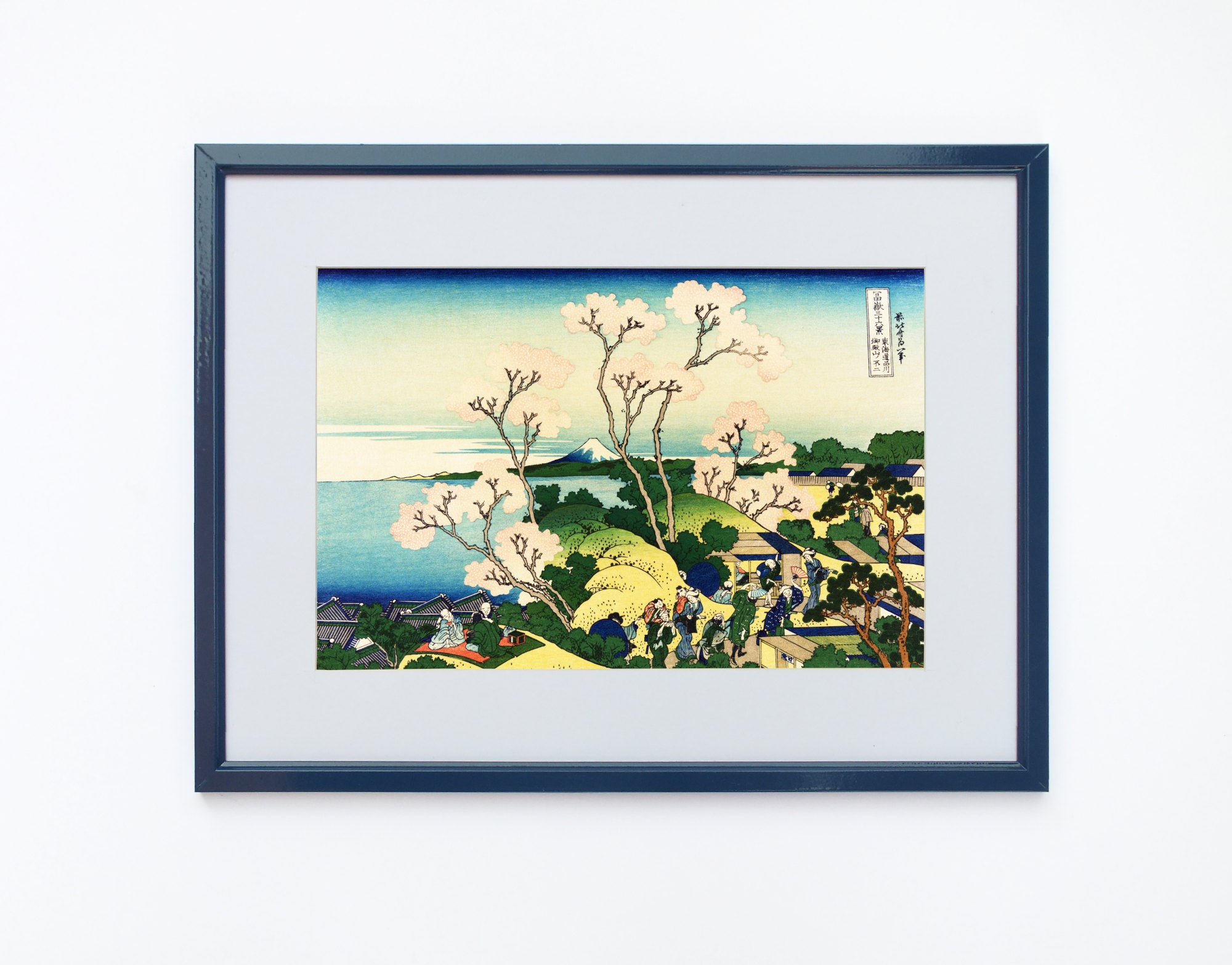
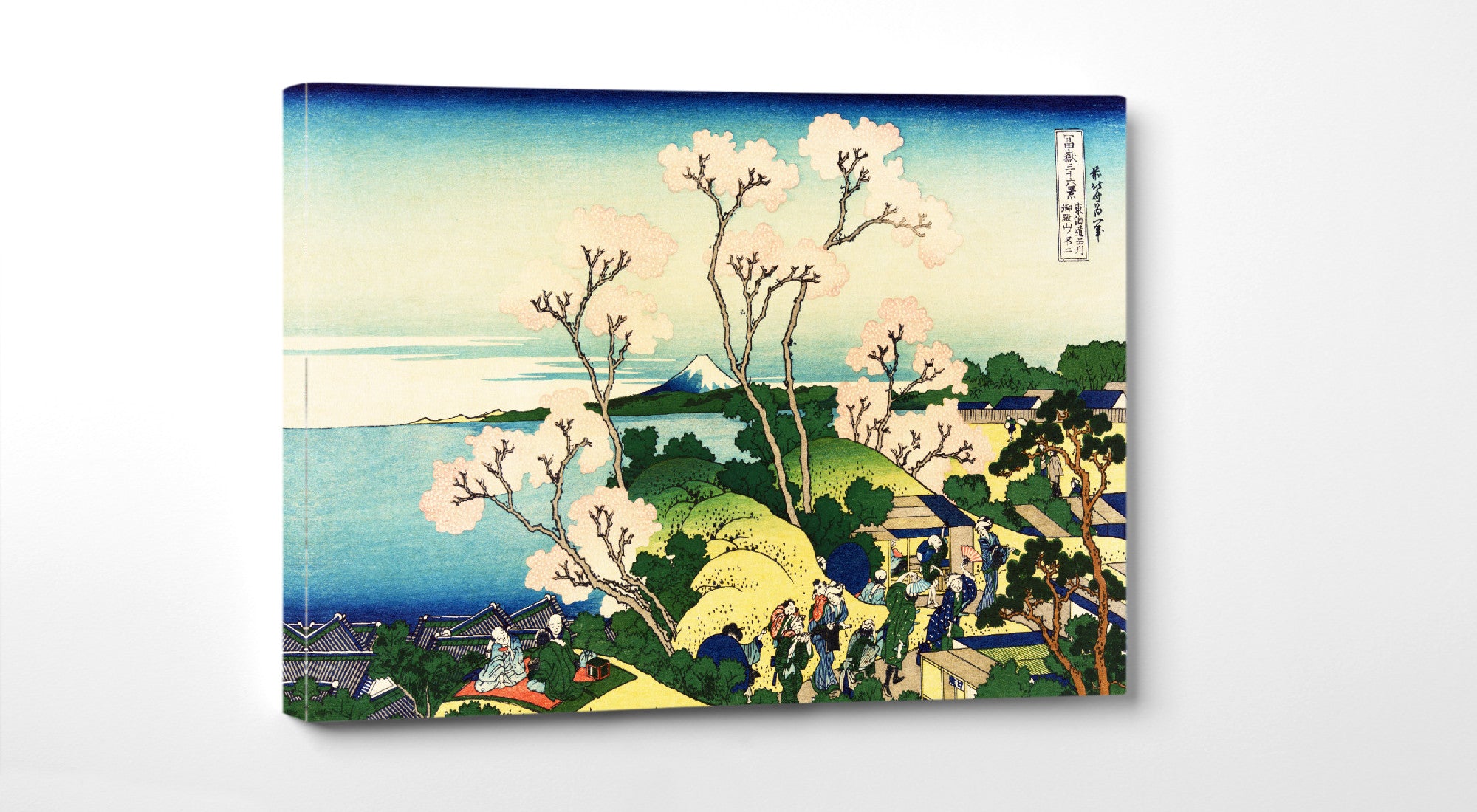
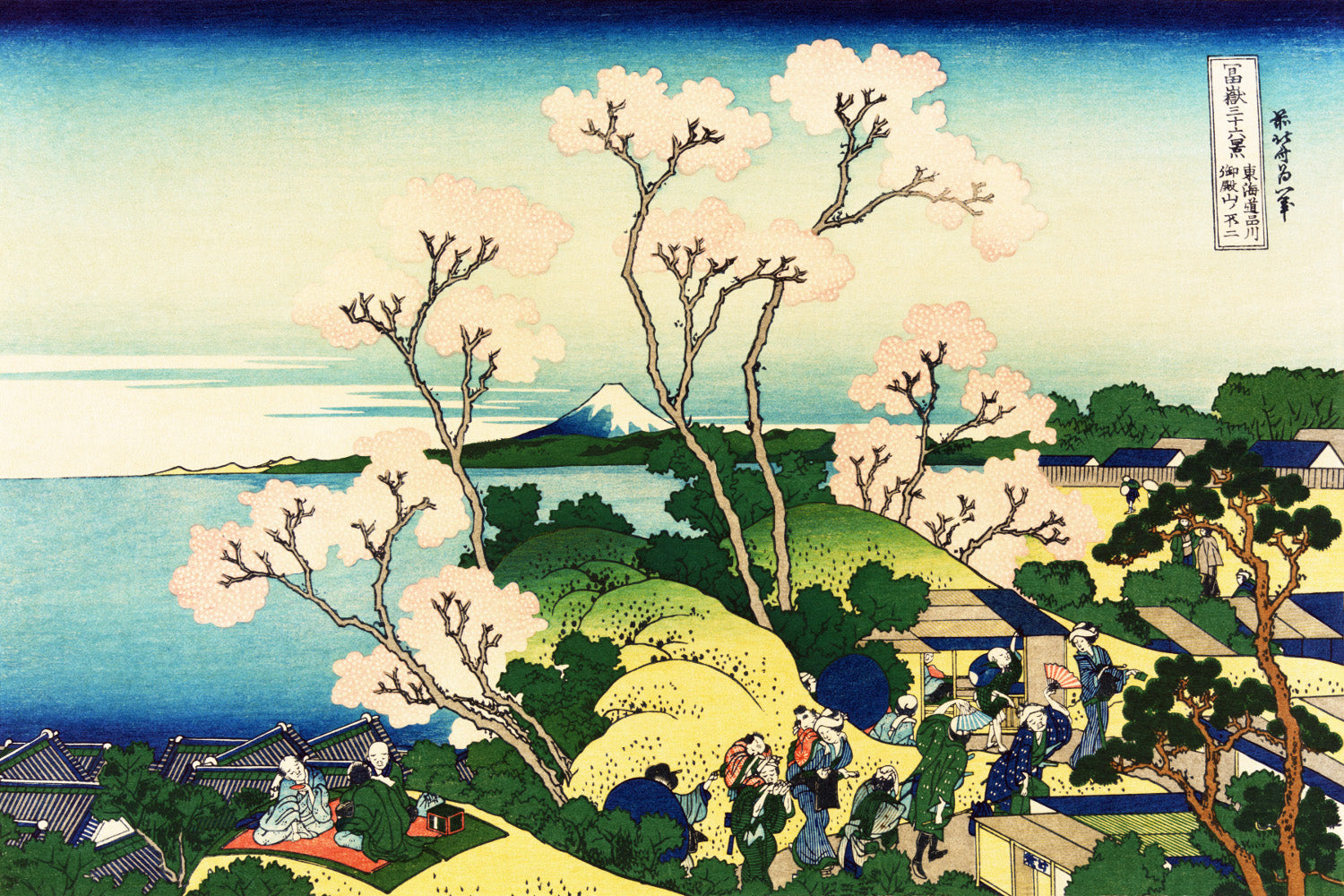
Utagawa Hiroshige (Japanese: 歌川 広重), also Andō Hiroshige (Japanese: 安藤 広重; 1797 – 12 October 1858), was a Japanese