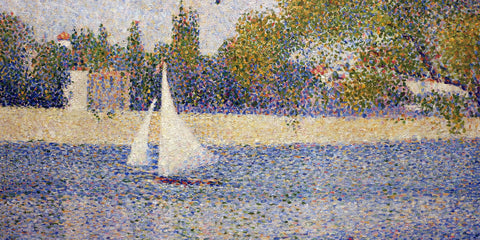Table of Contents:[hide]
Paul Signac, a prominent figure in the Post-Impressionist movement, left an indelible mark on the art world with his vibrant and meticulously crafted paintings. Born on November 11, 1863, in Paris, France, Signac's artistic journey traversed various styles, but he is best known for his association with Pointillism, a technique where small, distinct dots of color are applied in patterns to form an image. Signac's dedication to this method, along with his unique perspective, produced a body of work that continues to captivate art enthusiasts worldwide.
Paul Signac Paintings - The Complete Works (Video)
1. Accomplishments
Signac's artistic accomplishments are vast and varied. His mastery of Pointillism, a technique he refined alongside Georges Seurat, showcased his innovative approach to color theory and composition. Through his meticulous brushwork, Signac brought scenes to life in a way that was both captivating and thought-provoking.
2. Important Art by Paul Signac
2.1 Two Cypresses, Mistral, Opus 241 (1893)
Two Cypresses,' harmonizing Impressionism and Pointillism. Capturing nature's elegance, it inspires global artists, epitomizing the profound beauty found in simplicity. An enduring tribute to nature's splendor.
2.2 Opus 217. Against the Enamel of a Background Rhythmic with Beats and Angles, Tones, and Tints, Portrait of M. Félix Fénéon in 1890
This painting stands as a testament to Signac's technical prowess. The intricate patterns and harmonious color palette create a mesmerizing portrait, illustrating Signac's ability to convey depth and emotion through the careful arrangement of dots.
2.3 The Pink Cloud, Antibes
"The Pink Cloud, Antibes" transports viewers to the picturesque coastal town of Antibes in France. Signac's delicate rendering of the pink clouds at sunset creates a dreamlike atmosphere, capturing the ephemeral beauty of nature in a mesmerizing display of color and light.
3. Biography of Paul Signac
3.1 Childhood and Education
Signac's early life in Paris laid the foundation for his artistic pursuits. His exposure to the city's vibrant art scene and cultural diversity ignited his passion for painting. Signac's formal education in art provided him with the technical skills necessary to experiment with various styles and techniques.
3.2 Early Career
During his early career, Signac explored different artistic styles, drawing inspiration from Impressionism and Neo-Impressionism. His encounter with Georges Seurat proved to be a turning point, leading to their collaboration on developing Pointillism. This partnership significantly influenced Signac's artistic trajectory, shaping his distinctive approach to painting.
3.3 Collaboration with Seurat and Others
Signac's collaboration with Seurat and other artists of the Neo-Impressionist movement fostered a sense of camaraderie and shared artistic vision. Their innovative techniques challenged traditional norms, paving the way for a new era in art. Signac's contributions to this movement solidified his reputation as a pioneering artist.
3.4 Mature Period
During his mature period, Signac's art flourished, and he created some of his most iconic works. His paintings became increasingly vibrant and complex, reflecting his deepening understanding of color theory and composition. Signac's dedication to his craft was unwavering, evident in the meticulous details and emotive depth present in his later pieces.
3.5 The Legacy of Paul Signac
Paul Signac's legacy endures through his groundbreaking contributions to the art world. His mastery of Pointillism and his ability to infuse ordinary scenes with extraordinary depth and emotion continue to inspire artists and art enthusiasts alike. Signac's innovative spirit and dedication to his craft have left an indelible mark on the world of painting, ensuring his place among the most celebrated artists in history.
4. Influences and Connections
Signac's artistic influences were vast and diverse, ranging from Impressionist luminaries like Claude Monet to contemporary painters of his time. His interactions with fellow artists, critics, and intellectuals enriched his perspective and contributed to the evolution of his style. Signac's connections within the art community not only influenced his own work but also facilitated the exchange of ideas, fostering a fertile ground for artistic innovation.
In conclusion, Paul Signac's contributions to the art world are immeasurable. His innovative spirit, coupled with his technical brilliance, produced a body of work that continues to inspire and captivate audiences worldwide. Through his exploration of color, light, and form, Signac transcended traditional artistic boundaries, leaving behind a legacy that resonates with creativity, passion, and artistic ingenuity.
5. Paul Signac FAQ's
1. Q: Who was Paul Signac? A: Paul Signac (1863-1935) was a renowned French artist known for his contributions to the Neo-Impressionist and Pointillist movements.
2. Q: What is Pointillism? A: Pointillism is a painting technique in which small, distinct dots of color are applied in patterns to form an image. Signac, along with Georges Seurat, was a key proponent of this style.
3. Q: What were Paul Signac's most famous paintings? A: Some of Signac's most famous paintings include "The Milliners," "Les Andelys, the Riverbank," "The Dining Room," "Opus 217. Against the Enamel of a Background Rhythmic with Beats and Angles, Tones, and Tints, Portrait of M. Félix Fénéon in 1890," "Woman with a Parasol," "Lady on the Terrace," and "The Pink Cloud, Antibes."
4. Q: When and where was Paul Signac born? A: Paul Signac was born on November 11, 1863, in Paris, France.
5. Q: What was Signac's artistic style? A: Signac was known for his unique style of Pointillism, where he used small, distinct dots of color to create intricate and vibrant paintings.
6. Q: Did Paul Signac work closely with any other famous artists? A: Yes, Signac collaborated closely with Georges Seurat, another prominent artist associated with the Pointillist movement. Their collaboration played a significant role in the development of Pointillism.
7. Q: What themes did Signac often explore in his paintings? A: Signac's paintings often explored themes of nature, urban life, and maritime scenes. He was also known for depicting the play of light on water and capturing the essence of everyday life.
8. Q: What is the significance of "Opus 217. Against the Enamel of a Background Rhythmic with Beats and Angles, Tones, and Tints, Portrait of M. Félix Fénéon in 1890"? A: This painting is considered a masterpiece of Pointillism and is renowned for its intricate patterns and harmonious color palette. It showcases Signac's exceptional skill in creating depth and emotion through the use of dots.
9. Q: How did Signac's legacy impact the art world? A: Signac's innovative techniques and dedication to Pointillism inspired generations of artists. His legacy continues to influence contemporary artists and remains a vital part of art history.
10. Q: Where can I see Paul Signac's artworks today? A: Paul Signac's artworks are displayed in museums and galleries worldwide. Some notable institutions housing his paintings include the Musée d'Orsay in Paris, the Museum of Modern Art in New York, and the Art Institute of Chicago. You can purchase prints and canvas panels of his celebrated paintings at Gallerythane.com
6. Related Articles
6.1 Pointillism Explained