ukiyo-e artist, considered the last great master of that tradition. Hiroshige is best known for his landscapes, such as the series The Fifty-three Stations of the Tōkaidō and The Sixty-nine Stations of the Kiso Kaidō; and for his depictions of birds and flowers. The subjects of his work were atypical of the ukiyo-e genre, whose typical focus was on beautiful women, popular actors, and other scenes of the urban pleasure districts of Japan's Edo period (1603–1868). The popular Thirty-six Views of Mount Fuji series by Hokusai was a strong influence on Hiroshige's choice of subject, though Hiroshige's approach was more poetic and ambient than Hokusai's bolder, more formal prints.
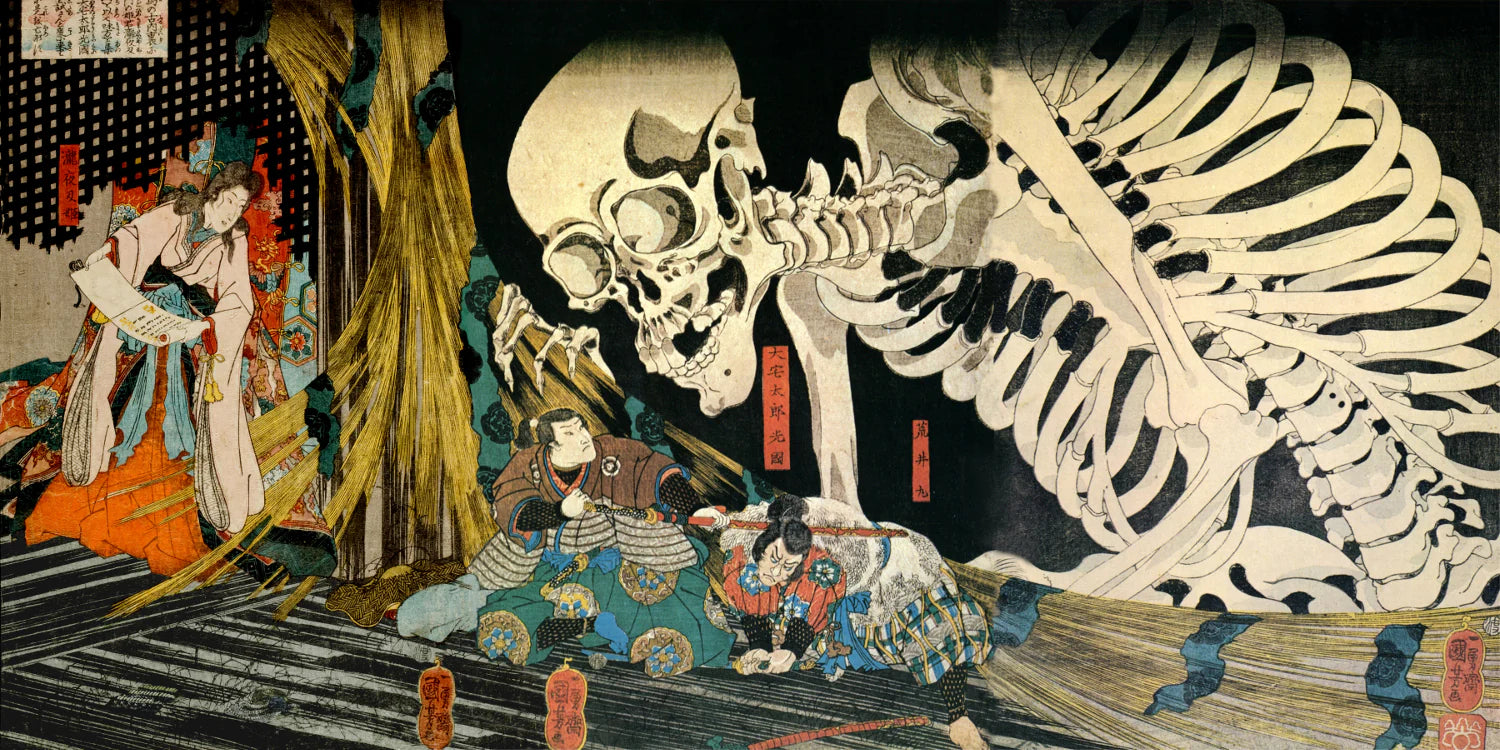
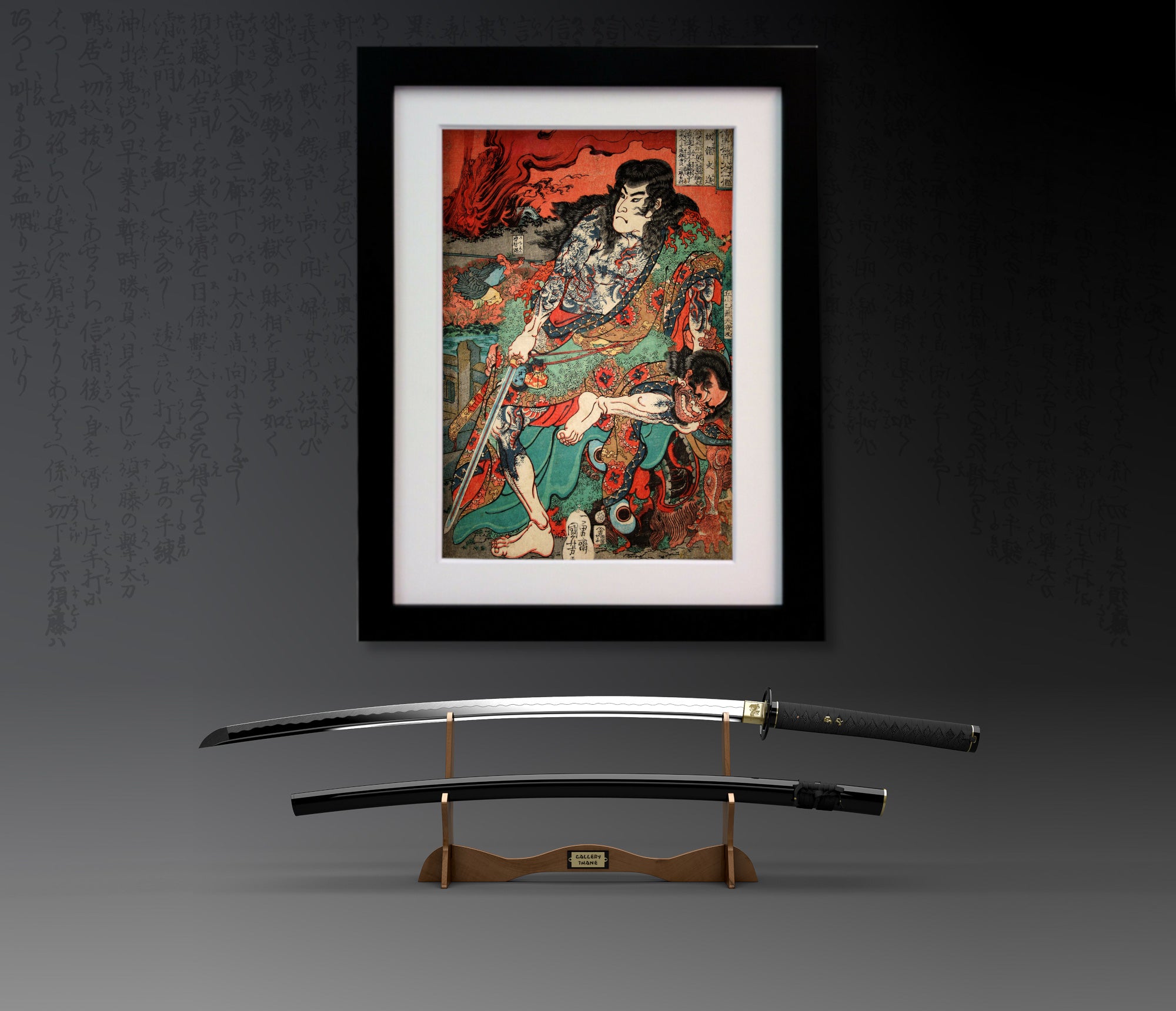
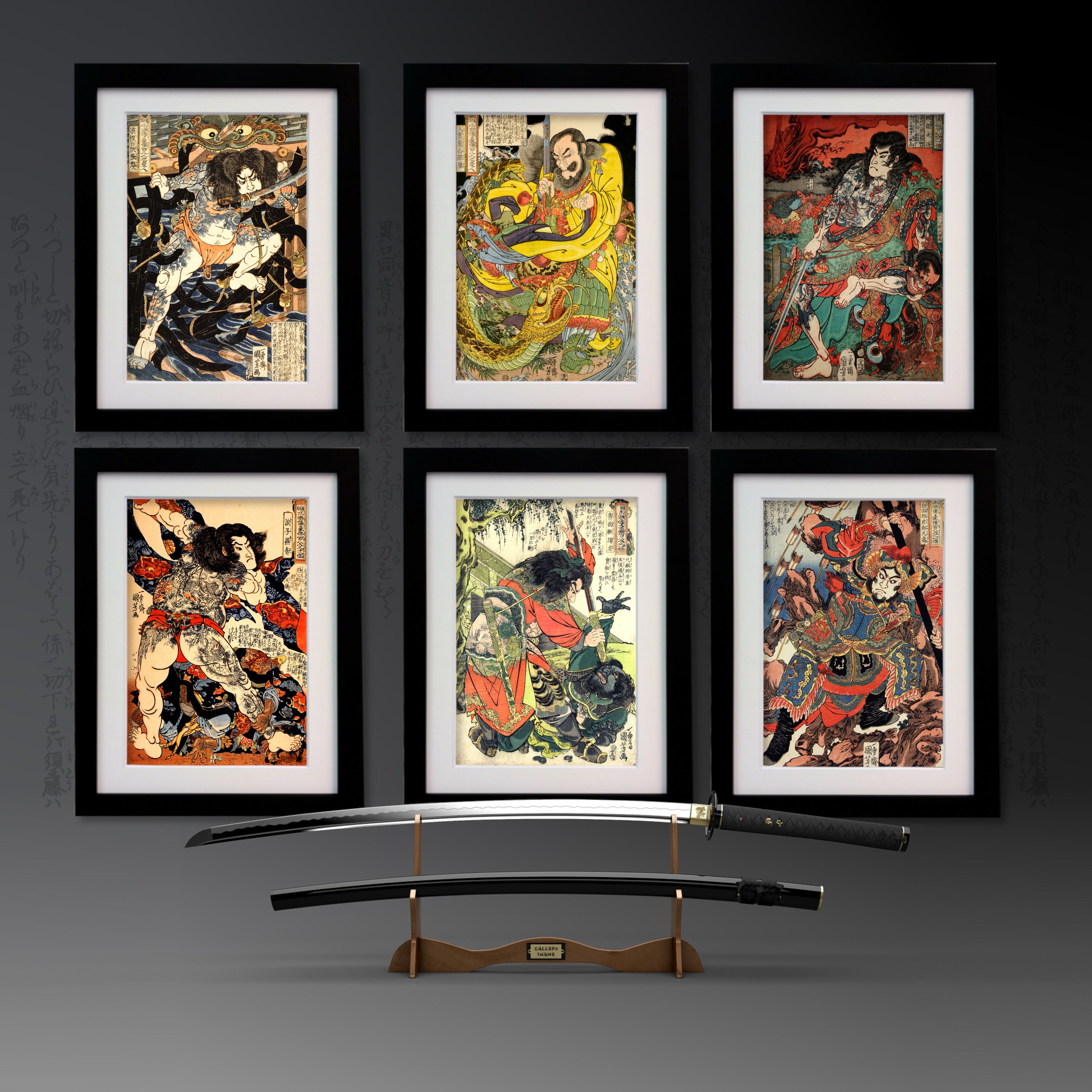
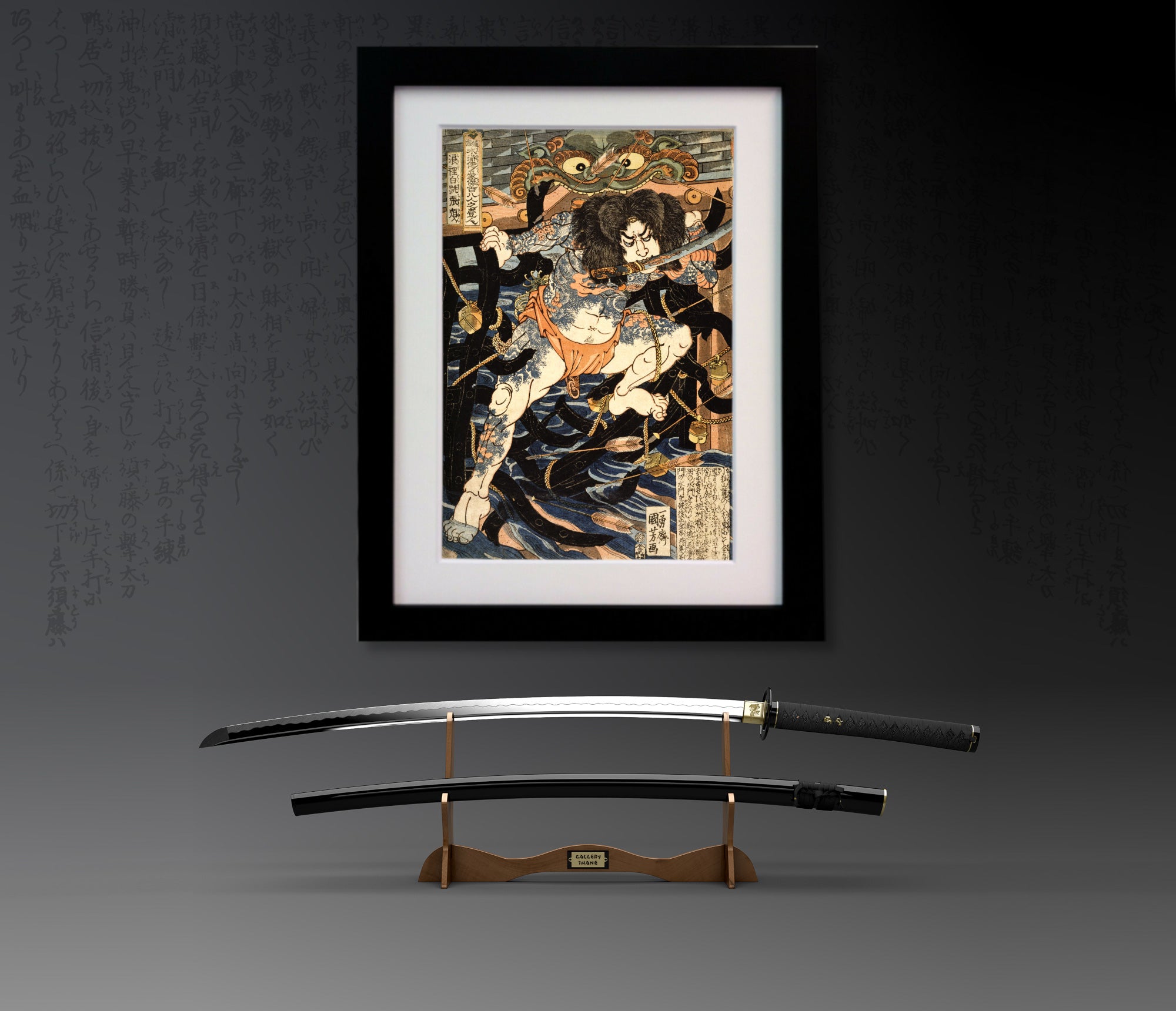
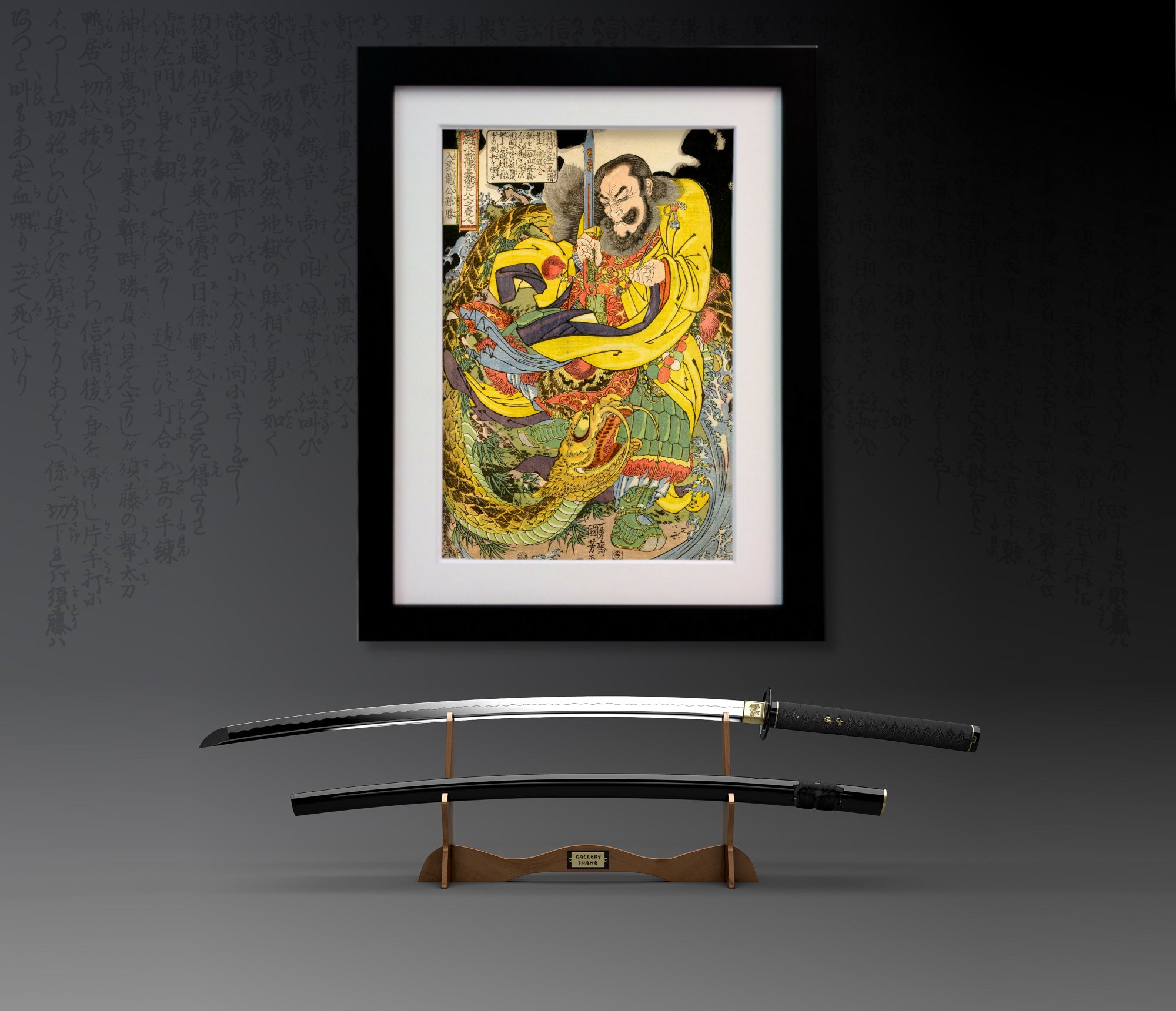
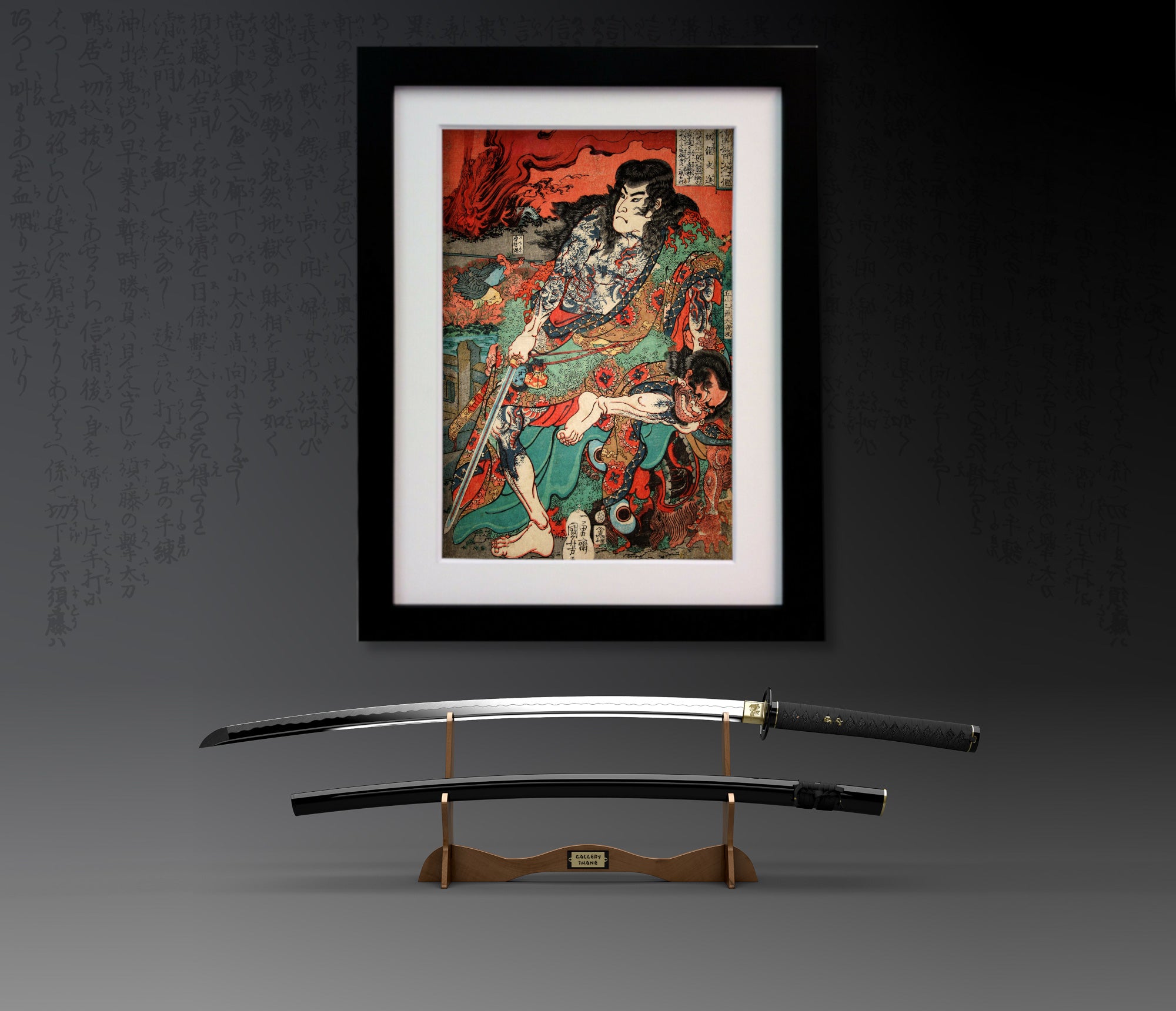
Utagawa Kuniyoshi ( 歌川 国芳, January 1, 1798[1] – April 14, 1861) was one of the last great masters of the Japanese ukiyo-e style of woodblock prints and painting. He was a member of the Utagawa school. The range of Kuniyoshi's subjects included many genres: landscapes, beautiful women, Kabuki actors, cats, and mythical animals. He is known for depictions of the battles of legendary samurai heroes. His artwork incorporated aspects of Western representation in landscape painting and caricature.
Ohara Koson, (Kanazawa 1877 – Tokyo 1945) was a Japanese painter and woodblock print designer of the late 19th and early 20th centuries, part of the shin-hanga ("new prints") movement. Ohara Koson was famous as a master of kachō-e (bird-and-flower) designs. Throughout a prolific career, in which he created around 500 prints, he went by three different titles: Ohara Hōson (小原豊邨), Ohara Shōson (小原祥邨) and Ohara Koson
Toyohara Kunichika (Japanese: 豊原 国周; 30 June 1835 – 1 July 1900) was a Japanese woodblock print artist. Talented as a child, at about thirteen he became a student of Tokyo's then-leading print maker, Utagawa Kunisada. His deep appreciation and knowledge of kabuki drama led to his production primarily of ukiyo-e actor-prints, which are woodblock prints of kabuki actors and scenes from popular plays of the time.
One Hundred and Eight Heroes of the Popular Suikoden
Kuniyoshi's commercial and artistic success came in 1827 with the series 'One Hundred and Eight Heroes of the Popular Suikoden'. He revisited the theme of the bandits many times over the course of his career. Suikoden (Water Margin) is a 14th century Chinese novel about 108 rebels and heroic bandits, very popular in Japan in the Edo period. The characters were also outlaws and brigands, seen as men of honour who would rebel against bureaucracy, a Robin-Hood-like band that made the story of a revolutionary novel with implications resenting the authority of the time. Many Japanese novels imitating the Suikoden were dramatised as Kabuki plays or were portrayed in woodblock prints.
108 Heroes prints:

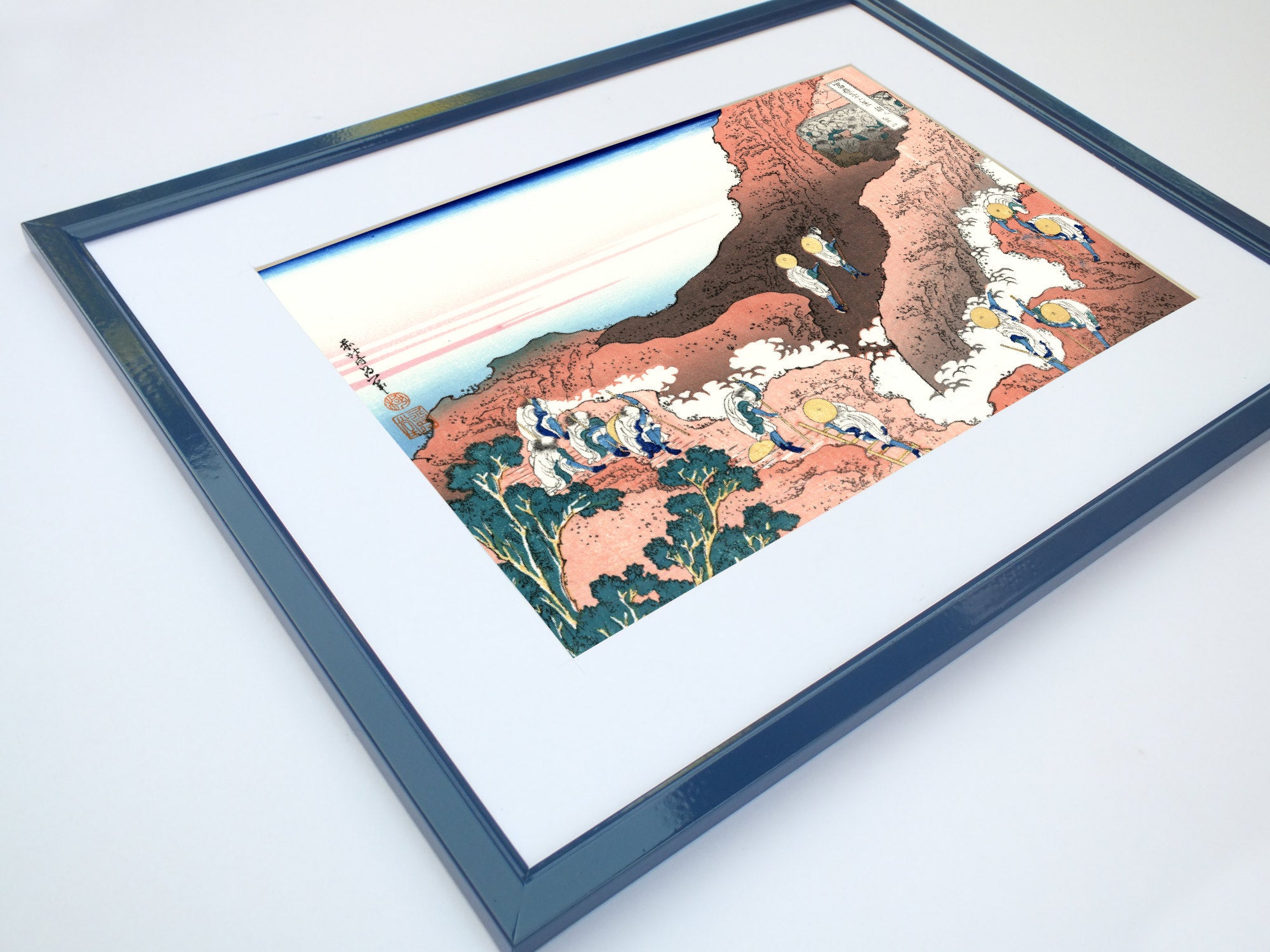
Some famous ukiyo-e artworks: